User Association and Channel Allocation in 5G Mobile Asymmetric Multi-band Heterogeneous Networks
2405.18797

0
0
Abstract
With the proliferation of mobile terminals and the continuous upgrading of services, 4G LTE networks are showing signs of weakness. To enhance the capacity of wireless networks, millimeter waves are introduced to drive the evolution of networks towards multi-band 5G heterogeneous networks. The distinct propagation characteristics of mmWaves and microwaves, as well as the vastly different hardware configurations of heterogeneous base stations, make traditional access strategies no longer effective. Therefore, to narrowing the gap between theory and practice, we investigate the access strategy in multi-band 5G heterogeneous networks, taking into account the characteristics of mobile users, asynchronous switching between uplink and downlink of pico base stations, asymmetric service requirements, and user communication continuity. We formulate the problem as integer nonlinear programming and prove its intractability. Thereby, we decouple it into three subproblems: user association, switch point selection, and subchannel allocation, and design an algorithm based on optimal matching and spectral clustering to solve it efficiently. The simulation results show that the proposed algorithm outperforms the comparison methods in terms of overall data rate, effective data rate, and number of satisfied users.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper explores user association and channel allocation in 5G mobile asymmetric multi-band heterogeneous networks (5G HetNets).
- It focuses on the challenges of providing seamless mobility and differentiated quality of service (QoS) for users across high-frequency millimeter wave (mmWave) and low-frequency sub-6 GHz bands.
- The authors propose a novel user association and channel allocation framework to jointly optimize user experience and network efficiency in 5G HetNets.
Plain English Explanation
In the evolving 5G mobile networks, there is a mix of different types of cell sites and wireless frequencies. This includes high-speed millimeter wave (mmWave) connections and lower-frequency sub-6 GHz connections. Users need to be able to move between these different types of connections seamlessly, while also receiving the appropriate quality of service for their needs.
The authors of this paper have developed a new system to help manage how users connect to the 5G network and which wireless channels they use. Their goal is to optimize the user experience while also making the overall network more efficient. This involves carefully balancing factors like user mobility, the available wireless channels, and the different service requirements of various applications and users.
By intelligently associating users with the right cell sites and allocating wireless channels, the proposed framework aims to deliver high-quality, uninterrupted service as users move around in the 5G network. This could enable better support for bandwidth-intensive applications like video streaming, as well as mission-critical services that require reliable low-latency connections.
Technical Explanation
The paper presents a user association and channel allocation framework for 5G mobile asymmetric multi-band heterogeneous networks. The authors consider a 5G HetNet with both mmWave and sub-6 GHz small cells, where users have diverse service requirements and mobility patterns.
The proposed approach jointly optimizes user-cell association and channel allocation to maximize the network's overall utility, which is a function of user experience and resource efficiency. The framework incorporates several key elements:
- User Mobility Modeling: The authors model user mobility using a semi-Markov process to capture the stochastic nature of user movement across cells.
- Asymmetric Service Modeling: The framework distinguishes between delay-sensitive services (e.g., real-time video) and delay-tolerant services (e.g., file downloads), allowing for differentiated quality of service.
- User Association Optimization: The user-cell association problem is formulated as a mixed-integer nonlinear program, aiming to maximize the network's utility while considering user mobility and service requirements.
- Channel Allocation Optimization: The channel allocation sub-problem is addressed using a Gibbs sampling-based approach to efficiently assign channels to associated users.
The authors evaluate the proposed framework through extensive simulations, comparing its performance to alternative user association and channel allocation strategies. The results demonstrate significant improvements in terms of user experience, resource utilization, and network-wide utility.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a well-designed and comprehensive framework for addressing the user association and channel allocation challenges in 5G asymmetric multi-band HetNets. The authors have carefully modeled the key aspects of the problem, including user mobility, service requirements, and network resources.
One potential limitation of the research is the assumption of perfect channel state information (CSI) at the network controller. In practice, acquiring accurate CSI can be challenging, especially in highly dynamic 5G environments. The authors acknowledge this limitation and suggest exploring CSI estimation techniques as an area for future research.
Additionally, the paper focuses on maximizing network-wide utility, which may not always align with individual user preferences or fairness considerations. Further research could investigate mechanisms to balance network efficiency with user-centric objectives, such as proportional fairness or min-max optimization.
Another aspect that could be explored is the interplay between user association, channel allocation, and cell switching strategies in 5G HetNets. Integrating these components could lead to a more holistic optimization framework for 5G network management.
Conclusion
This paper presents a novel user association and channel allocation framework for 5G mobile asymmetric multi-band heterogeneous networks. The proposed approach jointly optimizes user-cell association and channel allocation to maximize the network's overall utility, considering user mobility, service requirements, and resource efficiency.
The research demonstrates significant improvements in user experience, resource utilization, and network-wide performance compared to alternative strategies. The framework's ability to provide seamless mobility and differentiated quality of service across mmWave and sub-6 GHz bands makes it a promising solution for enabling the diverse applications and use cases envisioned for 5G networks.
Future research directions may include addressing practical limitations, such as imperfect CSI, and exploring mechanisms to balance network efficiency with user-centric objectives. Integrating user association, channel allocation, and cell switching strategies could also lead to a more comprehensive optimization framework for 5G network management.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers

Uplink resource allocation optimization for user-centric cell-free MIMO networks
Zehua Li, Raviraj Adve

0
0
We examine the problem of optimizing resource allocation in the uplink for a user-centric, cell-free, multi-input multi-output network. We start by modeling and developing resource allocation algorithms for two standard network operation modes. The centralized mode provides high data rates but suffers multiple issues, including scalability. On the other hand, the distributed mode has the opposite problem: relatively low rates, but is scalable. To address these challenges, we combine the strength of the two standard modes, creating a new semi-distributed operation mode. To avoid the need for information exchange between access points, we introduce a new quality of service metric to decentralize the resource allocation algorithms. Our results show that we can eliminate the need for information exchange with a relatively small penalty on data rates.
6/11/2024
Planning and Operation of Millimeter-wave Downlink Systems with Hybrid Beamforming
Yuan Quan, Shahram Shahsavari, Catherine Rosenberg

0
0
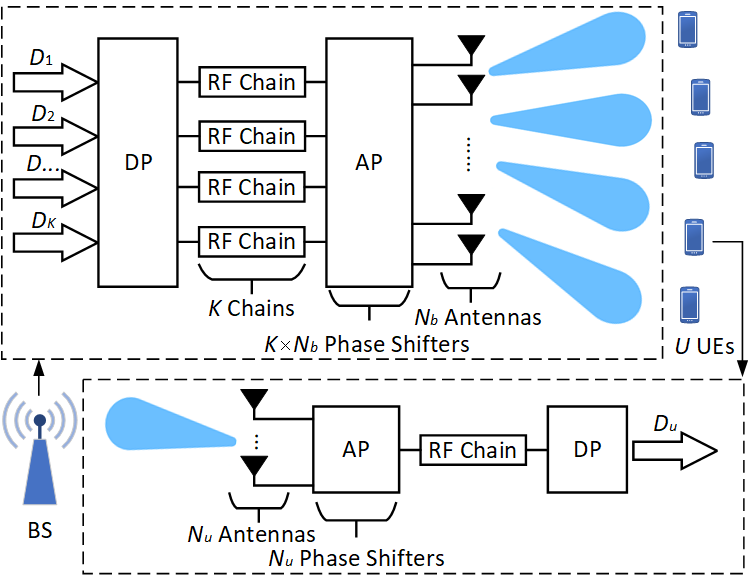
This paper investigates downlink radio resource management (RRM) in millimeter-wave systems with codebook-based hybrid beamforming in a single cell. We consider a practical but often overlooked multi-channel scenario where the base station is equipped with fewer radio frequency chains than there are user equipment (UEs) in the cell. In this case, analog beam selection is important because not all beams preferred by UEs can be selected simultaneously, and since the beam selection cannot vary across subchannels in a time slot, this creates a coupling between subchannels within a time slot. None of the solutions proposed in the literature deal with this important constraint. The paper begins with an offline study that analyzes the impact of different RRM procedures and system parameters on performance. An offline joint RRM optimization problem is formulated and solved that includes beam set selection, UE set selection, power distribution, modulation and coding scheme selection, and digital beamforming as a part of hybrid beamforming. The evaluation results of the offline study provide valuable insights that shows the importance of not neglecting the constraint and guide the design of low-complexity and high-performance online downlink RRM schemes in the second part of the paper. The proposed online RRM algorithms perform close to the performance targets obtained from the offline study while offering acceptable runtime.
4/22/2024

Slice-aware Resource Allocation and Admission Control for Smart Factory Wireless Networks
Regina Ochonu, Josep Vidal

0
0
The 5th generation (5G) and beyond network offers substantial promise as the ideal wireless technology to replace the existing inflexible wired connections in traditional factories of today. 5G network slicing allows for tailored allocation of resources to different network services, each with unique Quality of Service (QoS) requirements. This paper presents a novel solution for slice-aware radio resource allocation based on a convex optimisation control framework for applications in smart factory wireless networks. The proposed framework dynamically allocates minimum power and sub-channels to downlink mixed service type industrial users categorised into three slices: Capacity Limited (CL), Ultra Reliable Low Latency Communication (URLLC), and Time Sensitive (TS) slices. Given that the base station (BS) has limited transmission power, we enforce admission control by effectively relaxing the target rate constraints for current connections in the CL slice. This rate readjustment occurs whenever power consumption exceeds manageable levels. Simulation results show that our approach minimises power, allocates sub-channels to users, maintains slice isolation, and delivers QoS-specific communications to users in all the slices despite time-varying number of users and changing network conditions.
5/17/2024
Wireless Resource Optimization in Hybrid Semantic/Bit Communication Networks
Le Xia, Yao Sun, Dusit Niyato, Lan Zhang, Muhammad Ali Imran

0
0
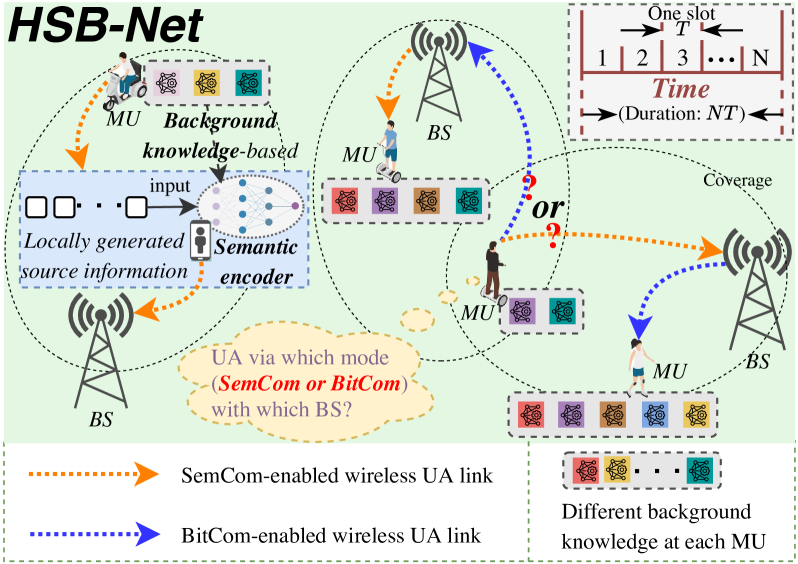
Recently, semantic communication (SemCom) has shown great potential in significant resource savings and efficient information exchanges, thus naturally introducing a novel and practical cellular network paradigm where two modes of SemCom and conventional bit communication (BitCom) coexist. Nevertheless, the involved wireless resource management becomes rather complicated and challenging, given the unique background knowledge matching and time-consuming semantic coding requirements in SemCom. To this end, this paper jointly investigates user association (UA), mode selection (MS), and bandwidth allocation (BA) problems in a hybrid semantic/bit communication network (HSB-Net). Concretely, we first identify a unified performance metric of message throughput for both SemCom and BitCom links. Next, we specially develop a knowledge matching-aware two-stage tandem packet queuing model and theoretically derive the average packet loss ratio and queuing latency. Combined with practical constraints, we then formulate a joint optimization problem for UA, MS, and BA to maximize the overall message throughput of HSB-Net. Afterward, we propose an optimal resource management strategy by utilizing a Lagrange primal-dual transformation method and a preference list-based heuristic algorithm with polynomial-time complexity. Numerical results not only demonstrate the accuracy of our analytical queuing model, but also validate the performance superiority of our proposed strategy compared with different benchmarks.
4/16/2024