Latent Diffusion Model-Enabled Real-Time Semantic Communication Considering Semantic Ambiguities and Channel Noises
2406.06644

0
0

Abstract
Semantic communication (SemCom) has emerged as a new paradigm for communication systems, with deep learning (DL) models being one of the key drives to shift from the accuracy of bit/symbol to the semantics and pragmatics of data. Nevertheless, DL-based SemCom systems often face performance bottlenecks due to overfitting, poor generalization, and sensitivity to outliers. Furthermore, the varying-fading gains and noises with uncertain signal-to-noise ratios (SNRs) commonly present in wireless channels usually restrict the accuracy of semantic information transmission. Consequently, to address the aforementioned issues, this paper constructs a SemCom system based on the latent diffusion model, and proposes three improvements compared to existing works: i) To handle potential outliers in the source data, semantic errors obtained by projected gradient descent based on the vulnerabilities of DL models, are utilized to update the parameters and obtain an outlier-robust encoder. ii) A lightweight single-layer latent space transformation adapter completes one-shot learning at transmitter and is placed before the decoder at receiver, enabling adaptation for out-of-distribution data or enhancing human-perceptual quality. iii) An end-to-end consistency distillation (EECD) strategy is used to distill the diffusion models trained in latent space, enabling deterministic single or few-step real-time denoising in various noisy channels while maintaining high semantic quality. Extensive numerical experiments across different datasets demonstrate the superiority of the proposed SemCom system, consistently proving its robustness to outliers, the capability to transmit data with unknown distributions, and the ability to perform real-time channel denoising tasks while preserving high human perceptual quality, outperforming the existing denoising approaches in semantic metrics such as MS-SSIM and LPIPS.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper presents a new approach for real-time semantic communication that addresses issues like semantic ambiguities and channel noises.
- The key elements include a latent diffusion model for efficient encoding and decoding, GAN inversion for semantic reconstruction, and channel denoising.
- The goal is to enable reliable and high-quality semantic communication even in the presence of challenging conditions.
Plain English Explanation
The researchers have developed a new system for real-time communication that focuses on the meaning and context of the information being shared, rather than just the raw data. This is called "semantic communication," and it's designed to work well even when there are things that can interfere with the communication, like ambiguity in the meaning of the words being used or noise in the communication channel.
At the heart of this system is a latent diffusion model, which is a type of machine learning model that can efficiently encode and decode the semantic content being communicated. This allows the information to be transmitted in a more compact and robust way.
The system also uses GAN inversion to help reconstruct the original semantic meaning on the receiving end, even if there's some ambiguity or noise present. And it includes a channel denoising component to help clean up any interference in the communication channel.
The goal is to enable reliable and high-quality semantic communication, even in challenging real-world conditions where things like misunderstandings or interference could be a problem. This could be useful in a variety of applications, like remote collaboration, virtual assistants, or even machine-to-machine communication.
Technical Explanation
The paper proposes a new approach for real-time semantic communication that addresses the challenges of semantic ambiguities and channel noises. The key components of the system include:
-
Latent Diffusion Model: The authors utilize a latent diffusion model to efficiently encode and decode the semantic content being communicated. This allows the information to be transmitted in a more compact and robust way.
-
GAN Inversion: The system employs GAN inversion techniques to help reconstruct the original semantic meaning on the receiving end, even in the presence of ambiguity.
-
Channel Denoising: The approach includes a channel denoising component to remove interference and noise in the communication channel, further improving the reliability of the semantic communication.
The authors evaluate the proposed system through extensive experiments, demonstrating its ability to maintain high-quality semantic communication in the face of semantic ambiguities and channel noises. The results showcase the potential of this approach to enable robust and reliable real-time semantic communication, which could have significant implications for a variety of applications.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a novel and promising approach to addressing the challenges of semantic ambiguities and channel noises in real-time communication. The use of a latent diffusion model, GAN inversion, and channel denoising techniques appears to be a well-designed solution to these problems.
However, the paper does not provide a detailed analysis of the potential limitations or caveats of the proposed system. For example, it would be valuable to understand the computational complexity and resource requirements of the system, as well as its performance in more diverse or extreme communication scenarios.
Additionally, the paper could have explored the potential ethical implications of this technology, such as its use in sensitive or high-stakes communication contexts, or its impact on privacy and security. Addressing these types of considerations would help readers form a more well-rounded understanding of the research.
Overall, the technical approach presented in the paper is sound and the results are promising. Further research and analysis could help refine and strengthen the system, as well as explore its broader implications for the field of semantic communication.
Conclusion
This paper introduces a novel approach to real-time semantic communication that addresses the challenges of semantic ambiguities and channel noises. By leveraging a latent diffusion model, GAN inversion, and channel denoising, the system demonstrates the ability to maintain high-quality semantic communication even in the face of these common obstacles.
The potential applications of this technology are wide-ranging, from remote collaboration and virtual assistants to machine-to-machine communication. As the field of semantic communication continues to evolve, this research represents an important step forward in enabling more reliable and effective communication in a variety of contexts.
While the paper presents a strong technical foundation, further exploration of the system's limitations and broader implications could help strengthen the research and guide future developments in this area. Overall, this work represents a valuable contribution to the ongoing efforts to enhance the efficiency and resilience of semantic communication systems.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
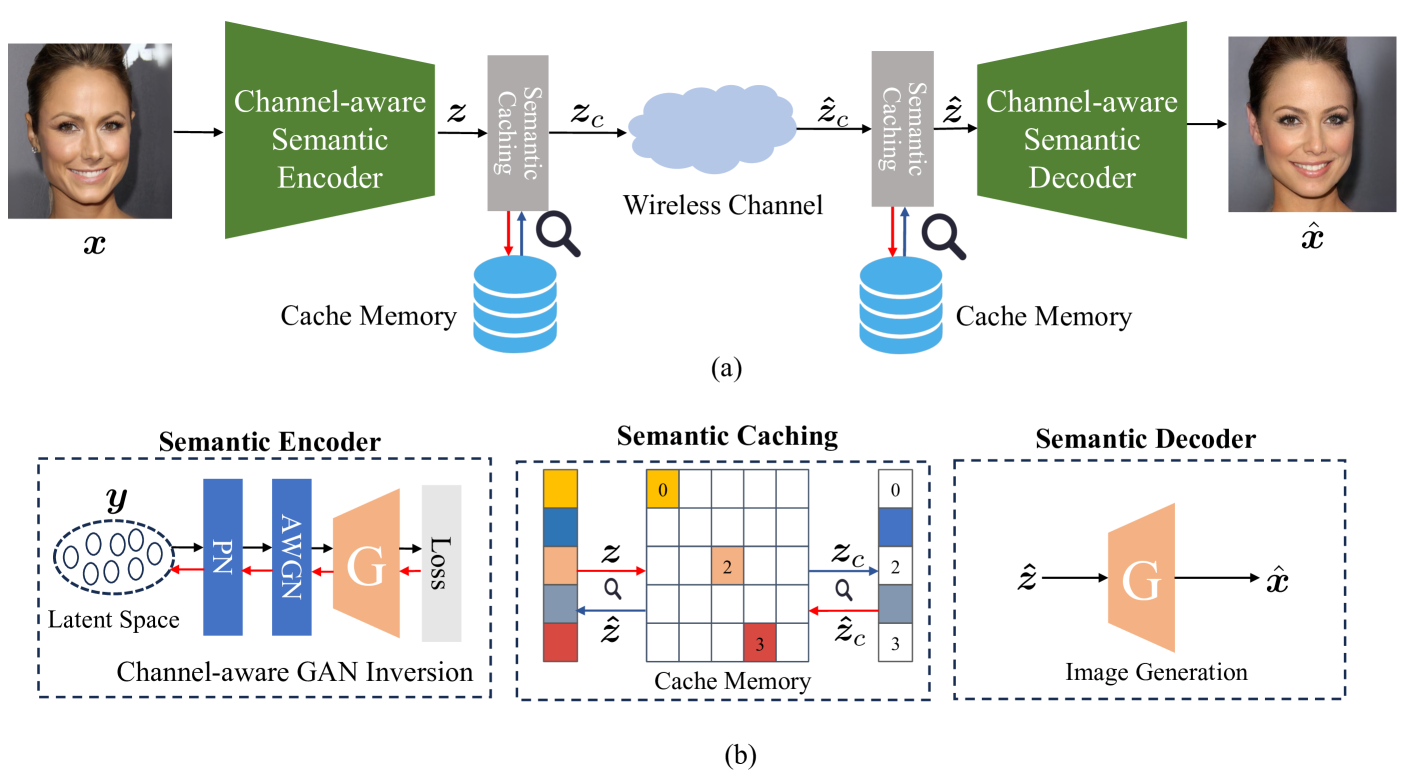
Evolving Semantic Communication with Generative Model
Shunpu Tang, Qianqian Yang, Deniz Gunduz, Zhaoyang Zhang

0
0
Recently, learning-based semantic communication (SemCom) has emerged as a promising approach in the upcoming 6G network and researchers have made remarkable efforts in this field. However, existing works have yet to fully explore the advantages of the evolving nature of learning-based systems, where knowledge accumulates during transmission have the potential to enhance system performance. In this paper, we explore an evolving semantic communication system for image transmission, referred to as ESemCom, with the capability to continuously enhance transmission efficiency. The system features a novel channel-aware semantic encoder that utilizes a pre-trained Semantic StyleGAN to extract the channel-correlated latent variables consisting of serval semantic vectors from the input images, which can be directly transmitted over a noisy channel without further channel coding. Moreover, we introduce a semantic caching mechanism that dynamically stores the transmitted semantic vectors in the local caching memory of both the transmitter and receiver. The cached semantic vectors are then exploited to eliminate the need to transmit similar codes in subsequent transmission, thus further reducing communication overhead. Simulation results highlight the evolving performance of the proposed system in terms of transmission efficiency, achieving superior perceptual quality with an average bandwidth compression ratio (BCR) of 1/192 for a sequence of 100 testing images compared to DeepJSCC and Inverse JSCC with the same BCR. Code of this paper is available at url{https://github.com/recusant7/GAN_SeCom}.
4/1/2024
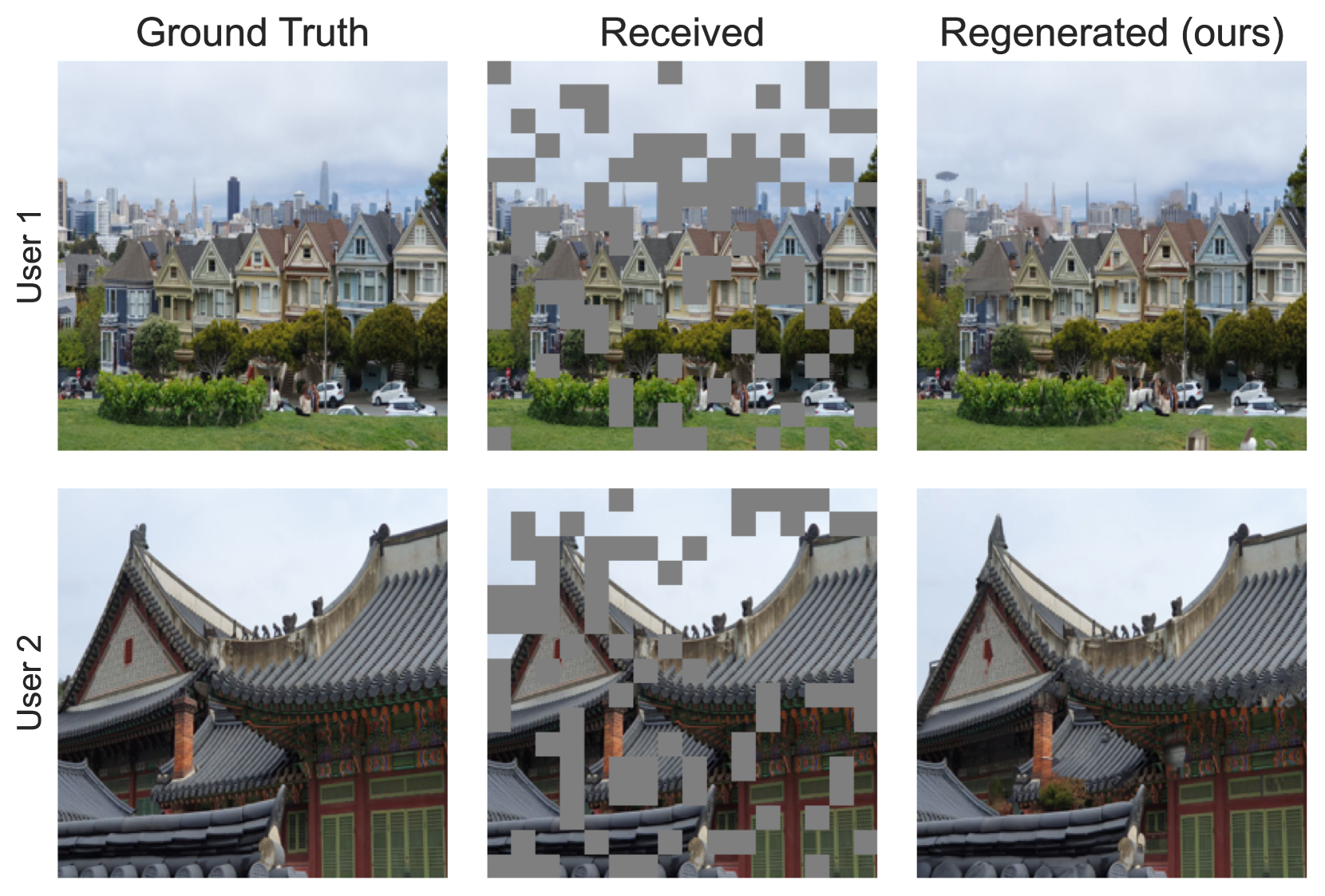
Rethinking Multi-User Semantic Communications with Deep Generative Models
Eleonora Grassucci, Jinho Choi, Jihong Park, Riccardo F. Gramaccioni, Giordano Cicchetti, Danilo Comminiello

0
0
In recent years, novel communication strategies have emerged to face the challenges that the increased number of connected devices and the higher quality of transmitted information are posing. Among them, semantic communication obtained promising results especially when combined with state-of-the-art deep generative models, such as large language or diffusion models, able to regenerate content from extremely compressed semantic information. However, most of these approaches focus on single-user scenarios processing the received content at the receiver on top of conventional communication systems. In this paper, we propose to go beyond these methods by developing a novel generative semantic communication framework tailored for multi-user scenarios. This system assigns the channel to users knowing that the lost information can be filled in with a diffusion model at the receivers. Under this innovative perspective, OFDMA systems should not aim to transmit the largest part of information, but solely the bits necessary to the generative model to semantically regenerate the missing ones. The thorough experimental evaluation shows the capabilities of the novel diffusion model and the effectiveness of the proposed framework, leading towards a GenAI-based next generation of communications.
5/17/2024
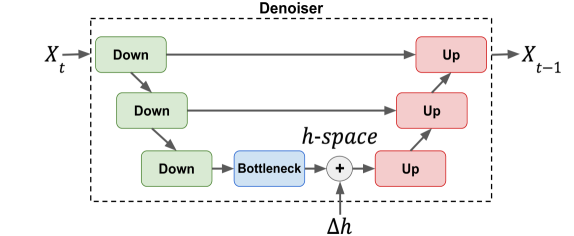
On the Semantic Latent Space of Diffusion-Based Text-to-Speech Models
Miri Varshavsky-Hassid, Roy Hirsch, Regev Cohen, Tomer Golany, Daniel Freedman, Ehud Rivlin

0
0
The incorporation of Denoising Diffusion Models (DDMs) in the Text-to-Speech (TTS) domain is rising, providing great value in synthesizing high quality speech. Although they exhibit impressive audio quality, the extent of their semantic capabilities is unknown, and controlling their synthesized speech's vocal properties remains a challenge. Inspired by recent advances in image synthesis, we explore the latent space of frozen TTS models, which is composed of the latent bottleneck activations of the DDM's denoiser. We identify that this space contains rich semantic information, and outline several novel methods for finding semantic directions within it, both supervised and unsupervised. We then demonstrate how these enable off-the-shelf audio editing, without any further training, architectural changes or data requirements. We present evidence of the semantic and acoustic qualities of the edited audio, and provide supplemental samples: https://latent-analysis-grad-tts.github.io/speech-samples/.
6/5/2024
🗣️
Semantic Communications for Speech Recognition
Zhenzi Weng, Zhijin Qin, Geoffrey Ye Li

0
0
The traditional communications transmit all the source data represented by bits, regardless of the content of source and the semantic information required by the receiver. However, in some applications, the receiver only needs part of the source data that represents critical semantic information, which prompts to transmit the application-related information, especially when bandwidth resources are limited. In this paper, we consider a semantic communication system for speech recognition by designing the transceiver as an end-to-end (E2E) system. Particularly, a deep learning (DL)-enabled semantic communication system, named DeepSC-SR, is developed to learn and extract text-related semantic features at the transmitter, which motivates the system to transmit much less than the source speech data without performance degradation. Moreover, in order to facilitate the proposed DeepSC-SR for dynamic channel environments, we investigate a robust model to cope with various channel environments without requiring retraining. The simulation results demonstrate that our proposed DeepSC-SR outperforms the traditional communication systems in terms of the speech recognition metrics, such as character-error-rate and word-error-rate, and is more robust to channel variations, especially in the low signal-to-noise (SNR) regime.
4/30/2024