Multi-stream Transmission for Directional Modulation Network via Distributed Multi-UAV-aided Multi-active-IRS
2404.15297

0
0

Abstract
Active intelligent reflecting surface (IRS) is a revolutionary technique for the future 6G networks. The conventional far-field single-IRS-aided directional modulation(DM) networks have only one (no direct path) or two (existing direct path) degrees of freedom (DoFs). This means that there are only one or two streams transmitted simultaneously from base station to user and will seriously limit its rate gain achieved by IRS. How to create multiple DoFs more than two for DM? In this paper, single large-scale IRS is divided to multiple small IRSs and a novel multi-IRS-aided multi-stream DM network is proposed to achieve a point-to-point multi-stream transmission by creating $K$ ($geq3$) DoFs, where multiple small IRSs are placed distributively via multiple unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). The null-space projection, zero-forcing (ZF) and phase alignment are adopted to design the transmit beamforming vector, receive beamforming vector and phase shift matrix (PSM), respectively, called NSP-ZF-PA. Here, $K$ PSMs and their corresponding beamforming vectors are independently optimized. The weighted minimum mean-square error (WMMSE) algorithm is involved in alternating iteration for the optimization variables by introducing the power constraint on IRS, named WMMSE-PC, where the majorization-minimization (MM) algorithm is used to solve the total PSM. To achieve a lower computational complexity, a maximum trace method, called Max-TR-SVD, is proposed by optimize the PSM of all IRSs. Numerical simulation results has shown that the proposed NSP-ZF-PA performs much better than Max-TR-SVD in terms of rate. In particular, the rate of NSP-ZF-PA with sixteen small IRSs is about five times that of NSP-ZF-PA with combining all small IRSs as a single large IRS. Thus, a dramatic rate enhancement may be achieved by multiple distributed IRSs.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper proposes a multi-stream transmission system for a directional modulation (DM) network using distributed multi-UAV-aided multi-intelligent reflecting surface (IRS) technology.
- The system aims to enhance the degree of freedom (DoF) and beamforming capabilities for secure and efficient wireless communications.
Plain English Explanation
The paper describes a new wireless communication system that uses multiple unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and multiple intelligent reflecting surfaces (IRSs) to improve the performance of directional modulation (DM) networks. DM networks are a type of wireless system that can selectively transmit information in specific directions, which is useful for secure communications.
The key idea is to use multiple UAVs and multiple IRSs together to increase the number of degrees of freedom (DoF) and improve the beamforming capabilities of the DM network. Degrees of freedom refers to the number of independent variables or parameters that can be adjusted to control the system. More DoF allows the system to be more flexible and adaptable. Beamforming is a technique used to focus the wireless signal in a particular direction, which enhances the signal strength and security.
By combining multiple UAVs and IRSs, the system can dynamically adjust the reflected signals from the IRSs to create highly directional and focused wireless beams. This improves the overall performance and capabilities of the DM network compared to using a single UAV or IRS. The researchers believe this multi-stream transmission approach can lead to more secure and efficient wireless communications.
Technical Explanation
The proposed system utilizes distributed multi-UAV-aided multi-IRS technology to enhance the degree of freedom (DoF) and beamforming capabilities of a directional modulation (DM) network.
The key components are:
- Multiple UAVs that can dynamically adjust their positions to optimize the wireless links
- Multiple IRSs that can independently control the phase and amplitude of the reflected signals
- A DM transmitter that encodes the information into the directional wireless beams
By coordinating the multiple UAVs and IRSs, the system can create a large number of adjustable reflection paths to achieve high DoF. This allows the system to generate highly directional wireless beams that are tailored for specific receivers, improving the signal strength and security.
The researchers also incorporate deep learning techniques for channel estimation to enhance the coordination and optimization of the multi-UAV, multi-IRS system. This joint training of the reflection pattern and beamforming further improves the overall system performance.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a novel and promising approach to enhance the capabilities of DM networks using distributed multi-UAV and multi-IRS technology. The key strengths are the increased DoF and sophisticated beamforming that can be achieved through the coordinated use of multiple aerial and surface-based components.
However, the paper does not fully address the practical challenges of deploying and coordinating such a complex multi-agent system in real-world scenarios. Potential issues include the reliability and latency of the UAV and IRS control mechanisms, as well as the overhead required for channel estimation and system optimization.
Additionally, the paper does not explore the potential limitations or failure modes of the proposed system, such as the impact of UAV or IRS malfunctions, environmental disruptions, or adversarial attacks. Further research is needed to understand the robustness and resilience of this approach.
Conclusion
This paper presents an innovative multi-stream transmission system for directional modulation networks that leverages distributed multi-UAV and multi-IRS technology. By increasing the degrees of freedom and beamforming capabilities, the system can achieve more secure and efficient wireless communications compared to traditional approaches.
While the proposed solution shows promise, further research is needed to address the practical challenges of deploying and coordinating such a complex multi-agent system. Exploring the reliability, scalability, and resilience of the approach will be crucial for its real-world application and adoption.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers

Intelligent Reflecting Surface Aided Target Localization With Unknown Transceiver-IRS Channel State Information
Taotao Ji, Meng Hua, Xuanhong Yan, Chunguo Li, Yongming Huang, Luxi Yang

0
0
Integrating wireless sensing capabilities into base stations (BSs) has become a widespread trend in the future beyond fifth-generation (B5G)/sixth-generation (6G) wireless networks. In this paper, we investigate intelligent reflecting surface (IRS) enabled wireless localization, in which an IRS is deployed to assist a BS in locating a target in its non-line-of-sight (NLoS) region. In particular, we consider the case where the BS-IRS channel state information (CSI) is unknown. Specifically, we first propose a separate BS-IRS channel estimation scheme in which the BS operates in full-duplex mode (FDM), i.e., a portion of the BS antennas send downlink pilot signals to the IRS, while the remaining BS antennas receive the uplink pilot signals reflected by the IRS. However, we can only obtain an incomplete BS-IRS channel matrix based on our developed iterative coordinate descent-based channel estimation algorithm due to the sign ambiguity issue. Then, we employ the multiple hypotheses testing framework to perform target localization based on the incomplete estimated channel, in which the probability of each hypothesis is updated using Bayesian inference at each cycle. Moreover, we formulate a joint BS transmit waveform and IRS phase shifts optimization problem to improve the target localization performance by maximizing the weighted sum distance between each two hypotheses. However, the objective function is essentially a quartic function of the IRS phase shift vector, thus motivating us to resort to the penalty-based method to tackle this challenge. Simulation results validate the effectiveness of our proposed target localization scheme and show that the scheme's performance can be further improved by finely designing the BS transmit waveform and IRS phase shifts intending to maximize the weighted sum distance between different hypotheses.
4/9/2024
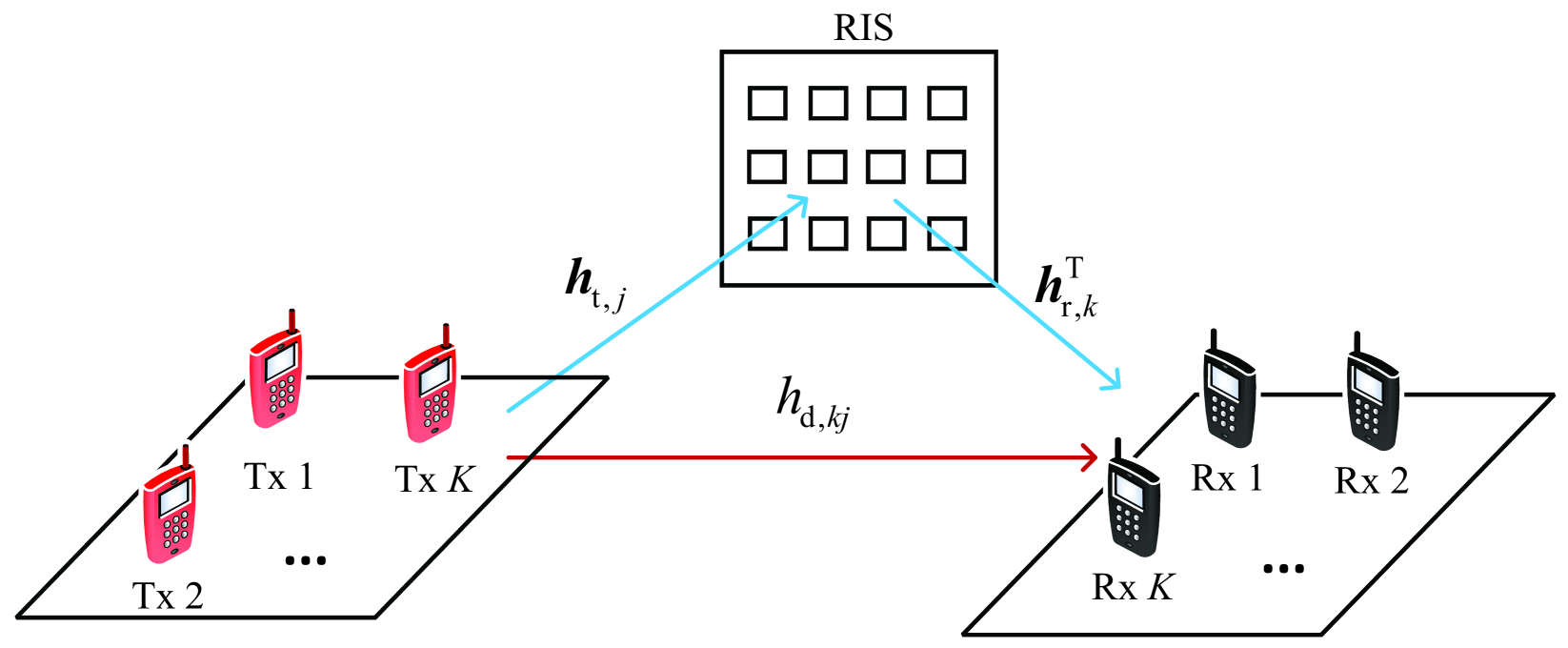
Power-Aware Sparse Reflect Beamforming in Active RIS-aided Interference Channels
Ruizhe Long, Hu Zhou, Ying-Chang Liang

0
0
Active reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS) has attracted significant attention in wireless communications, due to its reflecting elements (REs) capable of reflecting incident signals with not only phase shifts but also amplitude amplifications. In this paper, we are interested in active RIS-aided interference channels in which $K$ user pairs share the same time and frequency resources with the aid of active RIS. Thanks to the promising amplitude amplification capability, activating a moderate number of REs, rather than all of them, is sufficient for the active RIS to mitigate cross-channel interferences. Motivated by this, we propose a power-aware sparse reflect beamforming design for the active RIS-aided interference channels, which allows the active RIS to flexibly adjust the number of activated REs for the sake of reducing hardware and power costs. Specifically, we establish the power consumption model in which only those activated REs consume the biasing and operation power that supports the amplitude amplification, yielding an $ell_0$-norm power consumption function. Based on the proposed model, we investigate a sum-rate maximization problem and an active RIS power minimization problem by carefully designing the sparse reflect beamforming vector. To solve these problems, we first replace the nonconvex $ell_0$-norm function with an iterative reweighted $ell_1$-norm function. Then, fractional programming is used to solve the sum-rate maximization, while semidefinite programming together with the difference-of-convex algorithm (DCA) is used to solve the active RIS power minimization. Numerical results show that the proposed sparse designs can notably increase the sum rate of user pairs and decrease the power consumption of active RIS in interference channels.
4/1/2024
✅
Multi-hop Multi-RIS Wireless Communication Systems: Multi-reflection Path Scheduling and Beamforming
Xiaoyan Ma, Haixia Zhang, Xianhao Chen, Yuguang Fangmand Dongfeng Yuan

0
0
Reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS) provides a promising way to proactively augment propagation environments for better transmission performance in wireless communications. Existing multi-RIS works mainly focus on link-level optimization with predetermined transmission paths, which cannot be directly extended to system-level management, since they neither consider the interference caused by undesired scattering of RISs, nor the performance balancing between different transmission paths. To address this, we study an innovative multi-hop multi-RIS communication system, where a base station (BS) transmits information to a set of distributed users over multi-RIS configuration space in a multi-hop manner. The signals for each user are subsequently reflected by the selected RISs via multi-reflection line-of-sight (LoS) links. To ensure that all users have fair access to the system to avoid excessive number of RISs serving one user, we aim to find the optimal beam reflecting path for each user, while judiciously determining the path scheduling strategies with the corresponding beamforming design to ensure the fairness. Due to the presence of interference caused by undesired scattering of RISs, it is highly challenging to solve the formulated multi-RIS multi-path beamforming optimization problem. To solve it, we first derive the optimal RISs' phase shifts and the corresponding reflecting path selection for each user based on its practical deployment location. With the optimized multi-reflection paths, we obtain a feasible user grouping pattern for effective interference mitigation by constructing the maximum independent sets (MISs). Finally, we propose a joint heuristic algorithm to iteratively update the beamforming vectors and the group scheduling policies to maximize the minimum equivalent data rate of all users.
5/22/2024
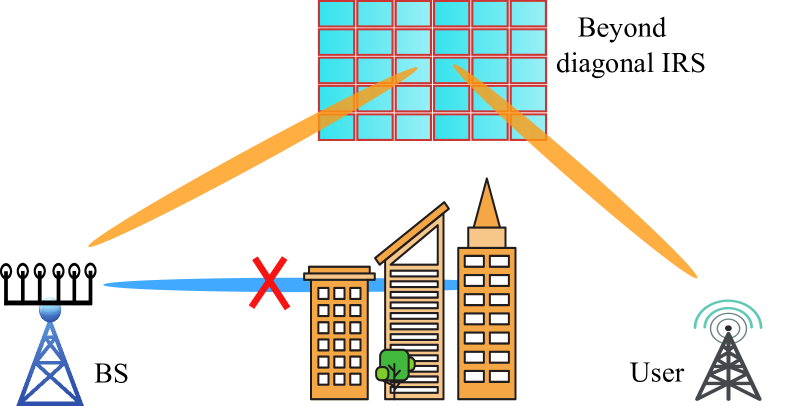
Beyond Diagonal IRS Assisted Ultra Massive THz Systems: A Low Resolution Approach
Wali Ullah Khan, Chandan Kumar Sheemar, Zaid Abdullah, Eva Lagunas, Symeon Chatzinotas

0
0
The terahertz communications have the potential to revolutionize data transfer with unmatched speed and facilitate the development of new high-bandwidth applications. This paper studies the performance of downlink terahertz system assisted by beyond diagonal intelligent reconfigurable surface (BD-IRS). For enhanced energy efficiency and low cost, a joint precoding and BD-IRS phase shift design satisfying the $1$-bit resolution constraints to maximize the spectral efficiency is presented. The original problem is non-linear, NP-hard, and intricately coupled, and obtaining an optimal solution is challenging. To reduce the complexity, we first transform the optimization problem into two problems and then iteratively solve them to achieve an efficient solution. Numerical results demonstrate that the proposed approach for the BD-IRS assisted terahertz system significantly enhances the spectral efficiency compared to the conventional diagonal IRS assisted system.
6/26/2024