Large Language Models as Instruments of Power: New Regimes of Autonomous Manipulation and Control
2405.03813

0
0
💬
Abstract
Large language models (LLMs) can reproduce a wide variety of rhetorical styles and generate text that expresses a broad spectrum of sentiments. This capacity, now available at low cost, makes them powerful tools for manipulation and control. In this paper, we consider a set of underestimated societal harms made possible by the rapid and largely unregulated adoption of LLMs. Rather than consider LLMs as isolated digital artefacts used to displace this or that area of work, we focus on the large-scale computational infrastructure upon which they are instrumentalised across domains. We begin with discussion on how LLMs may be used to both pollute and uniformize information environments and how these modalities may be leveraged as mechanisms of control. We then draw attention to several areas of emerging research, each of which compounds the capabilities of LLMs as instruments of power. These include (i) persuasion through the real-time design of choice architectures in conversational interfaces (e.g., via AI personas), (ii) the use of LLM-agents as computational models of human agents (e.g., silicon subjects), (iii) the use of LLM-agents as computational models of human agent populations (e.g., silicon societies) and finally, (iv) the combination of LLMs with reinforcement learning to produce controllable and steerable strategic dialogue models. We draw these strands together to discuss how these areas may be combined to build LLM-based systems that serve as powerful instruments of individual, social and political control via the simulation and disingenuous prediction of human behaviour, intent, and action.
Get summaries of the top AI research delivered straight to your inbox:
Overview
- This paper explores the potential societal harms of large language models (LLMs), which are powerful AI systems capable of generating human-like text across a wide range of styles and sentiments.
- Rather than viewing LLMs as isolated digital tools, the authors focus on the large-scale computational infrastructure that enables their application across various domains.
- The paper discusses how LLMs can be used to manipulate and control information environments, as well as emerging research areas that amplify their capabilities as instruments of power.
Plain English Explanation
Large language models (LLMs) are AI systems that can generate human-like text on a wide variety of topics. These models are becoming increasingly affordable and accessible, which makes them powerful tools for manipulating and controlling information.
Rather than just looking at how LLMs might replace certain tasks or jobs, this paper examines the broader ways in which these AI systems can be used to influence and control people. The authors discuss how LLMs can be used to pollute and homogenize information environments, which can then be leveraged as mechanisms of control.
The paper also explores several emerging research areas that further enhance the capabilities of LLMs as powerful instruments of control. These include using LLMs to design persuasive conversational interfaces, creating computational models of individual human agents and entire populations, and combining LLMs with reinforcement learning to produce [controllable and steerable strategic dialogue models].
The authors argue that by combining these various capabilities, it is possible to build LLM-based systems that can simulate and falsely predict human behavior, intentions, and actions in ways that can be used to exert control over individuals, social groups, and even political processes.
Technical Explanation
The paper begins by acknowledging the remarkable capacity of large language models (LLMs) to reproduce a wide variety of rhetorical styles and generate text that expresses a broad spectrum of sentiments. The authors highlight that this capability, now available at low cost, makes LLMs powerful tools for manipulation and control.
Rather than considering LLMs as isolated digital artifacts used to displace specific areas of work, the authors focus on the large-scale computational infrastructure upon which they are instrumentalized across domains. The paper then discusses how LLMs may be used to both pollute and uniformize information environments, and how these modalities may be leveraged as mechanisms of control.
The authors then draw attention to several areas of emerging research, each of which compounds the capabilities of LLMs as instruments of power. These include (i) persuasion through the real-time design of choice architectures in conversational interfaces (e.g., via AI personas), (ii) the use of LLM-agents as computational models of human agents (e.g., silicon subjects), (iii) the use of LLM-agents as computational models of human agent populations (e.g., silicon societies), and (iv) the combination of LLMs with reinforcement learning to produce controllable and steerable strategic dialogue models.
The authors draw these strands together to discuss how these areas may be combined to build LLM-based systems that serve as powerful instruments of individual, social, and political control via the simulation and disingenuous prediction of human behavior, intent, and action.
Critical Analysis
The paper raises important concerns about the potential societal harms of large language models, which are often overlooked in the excitement surrounding their rapid development and deployment. By focusing on the computational infrastructure underlying LLMs, rather than just their individual applications, the authors highlight the broader implications of these powerful AI systems.
One potential limitation of the paper is that it does not provide detailed empirical evidence or case studies to support its claims. While the authors present a compelling conceptual framework, further research may be needed to substantiate the specific ways in which LLMs can be used for manipulation and control.
Additionally, the paper does not directly address potential countermeasures or mitigation strategies that could be employed to address the risks it identifies. A more comprehensive discussion of regulatory frameworks, ethical guidelines, or technical safeguards could help readers understand how these issues might be addressed.
Overall, this paper encourages readers to think critically about the social and political implications of large language models, and to consider the broader context in which these AI systems are being developed and deployed. By highlighting the potential for misuse and control, the authors invite further discussion and research in this important area.
Conclusion
This paper presents a thought-provoking analysis of the potential societal harms associated with the rapid and largely unregulated adoption of large language models (LLMs). By shifting the focus from individual applications to the large-scale computational infrastructure that enables the use of LLMs across domains, the authors shed light on how these powerful AI systems can be leveraged as instruments of manipulation and control.
The paper's exploration of emerging research areas, such as the use of LLMs for persuasive conversational interfaces, computational modeling of human agents and populations, and the combination of LLMs with reinforcement learning, underscores the need for a more holistic understanding of the implications of these technologies.
As LLMs continue to advance and become more widely accessible, this paper serves as a call to action for policymakers, researchers, and the general public to engage in critical discussions and develop robust frameworks to ensure the responsible development and deployment of these technologies. By addressing the risks and potential harms identified in this paper, we can work towards harnessing the power of LLMs in ways that benefit society as a whole, rather than enabling new forms of manipulation and control.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
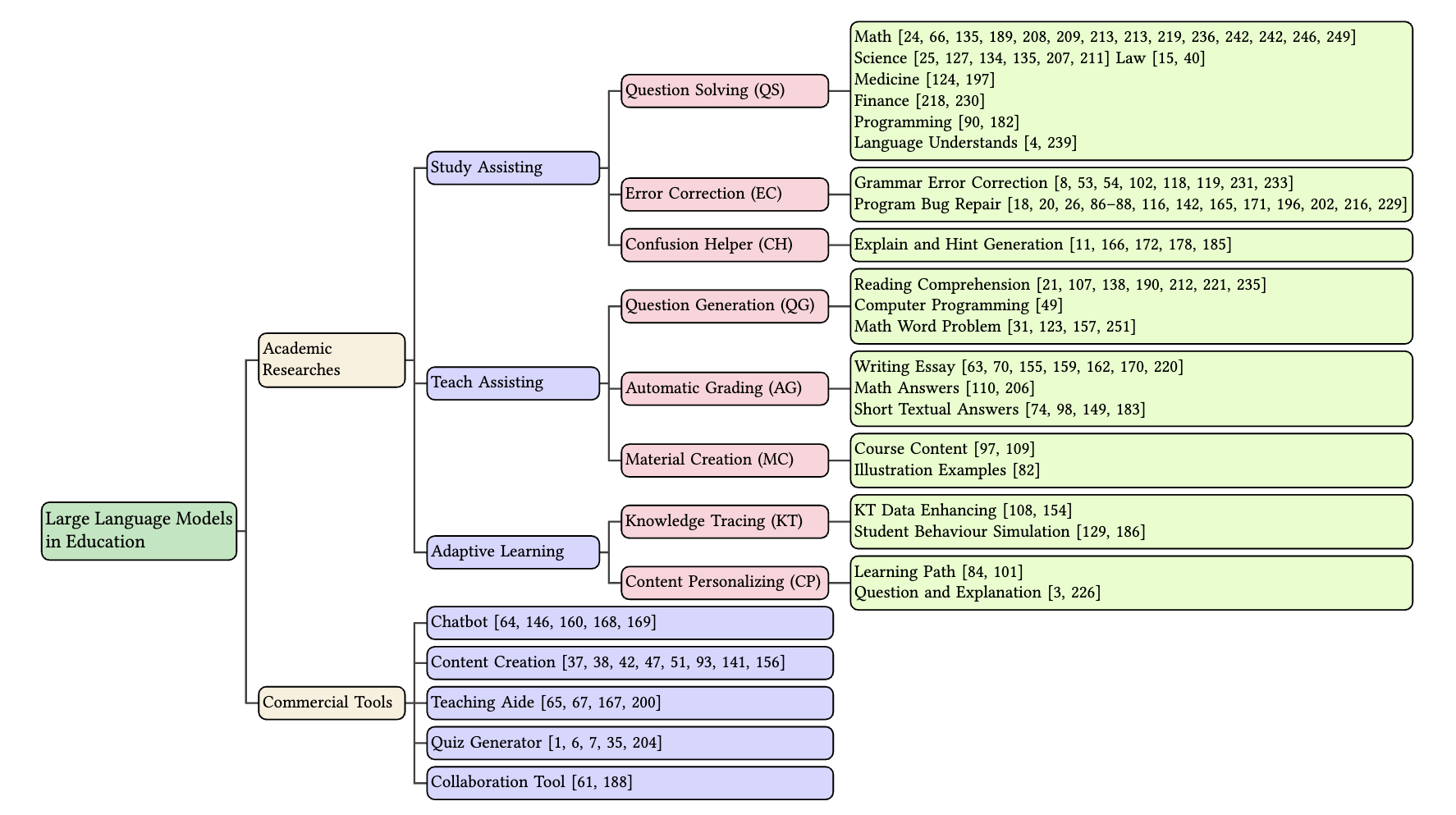
Large Language Models for Education: A Survey and Outlook
Shen Wang, Tianlong Xu, Hang Li, Chaoli Zhang, Joleen Liang, Jiliang Tang, Philip S. Yu, Qingsong Wen

0
0
The advent of Large Language Models (LLMs) has brought in a new era of possibilities in the realm of education. This survey paper summarizes the various technologies of LLMs in educational settings from multifaceted perspectives, encompassing student and teacher assistance, adaptive learning, and commercial tools. We systematically review the technological advancements in each perspective, organize related datasets and benchmarks, and identify the risks and challenges associated with deploying LLMs in education. Furthermore, we outline future research opportunities, highlighting the potential promising directions. Our survey aims to provide a comprehensive technological picture for educators, researchers, and policymakers to harness the power of LLMs to revolutionize educational practices and foster a more effective personalized learning environment.
4/3/2024

LLeMpower: Understanding Disparities in the Control and Access of Large Language Models
Vishwas Sathish, Hannah Lin, Aditya K Kamath, Anish Nyayachavadi

0
0
Large Language Models (LLMs) are a powerful technology that augment human skill to create new opportunities, akin to the development of steam engines and the internet. However, LLMs come with a high cost. They require significant computing resources and energy to train and serve. Inequity in their control and access has led to concentration of ownership and power to a small collection of corporations. In our study, we collect training and inference requirements for various LLMs. We then analyze the economic strengths of nations and organizations in the context of developing and serving these models. Additionally, we also look at whether individuals around the world can access and use this emerging technology. We compare and contrast these groups to show that these technologies are monopolized by a surprisingly few entities. We conclude with a qualitative study on the ethical implications of our findings and discuss future directions towards equity in LLM access.
4/16/2024
Exploring Autonomous Agents through the Lens of Large Language Models: A Review
Saikat Barua

0
0
Large Language Models (LLMs) are transforming artificial intelligence, enabling autonomous agents to perform diverse tasks across various domains. These agents, proficient in human-like text comprehension and generation, have the potential to revolutionize sectors from customer service to healthcare. However, they face challenges such as multimodality, human value alignment, hallucinations, and evaluation. Techniques like prompting, reasoning, tool utilization, and in-context learning are being explored to enhance their capabilities. Evaluation platforms like AgentBench, WebArena, and ToolLLM provide robust methods for assessing these agents in complex scenarios. These advancements are leading to the development of more resilient and capable autonomous agents, anticipated to become integral in our digital lives, assisting in tasks from email responses to disease diagnosis. The future of AI, with LLMs at the forefront, is promising.
4/9/2024
💬
Apprentices to Research Assistants: Advancing Research with Large Language Models
M. Namvarpour, A. Razi

0
0
Large Language Models (LLMs) have emerged as powerful tools in various research domains. This article examines their potential through a literature review and firsthand experimentation. While LLMs offer benefits like cost-effectiveness and efficiency, challenges such as prompt tuning, biases, and subjectivity must be addressed. The study presents insights from experiments utilizing LLMs for qualitative analysis, highlighting successes and limitations. Additionally, it discusses strategies for mitigating challenges, such as prompt optimization techniques and leveraging human expertise. This study aligns with the 'LLMs as Research Tools' workshop's focus on integrating LLMs into HCI data work critically and ethically. By addressing both opportunities and challenges, our work contributes to the ongoing dialogue on their responsible application in research.
4/10/2024