Hybrid Precoding and Combining for mmWave Full-Duplex Joint Radar and Communication Systems under Self-Interference
2311.14942

0
0

Abstract
In the context of integrated sensing and communication (ISAC), a full-duplex (FD) transceiver can operate as a monostatic radar while maintaining communication capabilities. This paper investigates the design of precoders and combiners for a joint radar and communication (JRC) system at mmWave frequencies. The primary goal of the design is to guarantee certain performance in terms of some sensing and communication metrics while minimizing the self-interference (SI) caused by FD operation and taking into account the hardware limitations coming from a hybrid MIMO architecture. Specifically, we introduce a generalized eigenvalue-based precoder design that considers the downlink user rate, the radar gain, and the SI suppression. Since the hybrid analog/digital architecture degrades the SI mitigation capability of the precoder, we further enhance SI suppression with the analog combiner. Our numerical results demonstrate that the proposed architecture achieves the required radar gain and SI mitigation while incurring a small loss in downlink spectral efficiency. Additionally, the numerical experiments also show that the use of orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) radar with the proposed beamforming architecture results in highly accurate range and velocity estimates for the detected targets.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This research paper explores a hybrid precoding and combining technique for mmWave full-duplex joint radar and communication systems, with a focus on addressing self-interference.
- The proposed approach aims to enable simultaneous radar sensing and high-speed data communication in the millimeter-wave (mmWave) frequency band.
- The key challenge addressed is the self-interference that arises when the radar and communication functions operate concurrently, which can degrade system performance.
Plain English Explanation
The paper looks at a way to combine radar and high-speed wireless communication in the same device, using the millimeter-wave (very short wavelength) part of the radio spectrum. Typically, trying to do both radar and communication at the same time causes interference that can mess up the signals. The researchers developed a new approach to precoding (preparing the signals before transmission) and combining (processing the received signals) that helps cancel out this self-interference. This allows the device to effectively perform radar sensing and high-speed data communication simultaneously, which could be useful for applications like self-driving cars that need both capabilities.
Technical Explanation
The paper proposes a hybrid analog-digital precoding and combining architecture for full-duplex mmWave systems that perform joint radar and communication functions. The key technical elements include:
- System model: Describes the full-duplex mmWave transceiver with separate radar and communication functionalities, and the self-interference channel model.
- Hybrid precoding and combining design: Develops an optimization-based approach to jointly design the analog and digital precoding/combining matrices to maximize the radar and communication performance while mitigating self-interference.
- Performance analysis: Provides analytical expressions for the achievable radar and communication rates, and evaluates the tradeoffs between these two functionalities.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a comprehensive technical solution to the challenging problem of enabling full-duplex joint radar and communication in the mmWave band. However, some potential limitations and areas for further research are:
- The analysis assumes perfect channel state information, which may be difficult to acquire in practice, especially for the self-interference channel.
- The optimization problem to design the hybrid precoders/combiners is non-convex, so the proposed solution may not guarantee a globally optimal result.
- The performance evaluation is primarily analytical, and more extensive simulations or experiments would be needed to validate the practical feasibility and benefits of the proposed approach.
- The paper does not consider the impact of hardware impairments, such as phase noise and power amplifier nonlinearities, which can significantly affect the full-duplex operation in the mmWave regime.
Conclusion
This research represents an important step towards realizing the vision of integrated radar and communication systems operating in the mmWave band. The proposed hybrid precoding and combining technique offers a promising solution to mitigate self-interference and enable the concurrent use of radar sensing and high-speed data communication. Further advancements in areas like channel estimation, optimization algorithms, and hardware design will be crucial to translating these theoretical insights into practical, real-world deployments of such advanced wireless systems.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
Cooperative Sensing and Communication for ISAC Networks: Performance Analysis and Optimization
Kaitao Meng, Christos Masouros

0
0
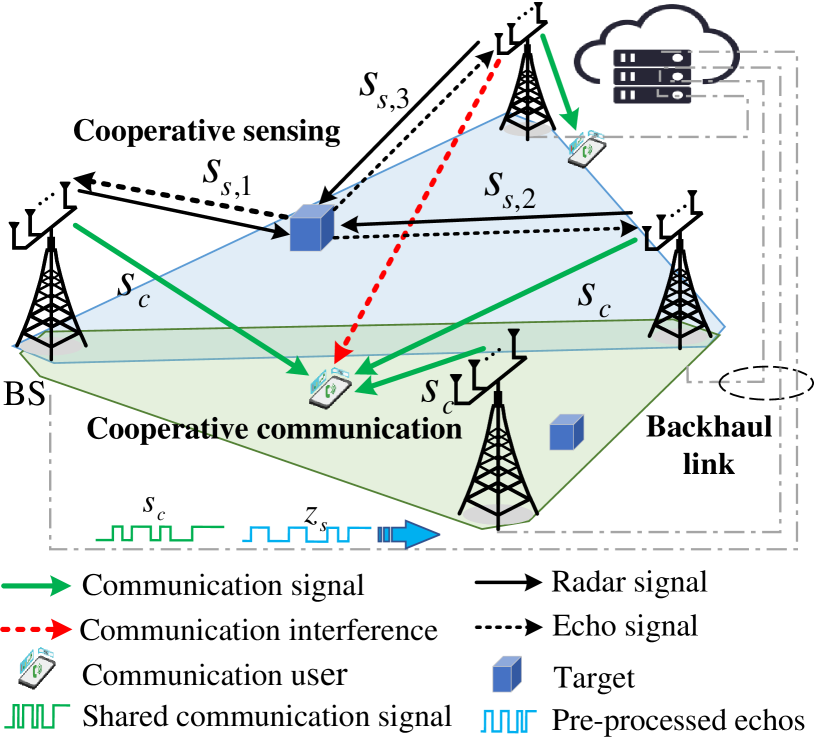
In this work, we study integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) networks intending to effectively balance sensing and communication (S&C) performance at the network level. Through the simultaneous utilization of multi-point (CoMP) coordinated joint transmission and distributed multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) radar techniques, we propose a cooperative networked ISAC scheme to enhance both S&C services. Then, the tool of stochastic geometry is exploited to capture the S&C performance, which allows us to illuminate key cooperative dependencies in the ISAC network. Remarkably, the derived expression of the Cramer-Rao lower bound (CRLB) of the localization accuracy unveils a significant finding: Deploying $N$ ISAC transceivers yields an enhanced sensing performance across the entire network, in accordance with the $ln^2N$ scaling law. Simulation results demonstrate that compared to the time-sharing scheme, the proposed cooperative ISAC scheme can effectively improve the average data rate and reduce the CRLB.
4/1/2024

Hybrid Beamforming Design for RSMA-assisted mmWave Integrated Sensing and Communications
Jun Gong, Wenchi Cheng, Jiangzhou Wang, Jingqing Wang

0
0
Integrated sensing and communications (ISAC) has been considered one of the new paradigms for sixth-generation (6G) wireless networks. In the millimeter-wave (mmWave) ISAC system, hybrid beamforming (HBF) is considered an emerging technology to exploit the limited number of radio frequency (RF) chains in order to reduce the system hardware cost and power consumption. However, the HBF structure reduces the spatial degrees of freedom for the ISAC system, which further leads to increased interference between multiple users and between users and radar sensing. To solve the above problem, rate split multiple access (RSMA), which is a flexible and robust interference management strategy, is considered. We investigate the joint common rate allocation and HBF design problem for the HBF-based RSMA-assisted mmWave ISAC scheme. We propose the penalty dual decomposition (PDD) method coupled with the weighted mean squared error (WMMSE) minimization method to solve this high-dimensional non-convex problem, which converges to the Karush-Kuhn-Tucker (KKT) point of the original problem. Then, we extend the proposed algorithm to the HBF design based on finite-resolution phase shifters (PSs) to further improve the energy efficiency of the system. Simulation results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm and show that the RSMA-ISAC scheme outperforms other benchmark schemes.
6/10/2024
🏷️
Multi-Antenna Dual-Blind Deconvolution for Joint Radar-Communications via SoMAN Minimization
Roman Jacome, Edwin Vargas, Kumar Vijay Mishra, Brian M. Sadler, Henry Arguello

0
0
In joint radar-communications (JRC) applications such as secure military receivers, often the radar and communications signals are overlaid in the received signal. In these passive listening outposts, the signals and channels of both radar and communications are unknown to the receiver. The ill-posed problem of recovering all signal and channel parameters from the overlaid signal is termed as textit{dual-blind deconvolution} (DBD). In this work, we investigate DBD for a multi-antenna receiver. We model the radar and communications channels with a few (sparse) textit{continuous-valued} parameters such as time delays, Doppler velocities, and directions-of-arrival (DoAs). To solve this highly ill-posed DBD, we propose to minimize the sum of multivariate atomic norms (SoMAN) that depend on unknown parameters. To this end, we devise an exact semidefinite program using theories of positive hyperoctant trigonometric polynomials (PhTP). Our theoretical analyses show that the minimum number of samples and antennas required for perfect recovery is logarithmically dependent on the maximum of the number of radar targets and communications paths rather than their sum. We show that our approach is easily generalized to include several practical issues such as gain/phase errors and additive noise. Numerical experiments show the exact parameter recovery for different JRC scenarios.
4/1/2024
🔄
Staggered Comb Reference Signal Design for Integrated Communication and Sensing
Rui Zhang, Shawn Tsai, Tzu-Han Chou, Jiaying Ren

0
0
Ambiguity performance is a critical criterion in radar sensor design, which indicates the ambiguities arising from multiple target estimation and detection. We considered a requirement-driven selection of OFDM reference signal (RS) patterns based on ambiguity performances for bi-static sensing in integrated communication and sensing with minimal modifications of current RSs. An RS pattern with a staggering offset of a linear slope that is relatively prime to the RS comb size is suggested for standard-resolution sensing algorithms to obtain the best ambiguity performances. Moreover, an extended guard interval design is proposed to increase the maximum time delay, that is inter-symbol interference (ISI) free using post-FFT sensing algorithms. The proposed techniques are promising to extend the distance and speed without ambiguities and ISI for sensing.
4/26/2024