Latency Reduction in Vehicular Sensing Applications by Dynamic 5G User Plane Function Allocation with Session Continuity
2403.19730

0
0
➖
Abstract
Vehicle automation is driving the integration of advanced sensors and new applications that demand high-quality information, such as collaborative sensing for enhanced situational awareness. In this work, we considered a vehicular sensing scenario supported by 5G communications, in which vehicle sensor data need to be sent to edge computing resources with stringent latency constraints. To ensure low latency with the resources available, we propose an optimization framework that deploys User Plane Functions (UPFs) dynamically at the edge to minimize the number of network hops between the vehicles and them. The proposed framework relies on a practical Software-Defined-Networking (SDN)-based mechanism that allows seamless re-assignment of vehicles to UPFs while maintaining session and service continuity. We propose and evaluate different UPF allocation algorithms that reduce communications latency compared to static, random, and centralized deployment baselines. Our results demonstrated that the dynamic allocation of UPFs can support latency-critical applications that would be unfeasible otherwise.
Create account to get full access
The paper proposes an optimization framework for vehicular sensing scenarios supported by 5G communications, where vehicle sensor data must be sent to edge computing resources with strict latency constraints. The framework dynamically deploys User Plane Functions (UPFs) at the edge to minimize the number of network hops between vehicles and the UPFs. It utilizes a practical Software-Defined-Networking (SDN)-based mechanism that enables seamless re-assignment of vehicles to UPFs while maintaining session and service continuity. The authors propose and evaluate various UPF allocation algorithms that reduce communication latency compared to static, random, and centralized deployment baselines. The results demonstrate that the dynamic allocation of UPFs can support latency-critical applications that would otherwise be unfeasible.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers

Slice-aware Resource Allocation and Admission Control for Smart Factory Wireless Networks
Regina Ochonu, Josep Vidal

0
0
The 5th generation (5G) and beyond network offers substantial promise as the ideal wireless technology to replace the existing inflexible wired connections in traditional factories of today. 5G network slicing allows for tailored allocation of resources to different network services, each with unique Quality of Service (QoS) requirements. This paper presents a novel solution for slice-aware radio resource allocation based on a convex optimisation control framework for applications in smart factory wireless networks. The proposed framework dynamically allocates minimum power and sub-channels to downlink mixed service type industrial users categorised into three slices: Capacity Limited (CL), Ultra Reliable Low Latency Communication (URLLC), and Time Sensitive (TS) slices. Given that the base station (BS) has limited transmission power, we enforce admission control by effectively relaxing the target rate constraints for current connections in the CL slice. This rate readjustment occurs whenever power consumption exceeds manageable levels. Simulation results show that our approach minimises power, allocates sub-channels to users, maintains slice isolation, and delivers QoS-specific communications to users in all the slices despite time-varying number of users and changing network conditions.
5/17/2024

Federated Learning-based Collaborative Wideband Spectrum Sensing and Scheduling for UAVs in UTM Systems
Sravan Reddy Chintareddy, Keenan Roach, Kenny Cheung, Morteza Hashemi

0
0
In this paper, we propose a data-driven framework for collaborative wideband spectrum sensing and scheduling for networked unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), which act as the secondary users (SUs) to opportunistically utilize detected spectrum holes. Our overall framework consists of three main stages. Firstly, in the model training stage, we explore dataset generation in a multi-cell environment and training a machine learning (ML) model using the federated learning (FL) architecture. Unlike the existing studies on FL for wireless that presume datasets are readily available for training, we propose a novel architecture that directly integrates wireless dataset generation, which involves capturing I/Q samples from over-the-air signals in a multi-cell environment, into the FL training process. Secondly, in the collaborative spectrum inference stage, we propose a collaborative spectrum fusion strategy that is compatible with the unmanned aircraft system traffic management (UTM) ecosystem. Finally, in the spectrum scheduling stage, we leverage reinforcement learning (RL) solutions to dynamically allocate the detected spectrum holes to the secondary users. To evaluate the proposed methods, we establish a comprehensive simulation framework that generates a near-realistic synthetic dataset using MATLAB LTE toolbox by incorporating base-station~(BS) locations in a chosen area of interest, performing ray-tracing, and emulating the primary users channel usage in terms of I/Q samples. This evaluation methodology provides a flexible framework to generate large spectrum datasets that could be used for developing ML/AI-based spectrum management solutions for aerial devices.
6/5/2024

Fuzzy Q-Learning-Based Opportunistic Communication for MEC-Enhanced Vehicular Crowdsensing
Trung Thanh Nguyen, Truong Thao Nguyen, Thanh Hung Nguyen, Phi Le Nguyen

0
0
This study focuses on MEC-enhanced, vehicle-based crowdsensing systems that rely on devices installed on automobiles. We investigate an opportunistic communication paradigm in which devices can transmit measured data directly to a crowdsensing server over a 4G communication channel or to nearby devices or so-called Road Side Units positioned along the road via Wi-Fi. We tackle a new problem that is how to reduce the cost of 4G while preserving the latency. We propose an offloading strategy that combines a reinforcement learning technique known as Q-learning with Fuzzy logic to accomplish the purpose. Q-learning assists devices in learning to decide the communication channel. Meanwhile, Fuzzy logic is used to optimize the reward function in Q-learning. The experiment results show that our offloading method significantly cuts down around 30-40% of the 4G communication cost while keeping the latency of 99% packets below the required threshold.
5/3/2024
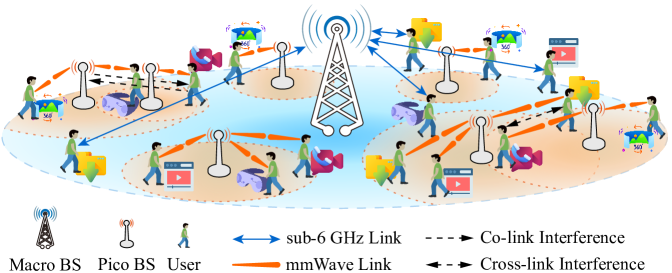
User Association and Channel Allocation in 5G Mobile Asymmetric Multi-band Heterogeneous Networks
Miao Dai, Gang Sun, Hongfang Yu, Sheng Wang, Dusit Niyato

0
0
With the proliferation of mobile terminals and the continuous upgrading of services, 4G LTE networks are showing signs of weakness. To enhance the capacity of wireless networks, millimeter waves are introduced to drive the evolution of networks towards multi-band 5G heterogeneous networks. The distinct propagation characteristics of mmWaves and microwaves, as well as the vastly different hardware configurations of heterogeneous base stations, make traditional access strategies no longer effective. Therefore, to narrowing the gap between theory and practice, we investigate the access strategy in multi-band 5G heterogeneous networks, taking into account the characteristics of mobile users, asynchronous switching between uplink and downlink of pico base stations, asymmetric service requirements, and user communication continuity. We formulate the problem as integer nonlinear programming and prove its intractability. Thereby, we decouple it into three subproblems: user association, switch point selection, and subchannel allocation, and design an algorithm based on optimal matching and spectral clustering to solve it efficiently. The simulation results show that the proposed algorithm outperforms the comparison methods in terms of overall data rate, effective data rate, and number of satisfied users.
5/30/2024