Helmsman of the Masses? Evaluate the Opinion Leadership of Large Language Models in the Werewolf Game
2404.01602

0
0
💬
Abstract
Large language models (LLMs) have exhibited memorable strategic behaviors in social deductive games. However, the significance of opinion leadership exhibited by LLM-based agents has been overlooked, which is crucial for practical applications in multi-agent and human-AI interaction settings. Opinion leaders are individuals who have a noticeable impact on the beliefs and behaviors of others within a social group. In this work, we employ the Werewolf game as a simulation platform to assess the opinion leadership of LLMs. The game features the role of the Sheriff, tasked with summarizing arguments and recommending decision options, and therefore serves as a credible proxy for an opinion leader. We develop a framework integrating the Sheriff role and devise two novel metrics for evaluation based on the critical characteristics of opinion leaders. The first metric measures the reliability of the opinion leader, and the second assesses the influence of the opinion leader on other players' decisions. We conduct extensive experiments to evaluate LLMs of different scales. In addition, we collect a Werewolf question-answering dataset (WWQA) to assess and enhance LLM's grasp of the game rules, and we also incorporate human participants for further analysis. The results suggest that the Werewolf game is a suitable test bed to evaluate the opinion leadership of LLMs and few LLMs possess the capacity for opinion leadership.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- Large language models (LLMs) have displayed interesting strategic behaviors in social deductive games.
- However, their potential as opinion leaders, which is crucial for practical applications, has been overlooked.
- This study examines the opinion leadership of LLMs using the Werewolf game as a simulation platform.
Plain English Explanation
Opinion leaders are individuals who can significantly influence the beliefs and behaviors of others within a social group. The Werewolf game features the role of the Sheriff, who is tasked with summarizing arguments and recommending decision options, making it a suitable proxy for an opinion leader.
In this research, the authors developed a framework that integrates the Sheriff role and devised two novel metrics to evaluate the opinion leadership of LLMs. The first metric measures the reliability of the opinion leader, while the second assesses the influence of the opinion leader on other players' decisions.
The study conducted extensive experiments to evaluate LLMs of different scales and also collected a Werewolf question-answering dataset (WWQA) to assess and enhance the LLMs' understanding of the game rules. Additionally, the researchers incorporated human participants for further analysis.
The results suggest that the Werewolf game is a suitable test bed to evaluate the opinion leadership of LLMs, but few LLMs currently possess the capacity for effective opinion leadership.
Technical Explanation
The researchers employed the Werewolf game as a simulation platform to assess the opinion leadership of LLMs. In the Werewolf game, the role of the Sheriff is tasked with summarizing arguments and recommending decision options, making it a credible proxy for an opinion leader.
The authors developed a framework that integrates the Sheriff role and devised two novel metrics for evaluating opinion leadership:
- Reliability Metric: This metric measures the reliability of the opinion leader in providing accurate and consistent recommendations.
- Influence Metric: This metric assesses the influence of the opinion leader on other players' decisions.
The researchers conducted extensive experiments to evaluate LLMs of different scales and also collected a Werewolf question-answering dataset (WWQA) to assess and enhance the LLMs' understanding of the game rules. Additionally, human participants were incorporated into the study for further analysis.
Critical Analysis
The researchers acknowledge that the Werewolf game serves as a suitable test bed for evaluating the opinion leadership of LLMs, but the results indicate that few LLMs currently possess the capacity for effective opinion leadership.
The study's limitations include the specific nature of the Werewolf game, which may not fully capture the complexities of real-world opinion leadership scenarios. Additionally, the reliance on automated metrics, while providing objective measures, may overlook nuanced aspects of opinion leadership that are better assessed through human evaluation.
Further research could explore the opinion leadership of LLMs in a wider range of social interaction scenarios, incorporating more diverse and realistic settings. Investigating the specific capabilities and limitations of LLMs in opinion leadership roles could also inform the development of more effective and trustworthy AI assistants for practical applications.
Conclusion
This study provides valuable insights into the opinion leadership capabilities of large language models (LLMs) using the Werewolf game as a simulation platform. The results suggest that while LLMs have exhibited strategic behaviors in social deductive games, few possess the capacity for effective opinion leadership.
The research highlights the need to further explore the opinion leadership capabilities of LLMs and their potential implications for multi-agent and human-AI interaction settings. Continued advancements in this area could lead to the development of more reliable and influential AI assistants, with significant applications in various domains.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
💬
Exploring Large Language Models for Communication Games: An Empirical Study on Werewolf
Yuzhuang Xu, Shuo Wang, Peng Li, Fuwen Luo, Xiaolong Wang, Weidong Liu, Yang Liu

0
0
Communication games, which we refer to as incomplete information games that heavily depend on natural language communication, hold significant research value in fields such as economics, social science, and artificial intelligence. In this work, we explore the problem of how to engage large language models (LLMs) in communication games, and in response, propose a tuning-free framework. Our approach keeps LLMs frozen, and relies on the retrieval and reflection on past communications and experiences for improvement. An empirical study on the representative and widely-studied communication game, ``Werewolf'', demonstrates that our framework can effectively play Werewolf game without tuning the parameters of the LLMs. More importantly, strategic behaviors begin to emerge in our experiments, suggesting that it will be a fruitful journey to engage LLMs in communication games and associated domains.
5/14/2024
💬
On the Principles behind Opinion Dynamics in Multi-Agent Systems of Large Language Models
Pedro Cisneros-Velarde

0
0
We study the evolution of opinions inside a population of interacting large language models (LLMs). Every LLM needs to decide how much funding to allocate to an item with three initial possibilities: full, partial, or no funding. We identify biases that drive the exchange of opinions based on the LLM's tendency to (i) find consensus with the other LLM's opinion, (ii) display caution when specifying funding, and (iii) consider ethical concerns in its opinion. We find these biases are affected by the perceived absence of compelling reasons for opinion change, the perceived willingness to engage in discussion, and the distribution of allocation values. Moreover, tensions among biases can lead to the survival of funding for items with negative connotations. We also find that the final distribution of full, partial, and no funding opinions is more diverse when an LLM freely forms its opinion after an interaction than when its opinion is a multiple-choice selection among the three allocation options. In the latter case, consensus or polarization is generally attained. When agents are aware of past opinions, they seek to maintain consistency with them, and more diverse updating rules emerge. Our study is performed using a Llama 3 LLM.
6/26/2024
💬
Enhance Reasoning for Large Language Models in the Game Werewolf
Shuang Wu, Liwen Zhu, Tao Yang, Shiwei Xu, Qiang Fu, Yang Wei, Haobo Fu

0
0
This paper presents an innovative framework that integrates Large Language Models (LLMs) with an external Thinker module to enhance the reasoning capabilities of LLM-based agents. Unlike augmenting LLMs with prompt engineering, Thinker directly harnesses knowledge from databases and employs various optimization techniques. The framework forms a reasoning hierarchy where LLMs handle intuitive System-1 tasks such as natural language processing, while the Thinker focuses on cognitive System-2 tasks that require complex logical analysis and domain-specific knowledge. Our framework is presented using a 9-player Werewolf game that demands dual-system reasoning. We introduce a communication protocol between LLMs and the Thinker, and train the Thinker using data from 18800 human sessions and reinforcement learning. Experiments demonstrate the framework's effectiveness in deductive reasoning, speech generation, and online game evaluation. Additionally, we fine-tune a 6B LLM to surpass GPT4 when integrated with the Thinker. This paper also contributes the largest dataset for social deduction games to date.
4/1/2024
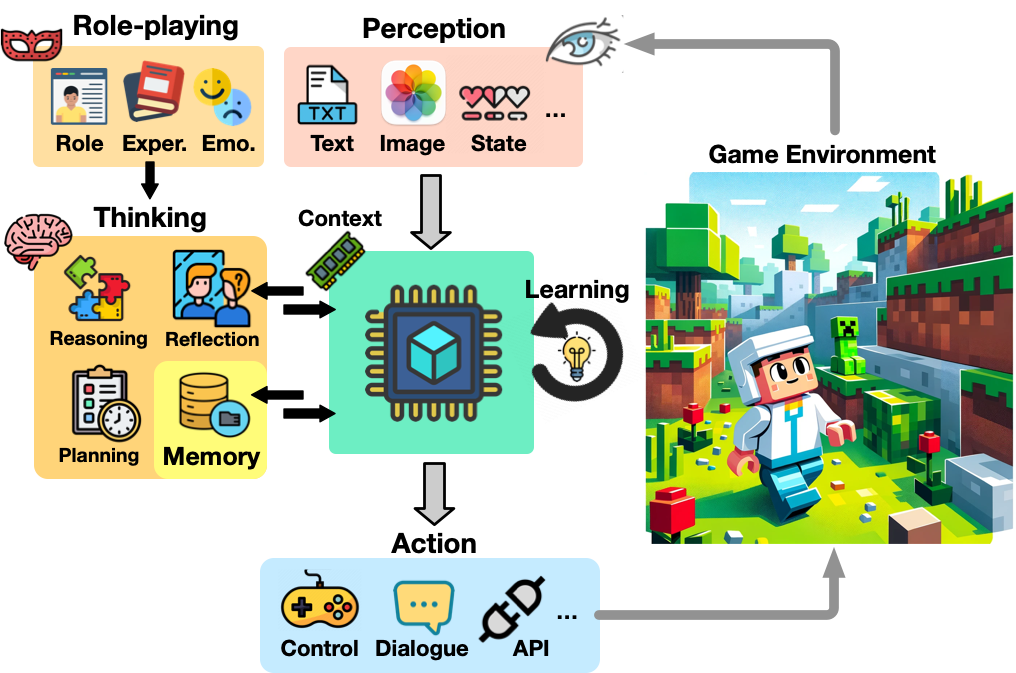
A Survey on Large Language Model-Based Game Agents
Sihao Hu, Tiansheng Huang, Fatih Ilhan, Selim Tekin, Gaowen Liu, Ramana Kompella, Ling Liu

0
0
The development of game agents holds a critical role in advancing towards Artificial General Intelligence (AGI). The progress of LLMs and their multimodal counterparts (MLLMs) offers an unprecedented opportunity to evolve and empower game agents with human-like decision-making capabilities in complex computer game environments. This paper provides a comprehensive overview of LLM-based game agents from a holistic viewpoint. First, we introduce the conceptual architecture of LLM-based game agents, centered around six essential functional components: perception, memory, thinking, role-playing, action, and learning. Second, we survey existing representative LLM-based game agents documented in the literature with respect to methodologies and adaptation agility across six genres of games, including adventure, communication, competition, cooperation, simulation, and crafting & exploration games. Finally, we present an outlook of future research and development directions in this burgeoning field. A curated list of relevant papers is maintained and made accessible at: https://github.com/git-disl/awesome-LLM-game-agent-papers.
4/3/2024