IRS-Assisted Lossy Communications Under Correlated Rayleigh Fading: Outage Probability Analysis and Optimization

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- Examines the performance of intelligent reflecting surface (IRS)-assisted lossy communications under correlated Rayleigh fading
- Analyzes the outage probability and optimizes the system parameters
- Proposes a deep reinforcement learning-based approach to optimize the IRS configuration
Plain English Explanation
In this research, the authors investigate a wireless communication system that uses an intelligent reflecting surface (IRS) to improve the quality of the signal. IRSs are special surfaces that can actively manipulate the wireless signals, allowing them to be more easily received by the intended device.
The researchers specifically look at a scenario where the wireless channel between the transmitter and receiver is affected by correlated Rayleigh fading. This means that the signal strength can fluctuate in a random way, and the fluctuations are correlated between different parts of the channel.
The key analysis the paper performs is to calculate the outage probability - the likelihood that the signal quality drops below a critical threshold, causing the communication to fail. The authors optimize the IRS configuration to minimize this outage probability.
To do this, they propose using a deep reinforcement learning approach. This allows the IRS to automatically adjust its configuration to adapt to the changing wireless conditions and optimize the performance.
Technical Explanation
The paper begins by developing a mathematical model for the IRS-assisted lossy communication system under correlated Rayleigh fading. This involves deriving expressions for the effective signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) at the receiver.
Using this model, the authors then analyze the outage probability of the system. They provide a closed-form expression for the outage probability in terms of the system parameters, such as the number of IRS elements, the correlation coefficient of the fading channels, and the target SNR threshold.
To optimize the system performance, the paper proposes a deep reinforcement learning-based approach to configure the IRS. The IRS adjusts its phase shifts to maximize the received SNR and minimize the outage probability. The authors develop a deep Q-learning algorithm to train the IRS control policy.
Numerical results demonstrate that the proposed IRS-assisted lossy communication system can significantly outperform conventional systems without IRS assistance, especially in highly correlated fading environments. The deep reinforcement learning-based optimization is shown to achieve near-optimal performance.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a comprehensive analysis of IRS-assisted lossy communications under correlated Rayleigh fading, which is an important practical scenario. The derivation of the outage probability expression and the deep reinforcement learning-based optimization are technically sound.
However, the paper does not discuss the potential challenges in implementing the proposed system in real-world settings. For example, it does not address the practical limitations of IRS deployment, such as the cost, size, and power consumption of the IRS elements. Additionally, the impact of imperfect channel state information on the system performance is not investigated.
Further research could explore the robustness of the proposed approach to imperfect channel knowledge, as well as the tradeoffs between system performance and implementation complexity. Incorporating these practical considerations would enhance the applicability of the research to real-world wireless communication systems.
Conclusion
This paper presents a detailed analysis of IRS-assisted lossy communications under correlated Rayleigh fading. The authors derive a closed-form expression for the outage probability and propose a deep reinforcement learning-based approach to optimize the IRS configuration for improved performance.
The results demonstrate the significant potential of IRS technology to enhance the reliability of wireless communications, especially in challenging fading environments. The deep learning-based optimization allows the IRS to adapt to the dynamic channel conditions, making it a promising solution for practical applications.
Overall, this research contributes to the growing body of work on IRS-assisted wireless communications and provides valuable insights for the design and optimization of future communication systems.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
IRS-Assisted Lossy Communications Under Correlated Rayleigh Fading: Outage Probability Analysis and Optimization
Guanchang Li, Wensheng Lin, Lixin Li, Yixuan He, Fucheng Yang, Zhu Han
This paper focuses on an intelligent reflecting surface (IRS)-assisted lossy communication system with correlated Rayleigh fading. We analyze the correlated channel model and derive the outage probability of the system. Then, we design a deep reinforce learning (DRL) method to optimize the phase shift of IRS, in order to maximize the received signal power. Moreover, this paper presents results of the simulations conducted to evaluate the performance of the DRL-based method. The simulation results indicate that the outage probability of the considered system increases significantly with more correlated channel coefficients. Moreover, the performance gap between DRL and theoretical limit increases with higher transmit power and/or larger distortion requirement.
Read more8/14/2024


0
Online Optimization for Learning to Communicate over Time-Correlated Channels
Zheshun Wu, Junfan Li, Zenglin Xu, Sumei Sun, Jie Liu
Machine learning techniques have garnered great interest in designing communication systems owing to their capacity in tacking with channel uncertainty. To provide theoretical guarantees for learning-based communication systems, some recent works analyze generalization bounds for devised methods based on the assumption of Independently and Identically Distributed (I.I.D.) channels, a condition rarely met in practical scenarios. In this paper, we drop the I.I.D. channel assumption and study an online optimization problem of learning to communicate over time-correlated channels. To address this issue, we further focus on two specific tasks: optimizing channel decoders for time-correlated fading channels and selecting optimal codebooks for time-correlated additive noise channels. For utilizing temporal dependence of considered channels to better learn communication systems, we develop two online optimization algorithms based on the optimistic online mirror descent framework. Furthermore, we provide theoretical guarantees for proposed algorithms via deriving sub-linear regret bound on the expected error probability of learned systems. Extensive simulation experiments have been conducted to validate that our presented approaches can leverage the channel correlation to achieve a lower average symbol error rate compared to baseline methods, consistent with our theoretical findings.
Read more9/4/2024
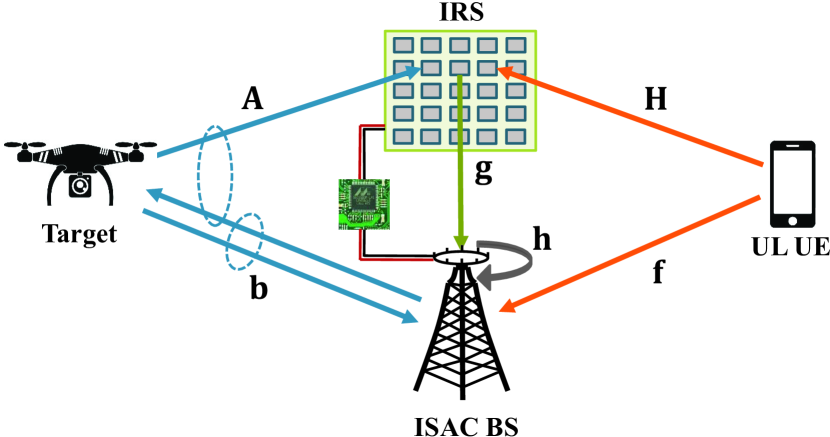

0
Deep-Learning Channel Estimation for IRS-Assisted Integrated Sensing and Communication System
Yu Liu, Ibrahim Al-Nahhal, Octavia A. Dobre, Fanggang Wang
Integrated sensing and communication (ISAC), and intelligent reflecting surface (IRS) are envisioned as revolutionary technologies to enhance spectral and energy efficiencies for next wireless system generations. For the first time, this paper focuses on the channel estimation problem in an IRS-assisted ISAC system. This problem is challenging due to the lack of signal processing capacity in passive IRS, as well as the presence of mutual interference between sensing and communication (SAC) signals in ISAC systems. A three-stage approach is proposed to decouple the estimation problem into sub-ones, including the estimation of the direct SAC channels in the first stage, reflected communication channel in the second stage, and reflected sensing channel in the third stage. The proposed three-stage approach is based on a deep-learning framework, which involves two different convolutional neural network (CNN) architectures to estimate the channels at the full-duplex ISAC base station. Furthermore, two types of input-output pairs to train the CNNs are carefully designed, which affect the estimation performance under various signal-to-noise ratio conditions and system parameters. Simulation results validate the superiority of the proposed estimation approach compared to the least-squares baseline scheme, and its computational complexity is also analyzed.
Read more4/9/2024
🎲

0
Outage Probability Analysis of Wireless Paths with Faulty Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces
Mounir Bensalem, Admela Jukan
We consider a next generation wireless network incorporating a base station a set of typically low-cost and faulty Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces (RISs). The base station needs to select the path including the RIS to provide the maximum signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) to the user. We study the effect of the number of elements, distance and RIS hardware failure on the path outage probability, and based on the known signal propagation model at high frequencies, derive the closed-form expression for the said probability of outage. Numerical results show the path outage likelihood as function of the probability of hardware failure of RIS elements, the number of elements, and the distance between mobile users and the RIS.
Read more4/24/2024