Intelligent Reflecting Surfaces assisted Laser-based Optical Wireless Communication Networks
2404.01850

0
4
🔮
Abstract
The increasing demand for wireless networks of higher capacity requires key-enabling technologies. Optical wireless communication (OWC) arises as a complementary technology to radio frequency (RF) systems that can support high aggregate data rates. However, OWC systems face some challenges including beam-blockage. Intelligent reflecting surfaces (IRSs) can offer alternative pathways for the optical signal, ensuring continuous connectivity. In this work, we investigate the potential of using IRS in an indoor OWC network. In particular, we define a system model of indoor OWC that employs IRS in conjunction with angle diversity transmitters (ADT) using vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser (VCSEL) arrays. The VCSEL beam is narrow, directed, and easy to block, however, it can deliver high data rates under eye safety regulations. Simulation results show that the deployment of IRS can significantly improve the achievable data rates of Laser-based OWC systems.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- Wireless networks need new technologies to support higher data demands
- Optical wireless communication (OWC) can offer high data rates as a complement to radio frequency (RF) systems
- OWC faces challenges like beam blockage
- Intelligent reflecting surfaces (IRS) can provide alternative pathways for optical signals to ensure continuous connectivity
- This research investigates using IRS in an indoor OWC network with angle diversity transmitters (ADT) and vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers (VCSELs)
Plain English Explanation
As people use more data-intensive applications on their wireless devices, existing radio frequency (RF) networks are struggling to keep up. Optical wireless communication (OWC) offers a potential solution, using light instead of radio waves to transmit data at very high speeds. However, OWC systems face the challenge of having their light beams easily blocked, disrupting the connection.
Intelligent reflecting surfaces (IRS) could help solve this problem by providing alternative pathways for the optical signals. If the direct line-of-sight between the transmitter and receiver is blocked, the IRS can reflect the light beam around the obstruction, maintaining the connection.
In this research, the scientists looked at using IRS in an indoor OWC network that also employs angle diversity transmitters (ADT) and vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers (VCSELs). ADTs use multiple transmitters pointed in different directions to improve coverage, while VCSELs are lasers that can achieve high data rates while meeting eye safety regulations.
The simulation results showed that deploying IRS can significantly improve the data rates achievable with these laser-based OWC systems, overcoming the challenge of beam blockage.
Technical Explanation
The researchers developed a system model for an indoor OWC network that utilizes IRS in conjunction with ADT using VCSEL arrays. VCSELs are advantageous for OWC because their narrow, directed beams can deliver high data rates while meeting eye safety regulations, but this directionality also makes them vulnerable to blockage.
By incorporating IRS into the system, the researchers aimed to provide alternative pathways for the optical signals when the direct line-of-sight is obstructed. The ADT approach, with multiple transmitters pointed in different angles, further enhances the coverage and resilience of the OWC network.
Through simulations, the team evaluated the performance of this IRS-enabled indoor OWC system in terms of the achievable data rates. The results demonstrated that the deployment of IRS can significantly improve the data rate performance compared to a baseline OWC system without IRS, effectively overcoming the beam-blockage challenge.
Critical Analysis
The research provides promising evidence for the potential of IRS to enhance the performance of indoor OWC networks. By offering alternative signal pathways, IRS can mitigate the impact of beam blockage, a key limitation of these systems.
However, the paper does not address some practical considerations, such as the cost and complexity of implementing IRS, or the impact of environmental factors like lighting conditions and user mobility on the system's performance. Additional research is needed to fully understand the real-world feasibility and limitations of this approach.
Furthermore, the study is based on simulations, and it would be valuable to validate the findings through experimental demonstrations in a controlled indoor environment. This could help identify any discrepancies between the theoretical model and actual system behavior.
Overall, the research represents an important step forward in addressing the challenges of OWC systems, but more work is needed to translate these theoretical insights into practical, deployable solutions.
Conclusion
This research explores the potential of using intelligent reflecting surfaces (IRS) to enhance the performance of indoor optical wireless communication (OWC) networks. By providing alternative pathways for optical signals, IRS can help overcome the issue of beam blockage that has historically limited the reliability of OWC systems.
The simulation results demonstrate that the integration of IRS with angle diversity transmitters (ADT) and vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers (VCSELs) can significantly improve the achievable data rates, opening up new possibilities for high-speed wireless connectivity in indoor environments.
While further research is needed to address practical implementation challenges and validate the findings in real-world settings, this work represents an important step towards realizing the full potential of OWC as a complementary technology to traditional radio frequency (RF) systems. As the demand for wireless data continues to grow, innovations like IRS-enabled OWC could play a crucial role in meeting the ever-increasing capacity requirements of modern communication networks.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers

Intelligent Reflecting Surface Aided Target Localization With Unknown Transceiver-IRS Channel State Information
Taotao Ji, Meng Hua, Xuanhong Yan, Chunguo Li, Yongming Huang, Luxi Yang

0
0
Integrating wireless sensing capabilities into base stations (BSs) has become a widespread trend in the future beyond fifth-generation (B5G)/sixth-generation (6G) wireless networks. In this paper, we investigate intelligent reflecting surface (IRS) enabled wireless localization, in which an IRS is deployed to assist a BS in locating a target in its non-line-of-sight (NLoS) region. In particular, we consider the case where the BS-IRS channel state information (CSI) is unknown. Specifically, we first propose a separate BS-IRS channel estimation scheme in which the BS operates in full-duplex mode (FDM), i.e., a portion of the BS antennas send downlink pilot signals to the IRS, while the remaining BS antennas receive the uplink pilot signals reflected by the IRS. However, we can only obtain an incomplete BS-IRS channel matrix based on our developed iterative coordinate descent-based channel estimation algorithm due to the sign ambiguity issue. Then, we employ the multiple hypotheses testing framework to perform target localization based on the incomplete estimated channel, in which the probability of each hypothesis is updated using Bayesian inference at each cycle. Moreover, we formulate a joint BS transmit waveform and IRS phase shifts optimization problem to improve the target localization performance by maximizing the weighted sum distance between each two hypotheses. However, the objective function is essentially a quartic function of the IRS phase shift vector, thus motivating us to resort to the penalty-based method to tackle this challenge. Simulation results validate the effectiveness of our proposed target localization scheme and show that the scheme's performance can be further improved by finely designing the BS transmit waveform and IRS phase shifts intending to maximize the weighted sum distance between different hypotheses.
4/9/2024
🖼️
Nonlocal Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces for Wireless Communication: Modeling and Physical Layer Aspects
Amine Mezghani, Faouzi Bellili, Ekram Hossain

0
0
Conventional Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RIS) for wireless communications have a local position-dependent (phase-gradient) scattering response on the surface. We consider more general RIS structures, called nonlocal (or redirective) RIS, that are capable of selectively manipulate the impinging waves depending on the incident angle. Redirective RIS have nonlocal wavefront-selective scattering behavior and can be implemented using multilayer arrays such as metalenses. We demonstrate that this more sophisticated type of surfaces has several advantages such as: lower overhead through coodebook-based reconfigurability, decoupled wave manipulations, and higher efficiency in multiuser scenarios via multifunctional operation. Additionally, redirective RIS architectures greatly benefit form the directional nature of wave propagation at high frequencies and can support integrated fronthaul and access (IFA) networks most efficiently. We also discuss the scalability and compactness issues and propose efficient nonlocal RIS architectures such as fractionated lens-based RIS and mirror-backed phase-masks structures that do not require additional control complexity and overhead while still offering better performance than conventional local RIS.
4/4/2024

Multi-stream Transmission for Directional Modulation Network via Distributed Multi-UAV-aided Multi-active-IRS
Ke Yang, Rongen Dong, Wei Gao, Feng Shu, Weiping Shi, Yan Wang, Xuehui Wang, Jiangzhou Wang

0
0
Active intelligent reflecting surface (IRS) is a revolutionary technique for the future 6G networks. The conventional far-field single-IRS-aided directional modulation(DM) networks have only one (no direct path) or two (existing direct path) degrees of freedom (DoFs). This means that there are only one or two streams transmitted simultaneously from base station to user and will seriously limit its rate gain achieved by IRS. How to create multiple DoFs more than two for DM? In this paper, single large-scale IRS is divided to multiple small IRSs and a novel multi-IRS-aided multi-stream DM network is proposed to achieve a point-to-point multi-stream transmission by creating $K$ ($geq3$) DoFs, where multiple small IRSs are placed distributively via multiple unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). The null-space projection, zero-forcing (ZF) and phase alignment are adopted to design the transmit beamforming vector, receive beamforming vector and phase shift matrix (PSM), respectively, called NSP-ZF-PA. Here, $K$ PSMs and their corresponding beamforming vectors are independently optimized. The weighted minimum mean-square error (WMMSE) algorithm is involved in alternating iteration for the optimization variables by introducing the power constraint on IRS, named WMMSE-PC, where the majorization-minimization (MM) algorithm is used to solve the total PSM. To achieve a lower computational complexity, a maximum trace method, called Max-TR-SVD, is proposed by optimize the PSM of all IRSs. Numerical simulation results has shown that the proposed NSP-ZF-PA performs much better than Max-TR-SVD in terms of rate. In particular, the rate of NSP-ZF-PA with sixteen small IRSs is about five times that of NSP-ZF-PA with combining all small IRSs as a single large IRS. Thus, a dramatic rate enhancement may be achieved by multiple distributed IRSs.
4/30/2024
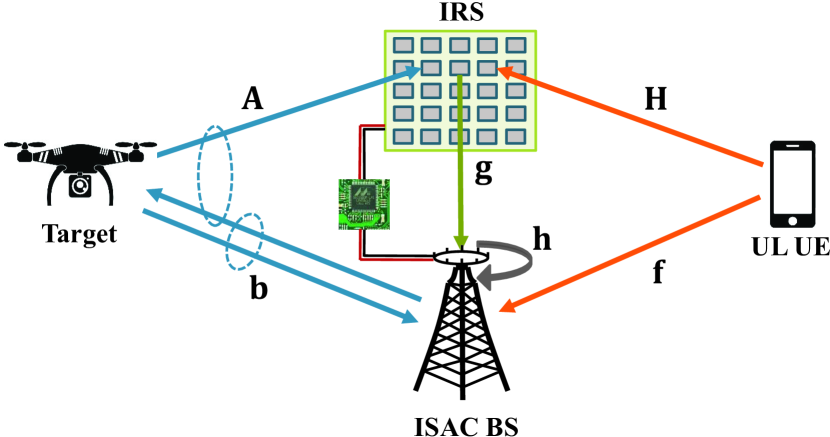
Deep-Learning Channel Estimation for IRS-Assisted Integrated Sensing and Communication System
Yu Liu, Ibrahim Al-Nahhal, Octavia A. Dobre, Fanggang Wang

0
0
Integrated sensing and communication (ISAC), and intelligent reflecting surface (IRS) are envisioned as revolutionary technologies to enhance spectral and energy efficiencies for next wireless system generations. For the first time, this paper focuses on the channel estimation problem in an IRS-assisted ISAC system. This problem is challenging due to the lack of signal processing capacity in passive IRS, as well as the presence of mutual interference between sensing and communication (SAC) signals in ISAC systems. A three-stage approach is proposed to decouple the estimation problem into sub-ones, including the estimation of the direct SAC channels in the first stage, reflected communication channel in the second stage, and reflected sensing channel in the third stage. The proposed three-stage approach is based on a deep-learning framework, which involves two different convolutional neural network (CNN) architectures to estimate the channels at the full-duplex ISAC base station. Furthermore, two types of input-output pairs to train the CNNs are carefully designed, which affect the estimation performance under various signal-to-noise ratio conditions and system parameters. Simulation results validate the superiority of the proposed estimation approach compared to the least-squares baseline scheme, and its computational complexity is also analyzed.
4/9/2024