WE-GS: An In-the-wild Efficient 3D Gaussian Representation for Unconstrained Photo Collections
2406.02407

0
0
Abstract
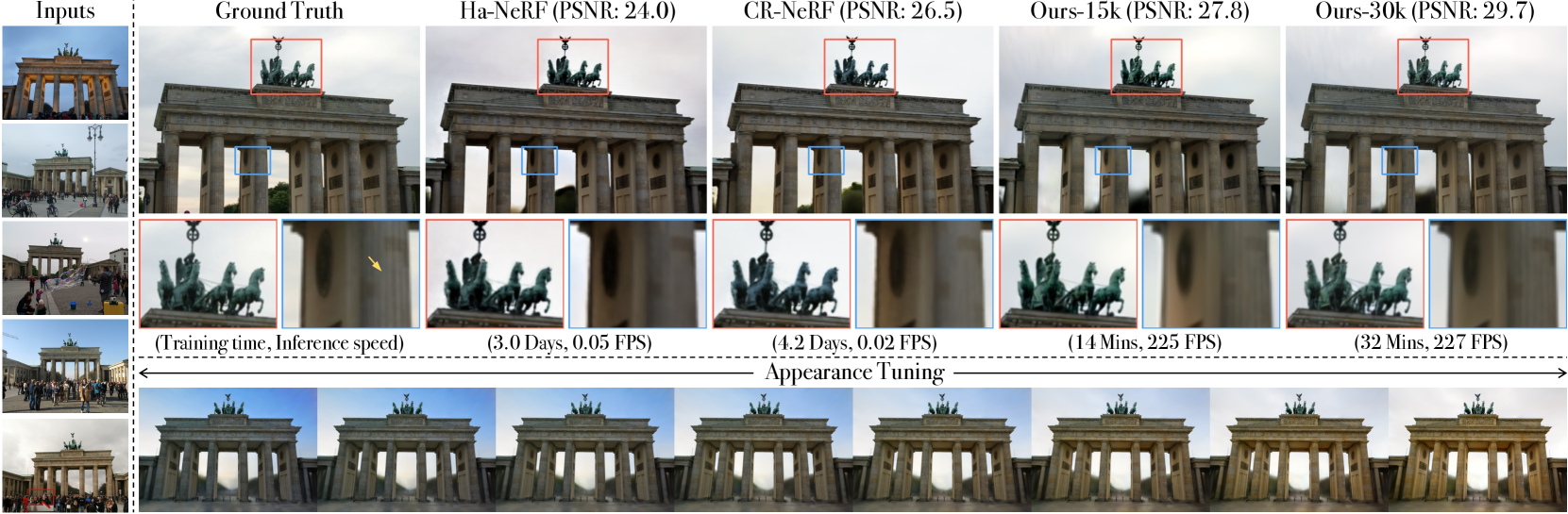
Novel View Synthesis (NVS) from unconstrained photo collections is challenging in computer graphics. Recently, 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has shown promise for photorealistic and real-time NVS of static scenes. Building on 3DGS, we propose an efficient point-based differentiable rendering framework for scene reconstruction from photo collections. Our key innovation is a residual-based spherical harmonic coefficients transfer module that adapts 3DGS to varying lighting conditions and photometric post-processing. This lightweight module can be pre-computed and ensures efficient gradient propagation from rendered images to 3D Gaussian attributes. Additionally, we observe that the appearance encoder and the transient mask predictor, the two most critical parts of NVS from unconstrained photo collections, can be mutually beneficial. We introduce a plug-and-play lightweight spatial attention module to simultaneously predict transient occluders and latent appearance representation for each image. After training and preprocessing, our method aligns with the standard 3DGS format and rendering pipeline, facilitating seamlessly integration into various 3DGS applications. Extensive experiments on diverse datasets show our approach outperforms existing approaches on the rendering quality of novel view and appearance synthesis with high converge and rendering speed.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- The paper provides a guide on how to use the IEEEtran LaTeX templates for formatting academic papers.
- It covers the design, intent, and limitations of the templates, as well as instructions on how to properly use them.
- The paper aims to help authors ensure their papers adhere to the specific formatting requirements of the IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers).
Plain English Explanation
The IEEEtran LaTeX templates are a set of pre-designed formatting tools for creating academic papers that follow the standards of the IEEE. The IEEE is a prominent professional organization in the fields of electrical engineering, electronics, and computer science, and it has specific requirements for the layout and styling of papers submitted to its conferences and journals.
The templates provided in this paper are intended to make it easier for authors to ensure their papers meet these formatting guidelines. By using the pre-configured IEEEtran templates, authors can focus on the content of their work rather than worrying about the technical details of page layout, font choices, and other formatting elements.
The paper explains the design choices behind the templates, their intended use, and their limitations. It provides step-by-step instructions on how to properly use the templates to format a paper, including guidance on things like inserting figures, managing references, and customizing the appearance of the document.
Technical Explanation
The IEEEtran LaTeX templates are a set of LaTeX document classes and style files designed to facilitate the formatting of papers for IEEE publications. The templates are based on the standard LaTeX article class, but they have been extensively customized to match the specific formatting requirements of the IEEE.
The paper explains the rationale behind the design of the templates, noting that they were created to provide a consistent and standardized appearance for IEEE papers, while also making the formatting process more efficient for authors. The templates handle a wide range of formatting elements, including page layout, font selection, citation and reference formatting, and the placement of figures and tables.
The paper also discusses the limitations of the templates, acknowledging that they may not be suitable for all types of IEEE papers or all author preferences. It provides guidance on how to customize the templates to suit specific needs, such as adjusting the font size or modifying the appearance of captions and equations.
Critical Analysis
The IEEEtran LaTeX templates are a valuable resource for authors looking to publish their work in IEEE venues. The templates provide a clear and consistent way to format papers, which can save authors a significant amount of time and effort.
However, the paper acknowledges that the templates may not be suitable for all types of IEEE papers, such as those with specialized formatting requirements or unique author preferences. While the templates provide a good starting point, authors may still need to make some customizations to match their specific needs.
Additionally, the paper does not address the potential limitations of LaTeX itself, which can be a complex and intimidating tool for some authors. While the templates simplify the formatting process, they do not eliminate the learning curve associated with using LaTeX.
Overall, the IEEEtran LaTeX templates are a valuable resource for authors, but their usefulness may be limited by the specific requirements of individual IEEE publications or the technical skills of the author.
Conclusion
The IEEEtran LaTeX templates provide a standardized and efficient way for authors to format their papers for IEEE publications. By using these pre-designed templates, authors can focus on the content of their work rather than the technical details of formatting.
The paper explains the design, intent, and limitations of the templates, providing guidance on how to properly use them. While the templates may not be suitable for all types of IEEE papers or all author preferences, they can be a valuable tool for ensuring that papers adhere to the specific formatting requirements of the IEEE.
Overall, the IEEEtran LaTeX templates can help authors save time and effort while producing IEEE-compliant papers, which can be an important factor in securing publication in prestigious IEEE venues.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers

Wild-GS: Real-Time Novel View Synthesis from Unconstrained Photo Collections
Jiacong Xu, Yiqun Mei, Vishal M. Patel

0
0
Photographs captured in unstructured tourist environments frequently exhibit variable appearances and transient occlusions, challenging accurate scene reconstruction and inducing artifacts in novel view synthesis. Although prior approaches have integrated the Neural Radiance Field (NeRF) with additional learnable modules to handle the dynamic appearances and eliminate transient objects, their extensive training demands and slow rendering speeds limit practical deployments. Recently, 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has emerged as a promising alternative to NeRF, offering superior training and inference efficiency along with better rendering quality. This paper presents Wild-GS, an innovative adaptation of 3DGS optimized for unconstrained photo collections while preserving its efficiency benefits. Wild-GS determines the appearance of each 3D Gaussian by their inherent material attributes, global illumination and camera properties per image, and point-level local variance of reflectance. Unlike previous methods that model reference features in image space, Wild-GS explicitly aligns the pixel appearance features to the corresponding local Gaussians by sampling the triplane extracted from the reference image. This novel design effectively transfers the high-frequency detailed appearance of the reference view to 3D space and significantly expedites the training process. Furthermore, 2D visibility maps and depth regularization are leveraged to mitigate the transient effects and constrain the geometry, respectively. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Wild-GS achieves state-of-the-art rendering performance and the highest efficiency in both training and inference among all the existing techniques.
6/18/2024
FSGS: Real-Time Few-shot View Synthesis using Gaussian Splatting
Zehao Zhu, Zhiwen Fan, Yifan Jiang, Zhangyang Wang

0
0
Novel view synthesis from limited observations remains an important and persistent task. However, high efficiency in existing NeRF-based few-shot view synthesis is often compromised to obtain an accurate 3D representation. To address this challenge, we propose a few-shot view synthesis framework based on 3D Gaussian Splatting that enables real-time and photo-realistic view synthesis with as few as three training views. The proposed method, dubbed FSGS, handles the extremely sparse initialized SfM points with a thoughtfully designed Gaussian Unpooling process. Our method iteratively distributes new Gaussians around the most representative locations, subsequently infilling local details in vacant areas. We also integrate a large-scale pre-trained monocular depth estimator within the Gaussians optimization process, leveraging online augmented views to guide the geometric optimization towards an optimal solution. Starting from sparse points observed from limited input viewpoints, our FSGS can accurately grow into unseen regions, comprehensively covering the scene and boosting the rendering quality of novel views. Overall, FSGS achieves state-of-the-art performance in both accuracy and rendering efficiency across diverse datasets, including LLFF, Mip-NeRF360, and Blender. Project website: https://zehaozhu.github.io/FSGS/.
6/18/2024

Self-Calibrating 4D Novel View Synthesis from Monocular Videos Using Gaussian Splatting
Fang Li, Hao Zhang, Narendra Ahuja

0
0
Gaussian Splatting (GS) has significantly elevated scene reconstruction efficiency and novel view synthesis (NVS) accuracy compared to Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF), particularly for dynamic scenes. However, current 4D NVS methods, whether based on GS or NeRF, primarily rely on camera parameters provided by COLMAP and even utilize sparse point clouds generated by COLMAP for initialization, which lack accuracy as well are time-consuming. This sometimes results in poor dynamic scene representation, especially in scenes with large object movements, or extreme camera conditions e.g. small translations combined with large rotations. Some studies simultaneously optimize the estimation of camera parameters and scenes, supervised by additional information like depth, optical flow, etc. obtained from off-the-shelf models. Using this unverified information as ground truth can reduce robustness and accuracy, which does frequently occur for long monocular videos (with e.g. > hundreds of frames). We propose a novel approach that learns a high-fidelity 4D GS scene representation with self-calibration of camera parameters. It includes the extraction of 2D point features that robustly represent 3D structure, and their use for subsequent joint optimization of camera parameters and 3D structure towards overall 4D scene optimization. We demonstrate the accuracy and time efficiency of our method through extensive quantitative and qualitative experimental results on several standard benchmarks. The results show significant improvements over state-of-the-art methods for 4D novel view synthesis. The source code will be released soon at https://github.com/fangli333/SC-4DGS.
6/4/2024
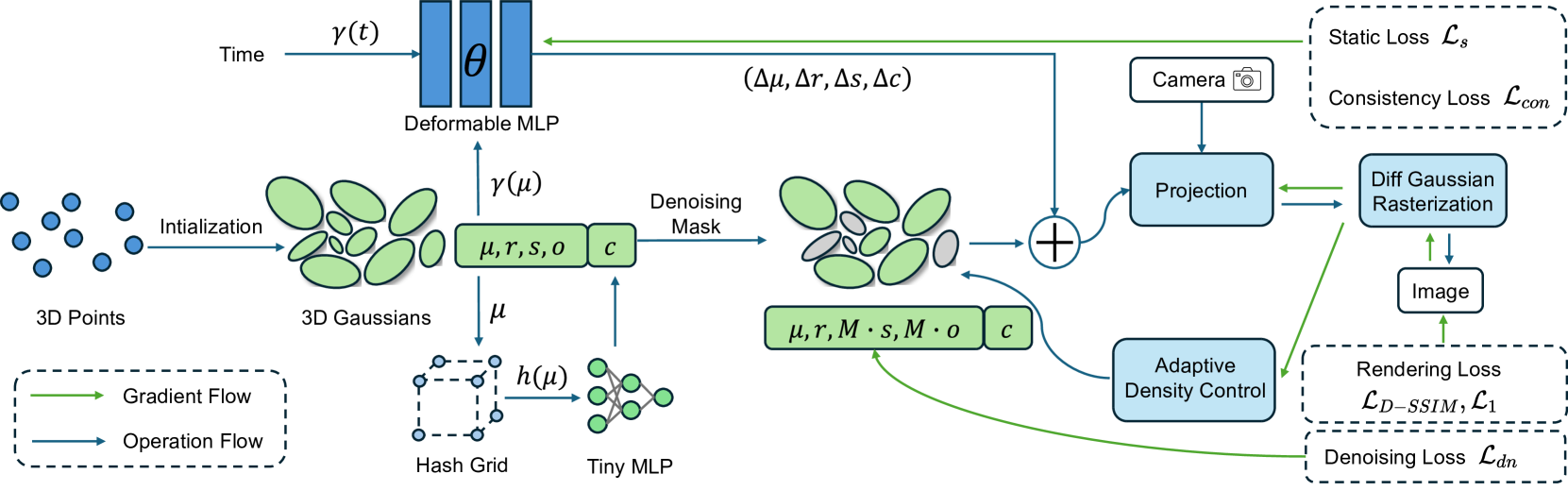
A Refined 3D Gaussian Representation for High-Quality Dynamic Scene Reconstruction
Bin Zhang, Bi Zeng, Zexin Peng

0
0
In recent years, Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) has revolutionized three-dimensional (3D) reconstruction with its implicit representation. Building upon NeRF, 3D Gaussian Splatting (3D-GS) has departed from the implicit representation of neural networks and instead directly represents scenes as point clouds with Gaussian-shaped distributions. While this shift has notably elevated the rendering quality and speed of radiance fields but inevitably led to a significant increase in memory usage. Additionally, effectively rendering dynamic scenes in 3D-GS has emerged as a pressing challenge. To address these concerns, this paper purposes a refined 3D Gaussian representation for high-quality dynamic scene reconstruction. Firstly, we use a deformable multi-layer perceptron (MLP) network to capture the dynamic offset of Gaussian points and express the color features of points through hash encoding and a tiny MLP to reduce storage requirements. Subsequently, we introduce a learnable denoising mask coupled with denoising loss to eliminate noise points from the scene, thereby further compressing 3D Gaussian model. Finally, motion noise of points is mitigated through static constraints and motion consistency constraints. Experimental results demonstrate that our method surpasses existing approaches in rendering quality and speed, while significantly reducing the memory usage associated with 3D-GS, making it highly suitable for various tasks such as novel view synthesis, and dynamic mapping.
5/29/2024