LLeMpower: Understanding Disparities in the Control and Access of Large Language Models
2404.09356

0
0

Abstract
Large Language Models (LLMs) are a powerful technology that augment human skill to create new opportunities, akin to the development of steam engines and the internet. However, LLMs come with a high cost. They require significant computing resources and energy to train and serve. Inequity in their control and access has led to concentration of ownership and power to a small collection of corporations. In our study, we collect training and inference requirements for various LLMs. We then analyze the economic strengths of nations and organizations in the context of developing and serving these models. Additionally, we also look at whether individuals around the world can access and use this emerging technology. We compare and contrast these groups to show that these technologies are monopolized by a surprisingly few entities. We conclude with a qualitative study on the ethical implications of our findings and discuss future directions towards equity in LLM access.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper examines disparities in the control and access of large language models (LLMs), which are powerful AI systems capable of generating human-like text.
- The researchers investigate how factors like race, gender, and socioeconomic status influence who has the ability to develop, deploy, and use these influential technologies.
- The goal is to better understand the power dynamics and equity issues surrounding the control and use of LLMs, which have become increasingly important in areas like education, research, and decision-making.
Plain English Explanation
Large language models (LLMs) are AI systems that can generate human-like text on a wide range of topics. These powerful technologies are being used in many areas, from education to research to decision-making. However, the researchers behind this paper are concerned that control and access to LLMs may not be equally distributed.
The researchers wanted to look at how factors like a person's race, gender, and socioeconomic status might influence their ability to develop, deploy, and use these influential AI systems. Their goal was to better understand the power dynamics and equity issues surrounding LLMs, which are becoming increasingly important in many parts of society.
For example, if certain groups have more control over LLMs, they may be able to shape how these technologies are used in ways that benefit them more than others. Or if access to LLMs is limited, some people and organizations may miss out on the benefits these AI systems can provide.
By investigating these disparities, the researchers hope to shed light on an important issue and work towards more equitable and inclusive development and use of large language models.
Technical Explanation
The researchers used a combination of methods to investigate disparities in the control and access of large language models (LLMs). First, they conducted a literature review to understand the current state of research on power dynamics and equity issues in the field of LLMs. This allowed them to identify key themes and gaps in the existing knowledge.
Next, the researchers gathered data on the demographics and institutional affiliations of individuals and organizations involved in LLM development and deployment. This included analyzing the authors and affiliations of academic papers, the leadership and staffing of major LLM companies and research labs, and the demographics of people using public LLM services.
By comparing this data across different groups, the researchers were able to identify disparities in who has the ability to shape the development and use of LLMs. For example, they found that LLM research and development tends to be dominated by individuals from higher socioeconomic backgrounds and certain racial and gender groups.
The researchers also examined how access to LLMs varies, looking at factors like cost, technical know-how, and geographic location. They found that certain communities and organizations face significant barriers to utilizing these powerful AI systems, potentially missing out on the benefits they can provide.
Overall, the study provides a comprehensive look at the disparities in the control and access of large language models. The findings shed light on important equity issues that will need to be addressed as these technologies become increasingly influential in society.
Critical Analysis
The researchers acknowledge several limitations and areas for further research in their paper. For example, they note that their data on demographics and institutional affiliations may not be fully comprehensive, as relevant information is not always publicly available. Additionally, the paper focuses primarily on LLMs developed in academic and industry settings in the United States and Europe, so the findings may not fully generalize to other contexts.
One potential issue the paper does not explore in depth is the role of intellectual property rights and commercialization in shaping access to LLMs. As these technologies become more valuable, there may be incentives for developers to restrict access in order to maintain competitive advantages or generate revenue. The researchers could have delved deeper into how this dynamic intersects with equity concerns.
Furthermore, the paper does not provide much insight into the lived experiences and perspectives of individuals and communities facing barriers to LLM access and usage. Incorporating more qualitative research to understand the real-world impacts of these disparities could strengthen the analysis and lead to more impactful solutions.
Despite these limitations, the paper makes an important contribution by systematically documenting disparities in the control and access of large language models. The researchers raise critical questions about power, equity, and the societal implications of these influential AI technologies. Their work serves as a valuable starting point for further research and discussion on these crucial issues.
Conclusion
This paper provides a comprehensive examination of disparities in the control and access of large language models (LLMs), powerful AI systems that are becoming increasingly influential across many domains. The researchers found that factors like race, gender, and socioeconomic status appear to significantly shape who has the ability to develop, deploy, and utilize these technologies.
By documenting these disparities, the paper sheds light on important equity issues that will need to be addressed as LLMs become more ubiquitous. The findings suggest that the development and use of LLMs may be concentrated among certain privileged groups, potentially amplifying existing social and economic inequalities.
Moving forward, the researchers call for greater diversity, transparency, and accountability in the LLM ecosystem. Ensuring more equitable control and access to these influential AI systems will be crucial for realizing their full potential to benefit society as a whole. This paper serves as an important starting point for further research and action on this critical issue.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
💬
Large Language Models as Instruments of Power: New Regimes of Autonomous Manipulation and Control
Yaqub Chaudhary, Jonnie Penn

0
0
Large language models (LLMs) can reproduce a wide variety of rhetorical styles and generate text that expresses a broad spectrum of sentiments. This capacity, now available at low cost, makes them powerful tools for manipulation and control. In this paper, we consider a set of underestimated societal harms made possible by the rapid and largely unregulated adoption of LLMs. Rather than consider LLMs as isolated digital artefacts used to displace this or that area of work, we focus on the large-scale computational infrastructure upon which they are instrumentalised across domains. We begin with discussion on how LLMs may be used to both pollute and uniformize information environments and how these modalities may be leveraged as mechanisms of control. We then draw attention to several areas of emerging research, each of which compounds the capabilities of LLMs as instruments of power. These include (i) persuasion through the real-time design of choice architectures in conversational interfaces (e.g., via AI personas), (ii) the use of LLM-agents as computational models of human agents (e.g., silicon subjects), (iii) the use of LLM-agents as computational models of human agent populations (e.g., silicon societies) and finally, (iv) the combination of LLMs with reinforcement learning to produce controllable and steerable strategic dialogue models. We draw these strands together to discuss how these areas may be combined to build LLM-based systems that serve as powerful instruments of individual, social and political control via the simulation and disingenuous prediction of human behaviour, intent, and action.
5/8/2024
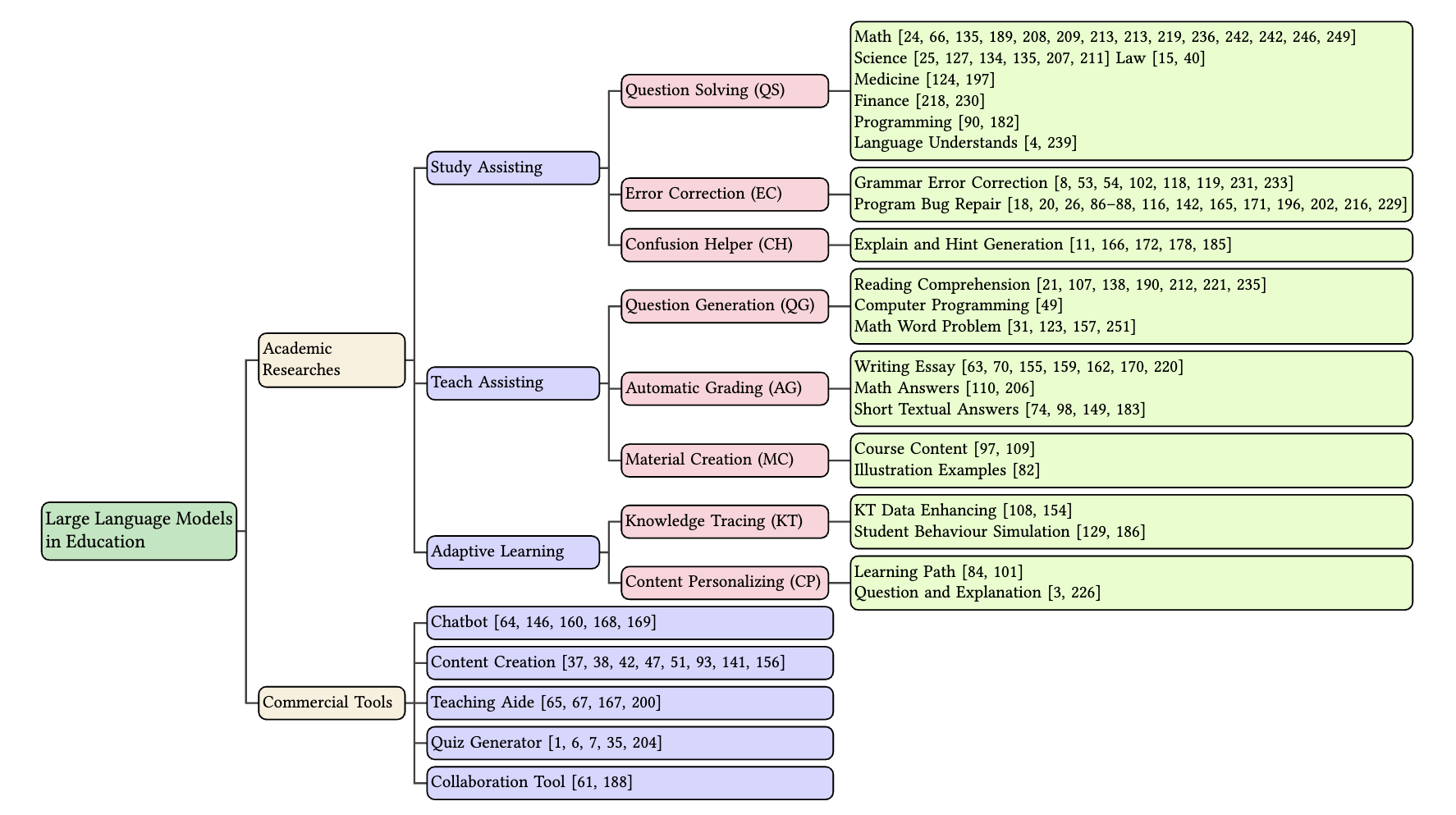
Large Language Models for Education: A Survey and Outlook
Shen Wang, Tianlong Xu, Hang Li, Chaoli Zhang, Joleen Liang, Jiliang Tang, Philip S. Yu, Qingsong Wen

0
0
The advent of Large Language Models (LLMs) has brought in a new era of possibilities in the realm of education. This survey paper summarizes the various technologies of LLMs in educational settings from multifaceted perspectives, encompassing student and teacher assistance, adaptive learning, and commercial tools. We systematically review the technological advancements in each perspective, organize related datasets and benchmarks, and identify the risks and challenges associated with deploying LLMs in education. Furthermore, we outline future research opportunities, highlighting the potential promising directions. Our survey aims to provide a comprehensive technological picture for educators, researchers, and policymakers to harness the power of LLMs to revolutionize educational practices and foster a more effective personalized learning environment.
4/3/2024
💬
Apprentices to Research Assistants: Advancing Research with Large Language Models
M. Namvarpour, A. Razi

0
0
Large Language Models (LLMs) have emerged as powerful tools in various research domains. This article examines their potential through a literature review and firsthand experimentation. While LLMs offer benefits like cost-effectiveness and efficiency, challenges such as prompt tuning, biases, and subjectivity must be addressed. The study presents insights from experiments utilizing LLMs for qualitative analysis, highlighting successes and limitations. Additionally, it discusses strategies for mitigating challenges, such as prompt optimization techniques and leveraging human expertise. This study aligns with the 'LLMs as Research Tools' workshop's focus on integrating LLMs into HCI data work critically and ethically. By addressing both opportunities and challenges, our work contributes to the ongoing dialogue on their responsible application in research.
4/10/2024
💬
A Survey of Large Language Models for Healthcare: from Data, Technology, and Applications to Accountability and Ethics
Kai He, Rui Mao, Qika Lin, Yucheng Ruan, Xiang Lan, Mengling Feng, Erik Cambria

0
0
The utilization of large language models (LLMs) in the Healthcare domain has generated both excitement and concern due to their ability to effectively respond to freetext queries with certain professional knowledge. This survey outlines the capabilities of the currently developed LLMs for Healthcare and explicates their development process, with the aim of providing an overview of the development roadmap from traditional Pretrained Language Models (PLMs) to LLMs. Specifically, we first explore the potential of LLMs to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of various Healthcare applications highlighting both the strengths and limitations. Secondly, we conduct a comparison between the previous PLMs and the latest LLMs, as well as comparing various LLMs with each other. Then we summarize related Healthcare training data, training methods, optimization strategies, and usage. Finally, the unique concerns associated with deploying LLMs in Healthcare settings are investigated, particularly regarding fairness, accountability, transparency and ethics. Our survey provide a comprehensive investigation from perspectives of both computer science and Healthcare specialty. Besides the discussion about Healthcare concerns, we supports the computer science community by compiling a collection of open source resources, such as accessible datasets, the latest methodologies, code implementations, and evaluation benchmarks in the Github. Summarily, we contend that a significant paradigm shift is underway, transitioning from PLMs to LLMs. This shift encompasses a move from discriminative AI approaches to generative AI approaches, as well as a shift from model-centered methodologies to data-centered methodologies. Also, we determine that the biggest obstacle of using LLMs in Healthcare are fairness, accountability, transparency and ethics.
6/12/2024