Hybrid Beamforming Design for RSMA-assisted mmWave Integrated Sensing and Communications

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- This paper explores a hybrid beamforming design for millimeter wave (mmWave) integrated sensing and communications (ISAC) systems that utilize rate-splitting multiple access (RSMA).
- The proposed approach aims to enhance the performance of mmWave ISAC systems by optimizing the beamforming design to support both sensing and communication objectives.
- Key aspects include the integration of RSMA to improve spectral efficiency, the development of a hybrid beamforming framework, and the optimization of the beamforming vectors to balance sensing and communication requirements.
Plain English Explanation
The paper discusses a new way to design the beamforming, which is a technique used to direct wireless signals in a specific direction, for millimeter wave (mmWave) communication and sensing systems. These systems are used in various applications, such as 5G and 6G networks, autonomous vehicles, and smart cities, to provide both sensing and communication capabilities.
The researchers propose integrating a technique called rate-splitting multiple access (RSMA) into the beamforming design. RSMA allows multiple users to share the same wireless channel, improving the overall efficiency of the system. The hybrid beamforming approach combines digital and analog components to further optimize the performance, balancing the needs of sensing and communication.
By carefully designing the beamforming vectors, the system can effectively support both the sensing and communication functions, potentially leading to improved performance and capabilities for mmWave ISAC applications. This could enable advanced features like better object detection and tracking, as well as more reliable and efficient wireless communication in various technological domains.
Technical Explanation
The paper presents a hybrid beamforming design for RSMA-assisted mmWave integrated sensing and communications (ISAC) systems. The researchers develop a framework that integrates RSMA into the beamforming design to enhance the performance of mmWave ISAC systems.
The proposed approach utilizes a hybrid beamforming architecture that combines digital and analog components. The beamforming vectors are optimized to jointly support the sensing and communication objectives, leveraging the benefits of RSMA to improve spectral efficiency.
The optimization problem is formulated to maximize the sensing-communication trade-off, considering factors such as the signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio (SINR) for communication and the beampattern correlation for sensing. The researchers develop an efficient algorithm to solve this optimization problem, enabling the system to adaptively adjust the beamforming based on the specific requirements and operating conditions.
Through simulations, the authors demonstrate the performance advantages of the proposed RSMA-assisted mmWave ISAC system compared to conventional approaches. The hybrid beamforming design with RSMA shows improvements in both communication and sensing metrics, highlighting its potential for real-world applications.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a comprehensive framework for designing hybrid beamforming in mmWave ISAC systems with RSMA. The authors have thoroughly addressed the technical details and provided a solid mathematical formulation for the optimization problem.
One potential limitation is the assumption of perfect channel state information, which may not always be realistic in practical deployments. The impact of channel estimation errors or imperfect knowledge of the environment on the system performance could be an interesting area for further research.
Additionally, the paper focuses on the theoretical aspects and simulation-based evaluations. Validating the proposed approach through real-world experiments or prototypes would be valuable to assess its feasibility and identify any additional challenges that may arise in practical implementations.
The authors have made a compelling case for the benefits of integrating RSMA into mmWave ISAC systems, but the actual deployment and adoption of this technology will depend on factors such as hardware complexity, cost, and regulatory considerations, which could be explored in future work.
Conclusion
This paper presents a hybrid beamforming design for RSMA-assisted mmWave integrated sensing and communications (ISAC) systems. The proposed approach combines the advantages of RSMA and hybrid beamforming to optimize the performance of mmWave ISAC systems, enabling them to effectively support both sensing and communication objectives.
The integration of RSMA enhances the spectral efficiency, while the hybrid beamforming framework allows for a flexible and adaptive allocation of resources between sensing and communication. The optimized beamforming vectors help to balance the trade-off between these two functionalities, potentially leading to improved capabilities in various applications, such as 5G/6G networks, autonomous vehicles, and smart city infrastructure.
The technical details and simulation-based evaluations provided in the paper demonstrate the viability and potential benefits of this approach. Further research exploring practical implementation aspects and real-world validation would be valuable to fully assess the impact of this innovation on the development of advanced mmWave ISAC systems.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Hybrid Beamforming Design for RSMA-assisted mmWave Integrated Sensing and Communications
Jun Gong, Wenchi Cheng, Jiangzhou Wang, Jingqing Wang
Integrated sensing and communications (ISAC) has been considered one of the new paradigms for sixth-generation (6G) wireless networks. In the millimeter-wave (mmWave) ISAC system, hybrid beamforming (HBF) is considered an emerging technology to exploit the limited number of radio frequency (RF) chains in order to reduce the system hardware cost and power consumption. However, the HBF structure reduces the spatial degrees of freedom for the ISAC system, which further leads to increased interference between multiple users and between users and radar sensing. To solve the above problem, rate split multiple access (RSMA), which is a flexible and robust interference management strategy, is considered. We investigate the joint common rate allocation and HBF design problem for the HBF-based RSMA-assisted mmWave ISAC scheme. We propose the penalty dual decomposition (PDD) method coupled with the weighted mean squared error (WMMSE) minimization method to solve this high-dimensional non-convex problem, which converges to the Karush-Kuhn-Tucker (KKT) point of the original problem. Then, we extend the proposed algorithm to the HBF design based on finite-resolution phase shifters (PSs) to further improve the energy efficiency of the system. Simulation results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm and show that the RSMA-ISAC scheme outperforms other benchmark schemes.
Read more6/10/2024


0
A Bistatic ISAC Framework for LEO Satellite Systems: A Rate-Splitting Approach
Juha Park, Jaehyup Seong, Jaehak Ryu, Yijie Mao, Wonjae Shin
Aiming to achieve ubiquitous global connectivity and target detection on the same platform with improved spectral/energy efficiency and reduced onboard hardware cost, low Earth orbit (LEO) satellite systems capable of simultaneously performing communications and radar have attracted significant attention. Designing such a joint system should address not only the challenges of integrating two functions but also the unique propagation characteristics of the satellites. To overcome severe echo signal path loss due to the high altitude of the satellite, we put forth a bistatic integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) framework with a radar receiver separated from the satellite. For robust and effective interference management, we employ rate-splitting multiple access (RSMA), which splits and encodes users messages into private and common streams. We optimize the dual-functional precoders to maximize the minimum rate among all users while satisfying the Cramer-Rao bound (CRB) constraints. Given the challenge of acquiring instantaneous channel state information (iCSI) for LEO satellites, we exploit the geometrical and statistical characteristics of the satellite channel. To develop an efficient optimization algorithm, semidefinite relaxation (SDR), sequential rank-1 constraint relaxation (SROCR), and successive convex approximation (SCA) are utilized. Numerical results show that the proposed framework efficiently performs both communication and radar, demonstrating superior interference control capabilities. Furthermore, it is validated that the common stream plays three vital roles: i) beamforming towards the radar target, ii) interference management between communications and radar, and iii) interference management among communication users.
Read more7/15/2024


0
Radio Resource Management Design for RSMA: Optimization of Beamforming, User Admission, and Discrete/Continuous Rates with Imperfect SIC
L. F. Abanto-Leon, A. Krishnamoorthy, A. Garcia-Saavedra, G. H. Sim, R. Schober, M. Hollick
This paper investigates the radio resource management (RRM) design for multiuser rate-splitting multiple access (RSMA), accounting for various characteristics of practical wireless systems, such as the use of discrete rates, the inability to serve all users, and the imperfect successive interference cancellation (SIC). Specifically, failure to consider these characteristics in RRM design may lead to inefficient use of radio resources. Therefore, we formulate the RRM of RSMA as optimization problems to maximize respectively the weighted sum rate (WSR) and weighted energy efficiency (WEE), and jointly optimize the beamforming, user admission, discrete/continuous rates, accounting for imperfect SIC, which result in nonconvex mixed-integer nonlinear programs that are challenging to solve. Despite the difficulty of the optimization problems, we develop algorithms that can find high-quality solutions. We show via simulations that carefully accounting for the aforementioned characteristics, can lead to significant gains. Precisely, by considering that transmission rates are discrete, the transmit power can be utilized more intelligently, allocating just enough power to guarantee a given discrete rate. Additionally, we reveal that user admission plays a crucial role in RSMA, enabling additional gains compared to random admission by facilitating the servicing of selected users with mutually beneficial channel characteristics. Furthermore, provisioning for possibly imperfect SIC makes RSMA more robust and reliable.
Read more5/1/2024

0
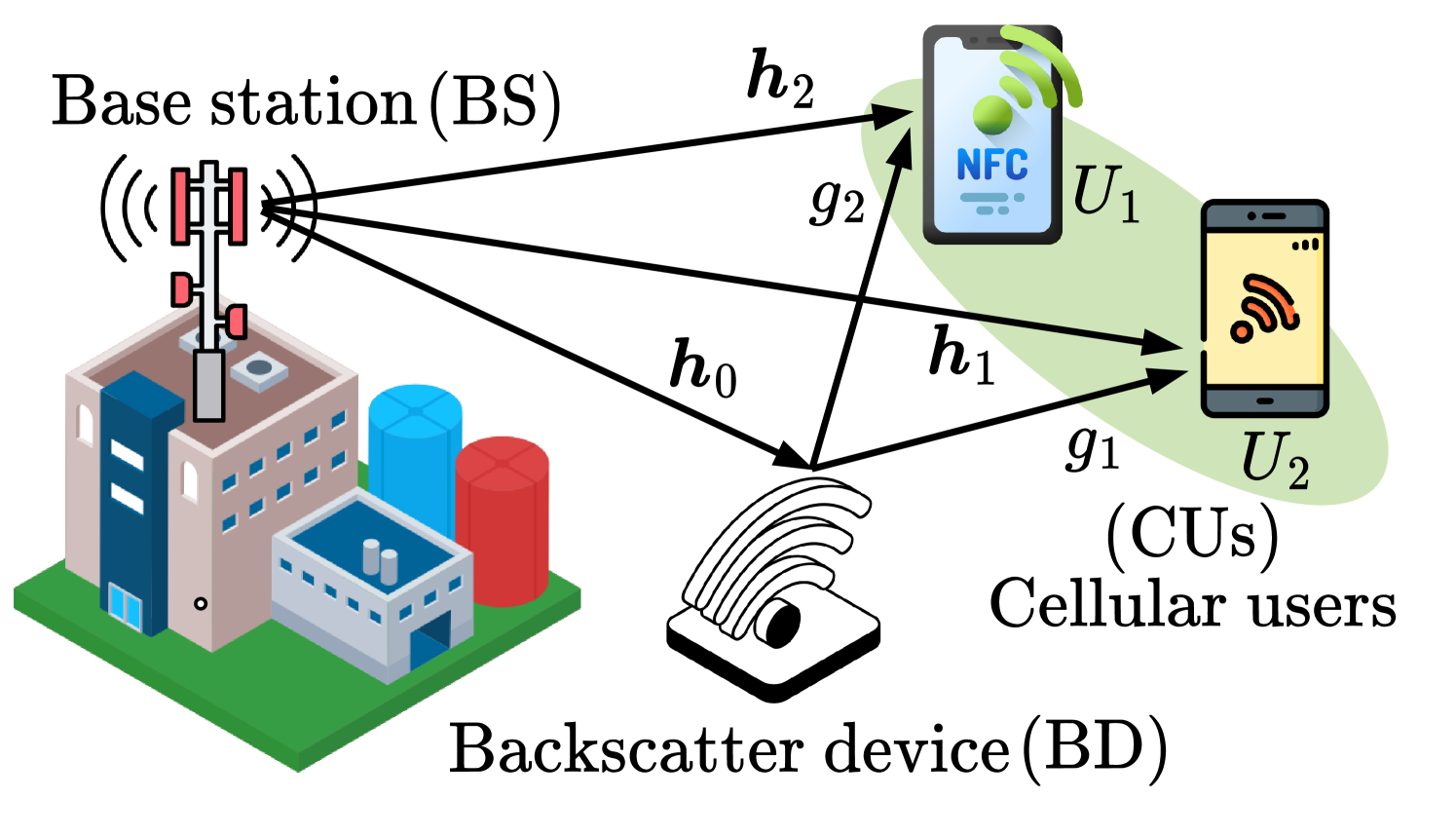
A Novel Paradigm Shift for Next-Generation: Symbiotic Backscatter Rate-Splitting Multiple Access Systems
Thai-Hoc Vu, Daniel Benevides da Costa, Bao Vo Nguyen Quoc, Sunghwan Kim
Next-generation wireless networks are projected to empower a broad range of Internet-of-things (IoT) applications and services with extreme data rates, posing new challenges in delivering large-scale connectivity at a low cost to current communication paradigms. Rate-splitting multiple access (RSMA) is one of the most spotlight nominees, conceived to address spectrum scarcity while reaching massive connectivity. Meanwhile, symbiotic communication is said to be an inexpensive way to realize future IoT on a large scale. To reach the goal of spectrum efficiency improvement and low energy consumption, we merge these advances by means of introducing a novel paradigm shift, called symbiotic backscatter RSMA, for the next generation. Specifically, we first establish the way to operate the symbiotic system to assist the readers in apprehending the proposed paradigm, then guide detailed design in beamforming weights with four potential gain-control (GC) strategies for enhancing symbiotic communication, and finally provide an information-theoretic framework using a new metric, called symbiotic outage probability (SOP) to characterize the proposed system performance. Through numerical result experiments, we show that the developed framework can accurately predict the actual SOP and the efficacy of the proposed GC strategies in improving the SOP performance.
Read more6/5/2024