Home Energy Management Systems: Challenges, Heterogeneity & Integration Architecture Towards A Smart City Ecosystem

0
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- Home Energy Management Systems (HEMS) are crucial for achieving sustainability in smart cities
- HEMS face challenges due to the heterogeneity of devices and data sources
- A comprehensive integration architecture is needed to enable HEMS within a smart city ecosystem
Plain English Explanation
Home Energy Management Systems (HEMS) play a vital role in making smart cities more sustainable. These systems help monitor and control energy usage in homes, allowing residents to reduce their energy consumption and carbon footprint. However, HEMS face several challenges due to the wide variety of devices and data sources involved.
Smart Cities often have a diverse range of energy-consuming appliances, renewable energy sources, and other systems that need to be integrated and managed. This heterogeneity can make it difficult to collect, process, and analyze energy data from multiple sources.
To address these challenges, researchers are working on developing a comprehensive integration architecture that can seamlessly connect all the different components of a smart city's energy ecosystem. This architecture would enable [object Object] and [object Object], ultimately contributing to the overall sustainability of the smart city.
Technical Explanation
The paper discusses the challenges and complexities involved in developing Home Energy Management Systems (HEMS) within the context of a smart city ecosystem. HEMS are essential for achieving sustainability in smart cities, as they enable the monitoring and optimization of energy usage in residential and commercial buildings.
One of the key challenges identified is the [object Object] of devices and data sources involved in a smart city's energy ecosystem. Smart cities often have a diverse range of energy-consuming appliances, renewable energy sources, and other systems that need to be integrated and managed. This diversity can make it challenging to collect, process, and analyze energy data from multiple sources.
To address these challenges, the paper proposes a comprehensive [object Object] that can seamlessly connect all the different components of a smart city's energy ecosystem. This architecture would enable efficient energy management and [object Object], allowing for the optimization of energy consumption and the integration of renewable energy sources.
The proposed architecture leverages [object Object] technologies and [object Object] to create a unified platform for data collection, processing, and decision-making. By addressing the heterogeneity challenge, this architecture aims to facilitate the seamless integration of HEMS within the broader smart city ecosystem, contributing to the overall sustainability of the urban environment.
Critical Analysis
The paper highlights the important role of HEMS in achieving sustainability in smart cities, but it also acknowledges the significant challenges posed by the heterogeneity of devices and data sources. The proposed integration architecture is a promising solution, but the authors do not provide a detailed evaluation of its implementation or effectiveness.
One potential limitation of the proposed architecture is the reliance on IoT technologies, which can introduce [object Object] that need to be addressed. Additionally, the integration of diverse energy-consuming systems and renewable energy sources may require complex [object Object] that are not fully explored in the paper.
Further research could investigate the practical implementation of the proposed architecture, including the development of [object Object] to facilitate the integration of heterogeneous systems. Additionally, the [object Object] within the broader smart city ecosystem could be an important area of study.
Conclusion
The paper highlights the critical role of Home Energy Management Systems (HEMS) in achieving sustainability within smart cities. However, the heterogeneity of devices and data sources involved in smart city energy ecosystems poses significant challenges for the development and integration of HEMS.
To address these challenges, the paper proposes a comprehensive integration architecture that leverages Internet of Things technologies and semantic modeling to enable efficient energy management and smart home automation. This architecture aims to facilitate the seamless integration of HEMS within the broader smart city ecosystem, contributing to the overall sustainability of urban environments.
While the proposed solution is promising, further research is needed to address potential limitations, such as security and privacy concerns, and to explore the practical implementation of the integration architecture. Ultimately, the successful development and integration of HEMS within smart cities is crucial for achieving sustainability and improving the overall quality of life for urban residents.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Home Energy Management Systems: Challenges, Heterogeneity & Integration Architecture Towards A Smart City Ecosystem
Georgios Kormpakis, Alexios Lekidis, Elissaios Sarmas, Giannis Papias, Filippos Serepas, George Stravodimos, Vangelis Marinakis
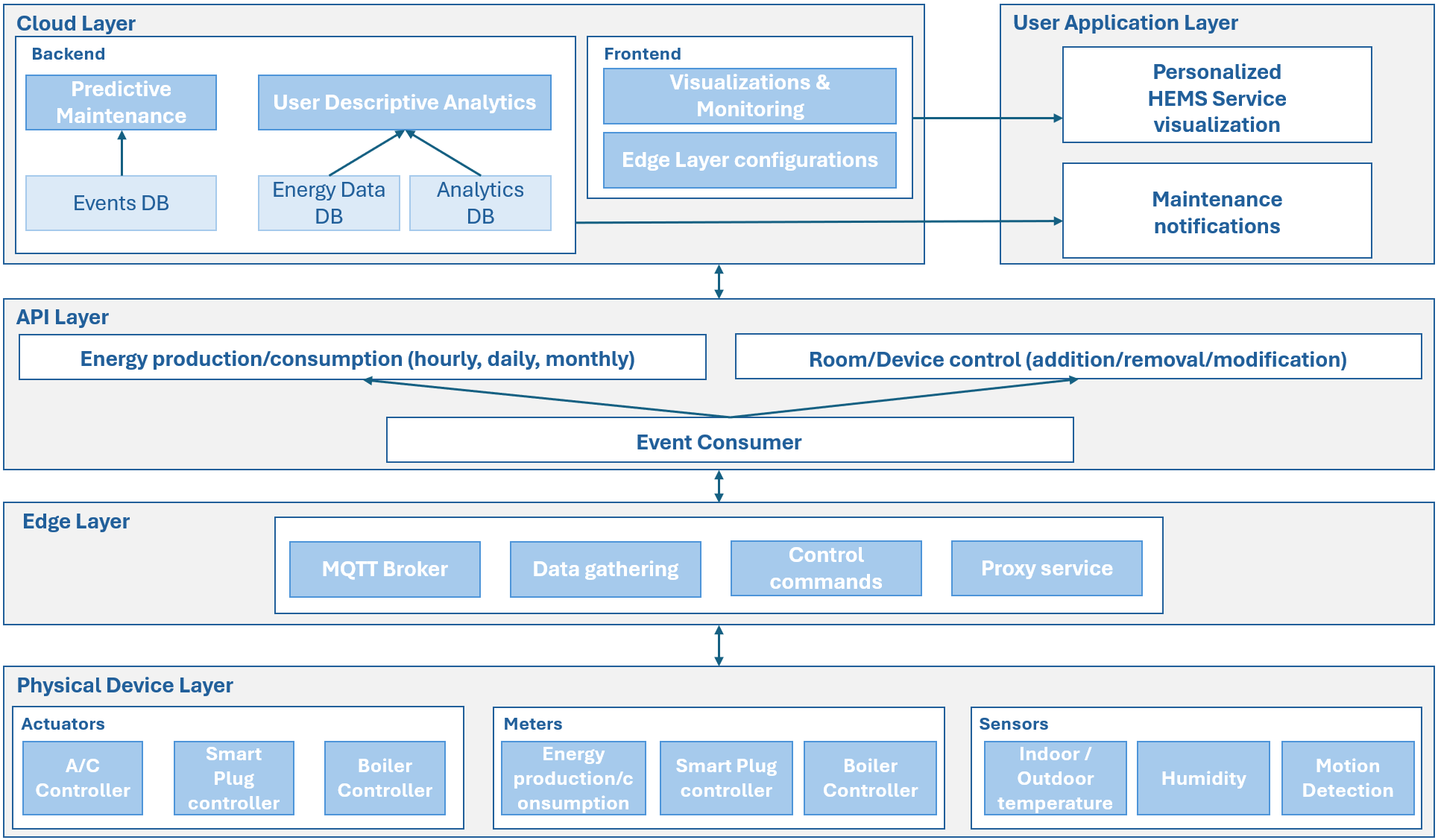
The contemporary era is marked by rapid urban growth and increasing population. A significant, and constantly growing, portion of the global population now resides in major cities, leading to escalating energy demands in urban centers. As urban population is expected to keep on expanding in the near future, the same is also expected to happen with the associated energy requirements. The situation with the continuously increasing energy demand, along with the emergence of smart grids and the capabilities that are already -- or can be -- offered by Home Energy Management System (HEMS), has created a lot of opportunities towards a more sustainable future, with optimized energy consumption and demand response, which leads to economic and environmental benefits, based on the actual needs of the consumers. In this paper, we begin by providing an analytical exploration of the challenges faced at both the development and deployment levels. We proceed with a thorough analysis and comparison between the abundance of devices, smart home technologies, and protocols currently used by various products. Following, aiming to blunt the currently existing challenges, we propose a reliable, flexible, and extendable architectural schema. Finally, we analyze a number of potential ways in which the data deriving from such implementations can be analyzed and leveraged, in order to produce services that offer useful insights and smart solutions towards enhanced energy efficiency.
Read more8/9/2024
📈

0
Intelligent Energy Management with IoT Framework in Smart Cities Using Intelligent Analysis: An Application of Machine Learning Methods for Complex Networks and Systems
Maryam Nikpour, Parisa Behvand Yousefi, Hadi Jafarzadeh, Kasra Danesh, Roya Shomali, Ahmad Gholizadeh Lonbar, Mohsen Ahmadi
This study confronts the growing challenges of energy consumption and the depletion of energy resources, particularly in the context of smart buildings. As the demand for energy increases alongside the necessity for efficient building maintenance, it becomes imperative to explore innovative energy management solutions. We present a comprehensive review of Internet of Things (IoT)-based frameworks aimed at smart city energy management, highlighting the pivotal role of IoT devices in addressing these issues due to their compactness, sensing, measurement, and computing capabilities. Our review methodology encompasses a thorough analysis of existing literature on IoT architectures and frameworks for intelligent energy management applications. We focus on systems that not only collect and store data but also support intelligent analysis for monitoring, controlling, and enhancing system efficiency. Additionally, we examine the potential for these frameworks to serve as platforms for the development of third-party applications, thereby extending their utility and adaptability. The findings from our review indicate that IoT-based frameworks offer significant potential to reduce energy consumption and environmental impact in smart buildings. Through the adoption of intelligent mechanisms and solutions, these frameworks facilitate effective energy management, leading to improved system efficiency and sustainability. Considering these findings, we recommend further exploration and adoption of IoT-based wireless sensing systems in smart buildings as a strategic approach to energy management. Our review underscores the importance of incorporating intelligent analysis and enabling the development of third-party applications within the IoT framework to efficiently meet the evolving energy demands and maintenance challenges
Read more8/26/2024
✅

0
Integrating Power-to-Heat Services in Geographically Distributed Multi-Energy Systems: A Case Study from the ERIGrid 2.0 Project
Giuseppe Silano, Evangelos Rikos, Vetrivel Rajkumar, Oliver Gehrke, Tesfaye Amare Zerihun, Carmine Rodio, Riccardo Lazzari
This paper investigates the integration and validation of multi-energy systems within the H2020 ERIGrid 2.0 project, focusing on the deployment of the JaNDER software middleware and universal API (uAPI) to establish a robust, high-data-rate, and low-latency communication link between Research Infrastructures (RIs). The middleware facilitates seamless integration of RIs through specifically designed transport layers, while the uAPI provides a simplified and standardized interface to ease deployment. A motivating case study explores the provision of power-to-heat services in a local multi-energy district, involving laboratories in Denmark, Greece, Italy, the Netherlands, and Norway, and analyzing their impact on electrical and thermal networks. This paper not only demonstrates the practical application of Geographically Distributed Simulations and Hardware-in-the-Loop technologies but also highlights their effectiveness in enhancing system flexibility and managing grid dynamics under various operational scenarios.
Read more7/2/2024
🎯

0
A Survey on Semantic Modeling for Building Energy Management
Miracle Aniakor, Vinicius V. Cogo, Pedro M. Ferreira
Buildings account for a substantial portion of global energy consumption. Reducing buildings' energy usage primarily involves obtaining data from building systems and environment, which are instrumental in assessing and optimizing the building's performance. However, as devices from various manufacturers represent their data in unique ways, this disparity introduces challenges for semantic interoperability and creates obstacles in developing scalable building applications. This survey explores the leading semantic modeling techniques deployed for energy management in buildings. Furthermore, it aims to offer tangible use cases for applying semantic models, shedding light on the pivotal concepts and limitations intrinsic to each model. Our findings will assist researchers in discerning the appropriate circumstances and methodologies for employing these models in various use cases.
Read more4/19/2024