The Impact of 2D and 3D Gamified VR on Learning American Sign Language
2405.08908

0
0

Abstract
Sign language has been extensively studied as a means of facilitating effective communication between hearing individuals and the deaf community. With the continuous advancements in virtual reality (VR) and gamification technologies, an increasing number of studies have begun to explore the application of these emerging technologies in sign language learning. This paper describes a user study that compares the impact of 2D and 3D games on the user experience in ASL learning. Empirical evidence gathered through questionnaires supports the positive impact of 3D game environments on user engagement and overall experience, particularly in relation to attractiveness, usability, and efficiency. Moreover, initial findings demonstrate a similar behaviour of 2D and 3D games in terms of enhancing user experience. Finally, the study identifies areas where improvements can be made to enhance the dependability and clarity of 3D game environments. These findings contribute to the understanding of how game-based approaches, and specifically the utilisation of 3D environments, can positively influence the learning experience of ASL.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper investigates the impact of 2D and 3D gamified virtual reality (VR) on learning American Sign Language (ASL).
- The researchers developed two different learning environments - a 2D game-based approach and a 3D immersive VR experience - to teach ASL vocabulary and grammar.
- They then conducted a user study to compare the effectiveness of these two approaches in improving ASL proficiency.
Plain English Explanation
The paper explores how different types of digital learning tools can help people learn American Sign Language (ASL) more effectively. The researchers created two versions of an ASL learning program - one that uses a 2D game-like interface, and another that puts the user in a 3D virtual reality environment.
They then had people try out these two versions and measured how well the participants learned ASL vocabulary and grammar. The goal was to see if the more immersive 3D VR experience would lead to better ASL learning compared to the 2D game. This could help inform the development of future educational tools for learning sign language and other visual-spatial languages.
Technical Explanation
The researchers developed two ASL learning environments - a 2D game-based approach and a 3D immersive VR experience. The 2D game used a point-and-click interface to teach ASL vocabulary and grammar through interactive lessons and mini-games. The 3D VR version placed users in a virtual environment where they could see and interact with 3D models of sign language instructors and practice ASL in a more natural, embodied way.
The team then conducted a user study with 60 participants, randomly assigning them to either the 2D or 3D VR learning condition. Participants completed pre- and post-tests to assess their ASL knowledge before and after using the learning tool. The researchers analyzed the test scores to compare the learning gains between the two groups and identify any significant differences in ASL proficiency improvement.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a valuable comparison of 2D and 3D approaches for ASL education, but it acknowledges some limitations. The sample size was relatively small, and the study only measured immediate learning gains, not long-term retention. Additionally, the researchers note that individual factors like prior experience with VR or gaming may have influenced the results.
Further research could explore the impact of these tools on different demographic groups, the optimal design of 3D VR experiences for sign language learning, and the relationship between learning modality and language acquisition over time. Longitudinal studies and more diverse participant pools would also help strengthen the generalizability of the findings.
Conclusion
This study suggests that both 2D game-based and 3D VR approaches can effectively support the learning of American Sign Language, with the 3D VR condition showing slightly stronger immediate learning gains. These results indicate the potential for immersive technologies to enhance sign language education and accessibility.
As Enhancing Sign Language Teaching with a Mixed Reality Approach and other related work have shown, the integration of AI, computer vision, and mixed reality offers promising avenues for developing innovative sign language learning tools. Continued research and development in this area could lead to more engaging and effective ways to teach visual-spatial languages like ASL.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
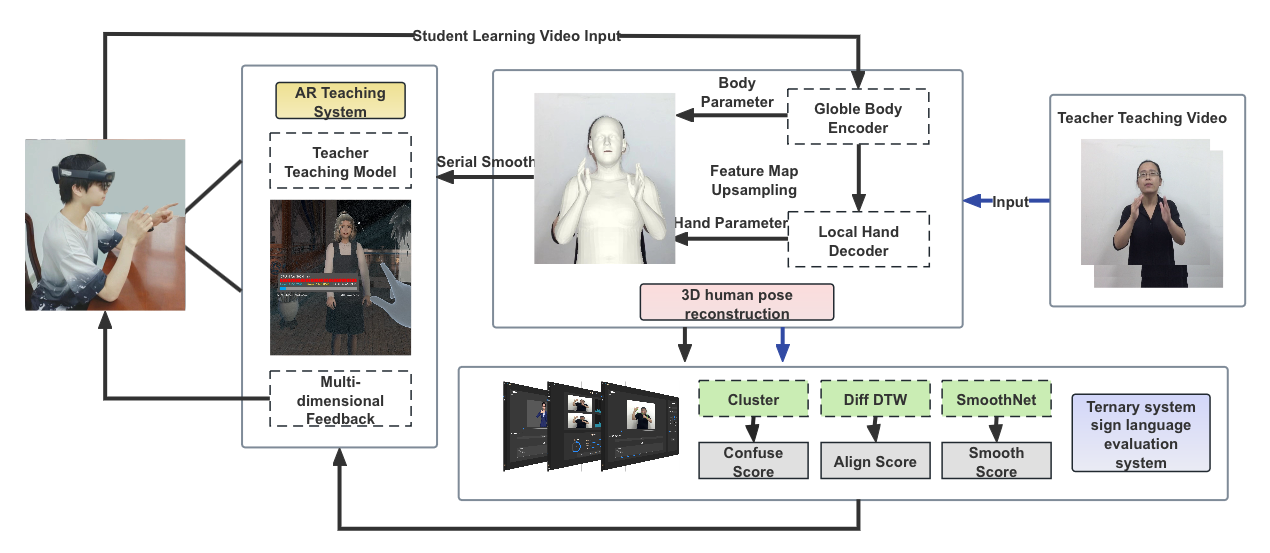
Teaching Chinese Sign Language with Feedback in Mixed Reality
Hongli Wen, Yang Xu, Lin Li, Xudong Ru, Xingce Wang, Zhongke Wu

0
0
Traditional sign language teaching methods face challenges such as limited feedback and diverse learning scenarios. Although 2D resources lack real-time feedback, classroom teaching is constrained by a scarcity of teacher. Methods based on VR and AR have relatively primitive interaction feedback mechanisms. This study proposes an innovative teaching model that uses real-time monocular vision and mixed reality technology. First, we introduce an improved hand-posture reconstruction method to achieve sign language semantic retention and real-time feedback. Second, a ternary system evaluation algorithm is proposed for a comprehensive assessment, maintaining good consistency with experts in sign language. Furthermore, we use mixed reality technology to construct a scenario-based 3D sign language classroom and explore the user experience of scenario teaching. Overall, this paper presents a novel teaching method that provides an immersive learning experience, advanced posture reconstruction, and precise feedback, achieving positive feedback on user experience and learning effectiveness.
5/7/2024
A real-time Artificial Intelligence system for learning Sign Language
Elisa Cabana

0
0
A primary challenge for the deaf and hearing-impaired community stems from the communication gap with the hearing society, which can greatly impact their daily lives and result in social exclusion. To foster inclusivity in society, our endeavor focuses on developing a cost-effective, resource-efficient, and open technology based on Artificial Intelligence, designed to assist people in learning and using Sign Language for communication. The analysis presented in this research paper intends to enrich the recent academic scientific literature on Sign Language solutions based on Artificial Intelligence, with a particular focus on American Sign Language (ASL). This research has yielded promising preliminary results and serves as a basis for further development.
4/12/2024
💬
SignAvatars: A Large-scale 3D Sign Language Holistic Motion Dataset and Benchmark
Zhengdi Yu, Shaoli Huang, Yongkang Cheng, Tolga Birdal

0
0
We present SignAvatars, the first large-scale, multi-prompt 3D sign language (SL) motion dataset designed to bridge the communication gap for Deaf and hard-of-hearing individuals. While there has been an exponentially growing number of research regarding digital communication, the majority of existing communication technologies primarily cater to spoken or written languages, instead of SL, the essential communication method for Deaf and hard-of-hearing communities. Existing SL datasets, dictionaries, and sign language production (SLP) methods are typically limited to 2D as annotating 3D models and avatars for SL is usually an entirely manual and labor-intensive process conducted by SL experts, often resulting in unnatural avatars. In response to these challenges, we compile and curate the SignAvatars dataset, which comprises 70,000 videos from 153 signers, totaling 8.34 million frames, covering both isolated signs and continuous, co-articulated signs, with multiple prompts including HamNoSys, spoken language, and words. To yield 3D holistic annotations, including meshes and biomechanically-valid poses of body, hands, and face, as well as 2D and 3D keypoints, we introduce an automated annotation pipeline operating on our large corpus of SL videos. SignAvatars facilitates various tasks such as 3D sign language recognition (SLR) and the novel 3D SL production (SLP) from diverse inputs like text scripts, individual words, and HamNoSys notation. Hence, to evaluate the potential of SignAvatars, we further propose a unified benchmark of 3D SL holistic motion production. We believe that this work is a significant step forward towards bringing the digital world to the Deaf and hard-of-hearing communities as well as people interacting with them.
4/4/2024

VR-GPT: Visual Language Model for Intelligent Virtual Reality Applications
Mikhail Konenkov, Artem Lykov, Daria Trinitatova, Dzmitry Tsetserukou

0
0
The advent of immersive Virtual Reality applications has transformed various domains, yet their integration with advanced artificial intelligence technologies like Visual Language Models remains underexplored. This study introduces a pioneering approach utilizing VLMs within VR environments to enhance user interaction and task efficiency. Leveraging the Unity engine and a custom-developed VLM, our system facilitates real-time, intuitive user interactions through natural language processing, without relying on visual text instructions. The incorporation of speech-to-text and text-to-speech technologies allows for seamless communication between the user and the VLM, enabling the system to guide users through complex tasks effectively. Preliminary experimental results indicate that utilizing VLMs not only reduces task completion times but also improves user comfort and task engagement compared to traditional VR interaction methods.
5/21/2024