ISAC-Fi: Enabling Full-fledged Monostatic Sensing over Wi-Fi Communication

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- ISAC-Fi is a system that enables full-fledged monostatic sensing over Wi-Fi communication
- It overcomes limitations of prior Wi-Fi sensing approaches by allowing simultaneous sensing and communication
- Key innovations include self-interference cancellation and leveraging the existing Wi-Fi infrastructure for sensing
Plain English Explanation
ISAC-Fi is a new technology that allows Wi-Fi devices to not only communicate, but also sense the environment around them. Prior Wi-Fi sensing approaches had restrictions, like only being able to sense in a certain direction bistatic/multistatic sensing or requiring additional hardware.
ISAC-Fi overcomes these limitations by using self-interference cancellation to enable a device to both transmit and receive signals for sensing, all while using the existing Wi-Fi infrastructure. This "monostatic sensing" allows the device to get a fuller picture of its surroundings compared to previous methods.
The key innovation is ISAC-Fi's ability to cancel out the device's own transmissions, which would otherwise interfere with its sensing capabilities. This allows the device to effectively use its Wi-Fi signals for both communication and sensing at the same time.
Technical Explanation
ISAC-Fi tackles the challenge of enabling integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) over standard Wi-Fi networks. Prior Wi-Fi sensing approaches were limited to bistatic or multistatic sensing, where the transmitter and receiver were physically separated.
ISAC-Fi introduces a monostatic sensing architecture, where the transmitter and receiver are co-located. This is achieved through self-interference cancellation, which allows the device to simultaneously transmit and receive signals for both communication and sensing. The system leverages the existing Wi-Fi infrastructure, avoiding the need for additional hardware.
The key technical components of ISAC-Fi include:
- Wideband self-interference cancellation: Removes the device's own transmission from the received signal, enabling monostatic sensing.
- Sensing waveform design: Optimizes the Wi-Fi signals for sensing tasks like target detection and localization.
- Sensing algorithm integration: Seamlessly integrates sensing capabilities with the existing Wi-Fi protocol.
Through these innovations, ISAC-Fi demonstrates the feasibility of full-fledged monostatic sensing over standard Wi-Fi communication networks.
Critical Analysis
The ISAC-Fi paper presents a compelling solution for enabling comprehensive sensing capabilities over Wi-Fi. However, some potential limitations and areas for further research are worth considering:
-
Interference management: While self-interference cancellation is a key innovation, ISAC-Fi may still face challenges with managing interference from other Wi-Fi devices in dense network environments. Cooperative sensing and communication strategies could help address this.
-
Sensing performance: The paper focuses on demonstrating the technical feasibility of monostatic sensing, but more research may be needed to fully characterize the sensing capabilities, such as range, accuracy, and robustness under different environmental conditions.
-
Energy efficiency: The additional processing required for self-interference cancellation and sensing could impact the energy consumption of Wi-Fi devices. Optimizing the energy efficiency of the ISAC-Fi system would be an important consideration.
-
Integration with existing Wi-Fi infrastructure: While ISAC-Fi leverages the existing Wi-Fi ecosystem, the seamless integration of sensing capabilities with legacy Wi-Fi systems may require further investigation and standardization efforts.
Overall, the ISAC-Fi paper presents a promising step towards enabling comprehensive sensing capabilities within Wi-Fi networks, but continued research and development will be necessary to address the challenges and fully realize the potential of this technology.
Conclusion
ISAC-Fi represents a significant advancement in the field of integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) by enabling full-fledged monostatic sensing over standard Wi-Fi communication networks. The key innovations, including self-interference cancellation and the leveraging of existing Wi-Fi infrastructure, overcome the limitations of prior Wi-Fi sensing approaches.
The ISAC-Fi system demonstrates the feasibility of simultaneously using Wi-Fi signals for both communication and comprehensive environmental sensing. This capability has the potential to unlock a wide range of applications, from indoor localization and human activity recognition to smart home automation and beyond.
As researchers continue to refine and build upon the ISAC-Fi approach, the integration of sensing and communication functionalities within ubiquitous Wi-Fi networks could fundamentally transform how we interact with and understand our surroundings, paving the way for more intelligent and responsive smart environments.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
ISAC-Fi: Enabling Full-fledged Monostatic Sensing over Wi-Fi Communication
Zhe Chen, Chao Hu, Tianyue Zheng, Hangcheng Cao, Yanbing Yang, Yen Chu, Hongbo Jiang, Jun Luo
Whereas Wi-Fi communications have been exploited for sensing purpose for over a decade, the bistatic or multistatic nature of Wi-Fi still poses multiple challenges, hampering real-life deployment of integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) within Wi-Fi framework. In this paper, we aim to re-design WiFi so that monostatic sensing (mimicking radar) can be achieved over the multistatic communication infrastructure. Specifically, we propose, design, and implement ISAC-Fi as an ISAC-ready Wi-Fi prototype. We first present a novel self-interference cancellation scheme, in order to extract reflected (radio frequency) signals for sensing purpose in the face of transmissions. We then subtly revise existing Wi-Fi framework so as to seamlessly operate monostatic sensing under Wi-Fi communication standard. Finally, we offer two ISAC-Fi designs: while a USRP-based one emulates a totally re-designed ISAC-Fi device, another plug-andplay design allows for backward compatibility by attaching an extra module to an arbitrary Wi-Fi device. We perform extensive experiments to validate the efficacy of ISAC-Fi and also to demonstrate its superiority over existing Wi-Fi sensing proposals.
Read more8/20/2024


0
A Bistatic ISAC Framework for LEO Satellite Systems: A Rate-Splitting Approach
Juha Park, Jaehyup Seong, Jaehak Ryu, Yijie Mao, Wonjae Shin
Aiming to achieve ubiquitous global connectivity and target detection on the same platform with improved spectral/energy efficiency and reduced onboard hardware cost, low Earth orbit (LEO) satellite systems capable of simultaneously performing communications and radar have attracted significant attention. Designing such a joint system should address not only the challenges of integrating two functions but also the unique propagation characteristics of the satellites. To overcome severe echo signal path loss due to the high altitude of the satellite, we put forth a bistatic integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) framework with a radar receiver separated from the satellite. For robust and effective interference management, we employ rate-splitting multiple access (RSMA), which splits and encodes users messages into private and common streams. We optimize the dual-functional precoders to maximize the minimum rate among all users while satisfying the Cramer-Rao bound (CRB) constraints. Given the challenge of acquiring instantaneous channel state information (iCSI) for LEO satellites, we exploit the geometrical and statistical characteristics of the satellite channel. To develop an efficient optimization algorithm, semidefinite relaxation (SDR), sequential rank-1 constraint relaxation (SROCR), and successive convex approximation (SCA) are utilized. Numerical results show that the proposed framework efficiently performs both communication and radar, demonstrating superior interference control capabilities. Furthermore, it is validated that the common stream plays three vital roles: i) beamforming towards the radar target, ii) interference management between communications and radar, and iii) interference management among communication users.
Read more7/15/2024


0
Gemini: Integrating Full-fledged Sensing upon Millimeter Wave Communications
Yilong Li, Zhe Chen, Jun Luo, Suman Banerjee
Integrating millimeter wave (mmWave)technology in both communication and sensing is promising as it enables the reuse of existing spectrum and infrastructure without draining resources. Most existing systems piggyback sensing onto conventional communication modes without fully exploiting the potential of integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) in mmWave radios (not full-fledged). In this paper, we design and implement a full-fledged mmWave ISAC system Gemini; it delivers raw channel states to serve a broad category of sensing applications. We first propose the mmWave self-interference cancellation approach to extract the weak reflected signals for near-field sensing purposes. Then, we develop a joint optimization scheduling framework that can be utilized in accurate radar sensing while maximizing the communication throughput. Finally, we design a united fusion sensing algorithm to offer a better sensing performance via combining monostatic and bistatic modes. We evaluate our system in extensive experiments to demonstrate Gemini's capability of simultaneously operating sensing and communication, enabling mmWave ISAC to perform better than the commercial off-the-shelf mmWave radar for 5G cellular networks.
Read more9/14/2024

0
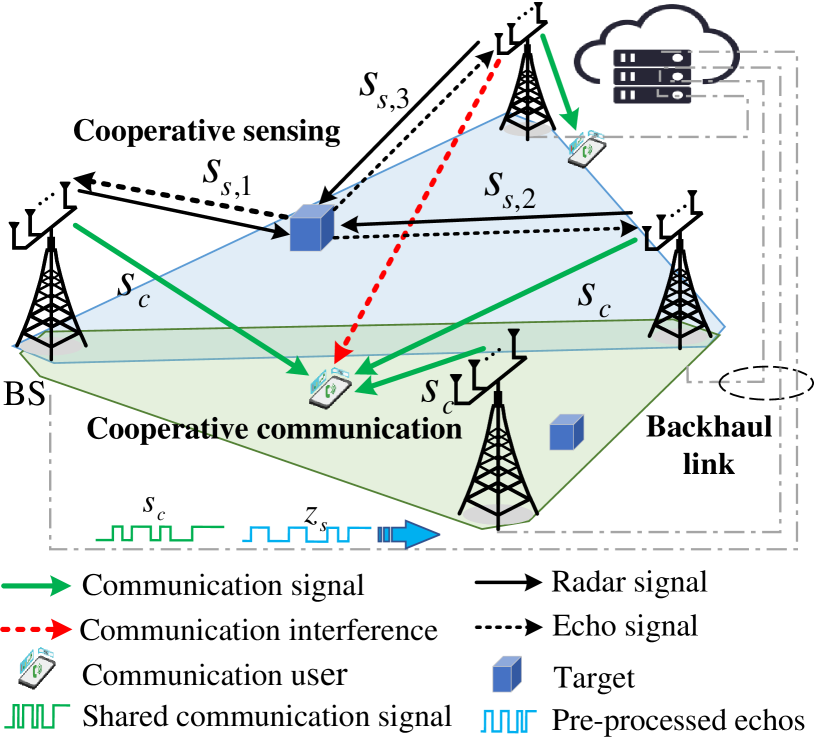
Cooperative Sensing and Communication for ISAC Networks: Performance Analysis and Optimization
Kaitao Meng, Christos Masouros
In this work, we study integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) networks intending to effectively balance sensing and communication (S&C) performance at the network level. Through the simultaneous utilization of multi-point (CoMP) coordinated joint transmission and distributed multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) radar techniques, we propose a cooperative networked ISAC scheme to enhance both S&C services. Then, the tool of stochastic geometry is exploited to capture the S&C performance, which allows us to illuminate key cooperative dependencies in the ISAC network. Remarkably, the derived expression of the Cramer-Rao lower bound (CRLB) of the localization accuracy unveils a significant finding: Deploying $N$ ISAC transceivers yields an enhanced sensing performance across the entire network, in accordance with the $ln^2N$ scaling law. Simulation results demonstrate that compared to the time-sharing scheme, the proposed cooperative ISAC scheme can effectively improve the average data rate and reduce the CRLB.
Read more4/1/2024