Intelligent Control in 6G Open RAN: Security Risk or Opportunity?

0
🧠
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- The paper examines the security considerations around the RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC) in the context of Open Radio Access Network (Open RAN) and 6G mobile networks.
- It provides a comprehensive analysis of RAN security, tracing its evolution from 2G to 5G, and an in-depth exploration of RIC security.
- The study evaluates the security implications of the RIC within the 6G Open RAN context, addressing vulnerabilities, mitigation strategies, and potential enhancements.
Plain English Explanation
The paper focuses on the security of the RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC), which is a key component in the emerging Open Radio Access Network (Open RAN) framework. Open RAN is seen as a cornerstone for Artificial Intelligence (AI)-enabled Sixth-Generation (6G) mobile networks, as it represents a shift in the way radio access networks are designed and managed.
The RIC plays a central role in Open RAN by improving network efficiency and flexibility. However, this also introduces potential security risks that need to be carefully examined. The paper provides a comprehensive overview of RAN security, starting from 2G networks and tracing its evolution to the current 5G technology. It then delves into a detailed exploration of the security considerations surrounding the RIC.
The study uses real-world security incidents involving the RIC to provide practical insights. It evaluates the security implications of the RIC within the 6G Open RAN context, addressing vulnerabilities, potential mitigation strategies, and opportunities for security enhancements. This analysis aims to guide stakeholders in the telecom industry towards building a more secure and dependable telecommunications infrastructure.
The paper also explores the promising security opportunities that the RIC presents for enhancing network security and resilience in the context of 6G mobile networks. It outlines open issues, lessons learned, and future research directions in the domain of intelligent control in 6G Open RAN, helping to facilitate a comprehensive understanding of this dynamic landscape.
Technical Explanation
The paper begins by highlighting the transformative shift in radio access network architecture brought about by the Open RAN framework, which is emerging as the cornerstone for Artificial Intelligence (AI)-enabled Sixth-Generation (6G) mobile networks. As the adoption of Open RAN accelerates, ensuring its security becomes increasingly critical.
The RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC) plays a central role in Open RAN by improving network efficiency and flexibility. However, the introduction of the RIC also brings about potential security risks that need careful scrutiny. Therefore, the study aims to comprehensively evaluate the current state of RIC security.
The research combines a thorough analysis of RAN security, tracing its evolution from 2G to 5G, with an in-depth exploration of RIC security. This represents the first comprehensive examination of its kind in the literature. The study vividly illustrates real-world security incidents involving the RIC, providing practical insights.
The paper evaluates the security implications of the RIC within the 6G Open RAN context, addressing security vulnerabilities, mitigation strategies, and potential enhancements. It also explores the promising security opportunities that the RIC presents for enhancing network security and resilience in the context of 6G mobile networks.
The study outlines open issues, lessons learned, and future research directions in the domain of intelligent control in 6G open RAN, facilitating a comprehensive understanding of this dynamic landscape.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a thorough and well-researched analysis of the security considerations surrounding the RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC) in the context of Open RAN and 6G mobile networks. The authors' comprehensive approach, which includes tracing the evolution of RAN security from 2G to 5G and then diving deep into RIC security, is commendable.
One strength of the paper is the use of real-world security incidents to illustrate the practical implications and challenges faced in the field. This helps ground the theoretical discussion in tangible examples, making the security concerns more relatable and compelling.
However, the paper could have delved deeper into the specific security vulnerabilities and attack vectors associated with the RIC. While the authors touch upon these aspects, a more detailed exploration of the technical security risks and potential mitigation strategies could have further strengthened the analysis.
Additionally, the paper could have benefited from a more critical examination of the promises and limitations of the RIC in enhancing network security and resilience within the 6G Open RAN context. A more nuanced discussion of the trade-offs and potential unintended consequences would have provided a more balanced perspective.
Overall, the paper serves as a valuable reference for stakeholders in the telecom industry, highlighting the crucial role of the RIC within the broader network infrastructure and emphasizing the paramount importance of security in this evolving landscape. The study provides a solid foundation for further research and discussions around securing Open RAN and 6G mobile networks.
Conclusion
The paper presents a comprehensive analysis of the security considerations surrounding the RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC) in the context of the Open Radio Access Network (Open RAN) framework and its role in the development of Sixth-Generation (6G) mobile networks.
The study traces the evolution of RAN security from 2G to 5G, providing a broader context, and then delves deeply into the security implications of the RIC. By illustrating real-world security incidents, the authors offer practical insights that can guide stakeholders in the telecom industry towards building a more secure and dependable telecommunications infrastructure.
The paper's evaluation of the security vulnerabilities, mitigation strategies, and potential enhancements related to the RIC within the 6G Open RAN context is particularly valuable. It also explores the promising security opportunities that the RIC presents for enhancing network security and resilience, outlining open issues and future research directions.
Overall, this survey serves as a crucial reference, shedding light on the RIC's pivotal role within the broader network infrastructure and emphasizing the paramount importance of security in the evolving landscape of Open RAN and 6G mobile networks.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
🧠

0
Intelligent Control in 6G Open RAN: Security Risk or Opportunity?
Sanaz Soltani, Mohammad Shojafar, Ali Amanlou, Rahim Tafazolli
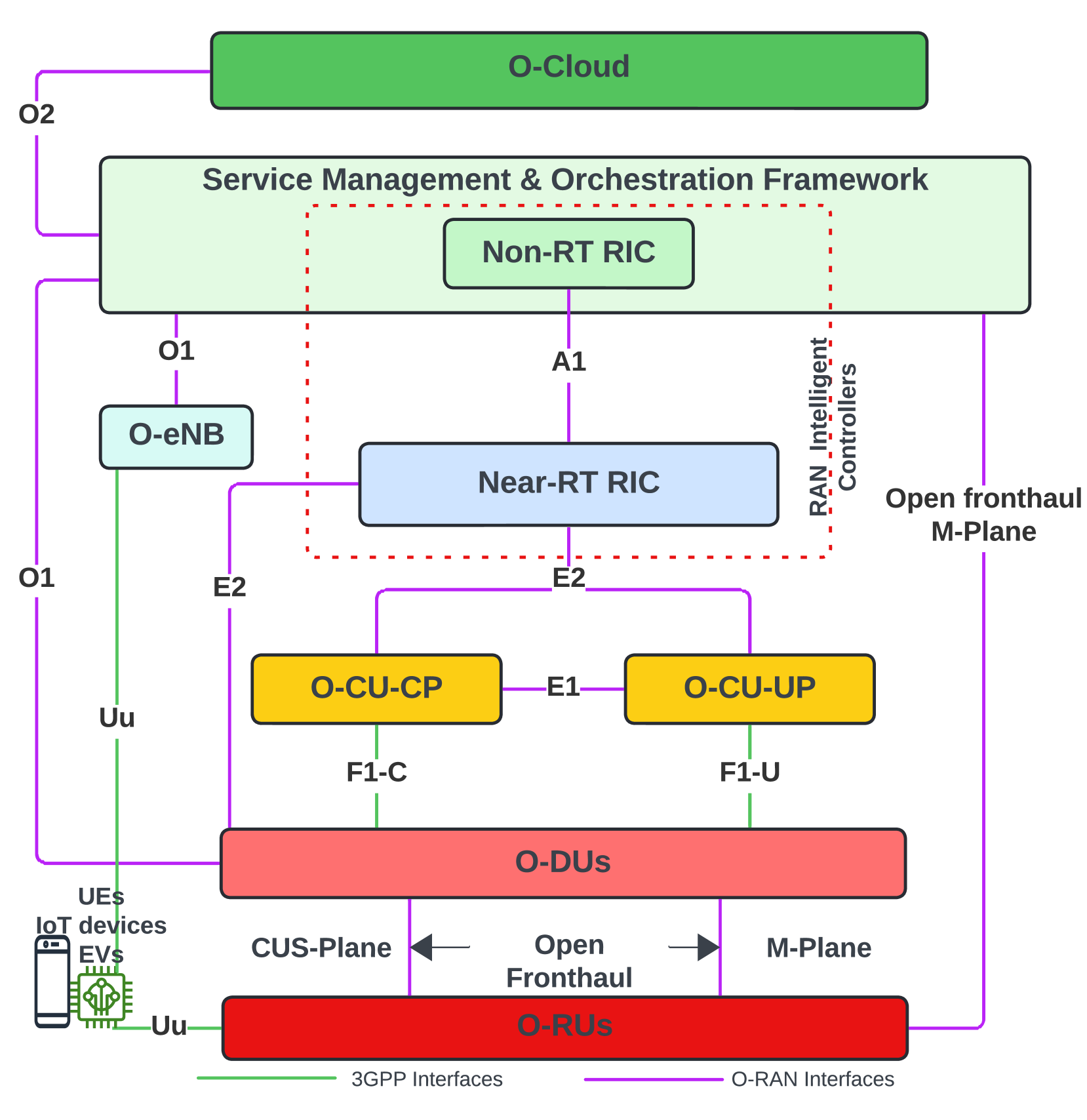
The Open Radio Access Network (Open RAN) framework, emerging as the cornerstone for Artificial Intelligence (AI)-enabled Sixth-Generation (6G) mobile networks, heralds a transformative shift in radio access network architecture. As the adoption of Open RAN accelerates, ensuring its security becomes critical. The RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC) plays a central role in Open RAN by improving network efficiency and flexibility. Nevertheless, it also brings about potential security risks that need careful scrutiny. Therefore, it is imperative to evaluate the current state of RIC security comprehensively. This assessment is essential to gain a profound understanding of the security considerations associated with RIC. This survey combines a comprehensive analysis of RAN security, tracing its evolution from 2G to 5G, with an in-depth exploration of RIC security, marking the first comprehensive examination of its kind in the literature. Real-world security incidents involving RIC are vividly illustrated, providing practical insights. The study evaluates the security implications of the RIC within the 6G Open RAN context, addressing security vulnerabilities, mitigation strategies, and potential enhancements. It aims to guide stakeholders in the telecom industry toward a secure and dependable telecommunications infrastructure. The article serves as a valuable reference, shedding light on the RIC's crucial role within the broader network infrastructure and emphasizing security's paramount importance. This survey also explores the promising security opportunities that the RIC presents for enhancing network security and resilience in the context of 6G mobile networks. It outlines open issues, lessons learned, and future research directions in the domain of intelligent control in 6G open RAN, facilitating a comprehensive understanding of this dynamic landscape.
Read more5/15/2024

0
Exploiting and Securing ML Solutions in Near-RT RIC: A Perspective of an xApp
Thusitha Dayaratne, Viet Vo, Shangqi Lai, Sharif Abuadbba, Blake Haydon, Hajime Suzuki, Xingliang Yuan, Carsten Rudolph
Open Radio Access Networks (O-RAN) are emerging as a disruptive technology, revolutionising traditional mobile network architecture and deployments in the current 5G and the upcoming 6G era. Disaggregation of network architecture, inherent support for AI/ML workflows, cloud-native principles, scalability, and interoperability make O-RAN attractive to network providers for beyond-5G and 6G deployments. Notably, the ability to deploy custom applications, including Machine Learning (ML) solutions as xApps or rApps on the RAN Intelligent Controllers (RICs), has immense potential for network function and resource optimisation. However, the openness, nascent standards, and distributed architecture of O-RAN and RICs introduce numerous vulnerabilities exploitable through multiple attack vectors, which have not yet been fully explored. To address this gap and ensure robust systems before large-scale deployments, this work analyses the security of ML-based applications deployed on the RIC platform. We focus on potential attacks, defence mechanisms, and pave the way for future research towards a more robust RIC platform.
Read more6/19/2024
🤖

0
Implementing and Evaluating Security in O-RAN: Interfaces, Intelligence, and Platforms
Joshua Groen, Salvatore DOro, Utku Demir, Leonardo Bonati, Michele Polese, Tommaso Melodia, Kaushik Chowdhury
The Open Radio Access Network (RAN) is a networking paradigm that builds on top of cloud-based, multi-vendor, open and intelligent architectures to shape the next generation of cellular networks for 5G and beyond. While this new paradigm comes with many advantages in terms of observatibility and reconfigurability of the network, it inevitably expands the threat surface of cellular systems and can potentially expose its components to several cyber attacks, thus making securing O-RAN networks a necessity. In this paper, we explore the security aspects of O-RAN systems by focusing on the specifications and architectures proposed by the O-RAN Alliance. We address the problem of securing O-RAN systems with a holistic perspective, including considerations on the open interfaces used to interconnect the different O-RAN components, on the overall platform, and on the intelligence used to monitor and control the network. For each focus area we identify threats, discuss relevant solutions to address these issues, and demonstrate experimentally how such solutions can effectively defend O-RAN systems against selected cyber attacks. This article is the first work in approaching the security aspect of O-RAN holistically and with experimental evidence obtained on a state-of-the-art programmable O-RAN platform, thus providing unique guideline for researchers in the field.
Read more7/26/2024
⛏️

0
Securing O-RAN Open Interfaces
Joshua Groen, Salvatore D'Oro, Utku Demir, Leonardo Bonati, Davide Villa, Michele Polese, Tommaso Melodia, Kaushik Chowdhury
The next generation of cellular networks will be characterized by openness, intelligence, virtualization, and distributed computing. The Open Radio Access Network (Open RAN) framework represents a significant leap toward realizing these ideals, with prototype deployments taking place in both academic and industrial domains. While it holds the potential to disrupt the established vendor lock-ins, Open RAN's disaggregated nature raises critical security concerns. Safeguarding data and securing interfaces must be integral to Open RAN's design, demanding meticulous analysis of cost/benefit tradeoffs. In this paper, we embark on the first comprehensive investigation into the impact of encryption on two pivotal Open RAN interfaces: the E2 interface, connecting the base station with a near-real-time RAN Intelligent Controller, and the Open Fronthaul, connecting the Radio Unit to the Distributed Unit. Our study leverages a full-stack O-RAN ALLIANCE compliant implementation within the Colosseum network emulator and a production-ready Open RAN and 5G-compliant private cellular network. This research contributes quantitative insights into the latency introduced and throughput reduction stemming from using various encryption protocols. Furthermore, we present four fundamental principles for constructing security by design within Open RAN systems, offering a roadmap for navigating the intricate landscape of Open RAN security.
Read more4/26/2024