On the Semantic Latent Space of Diffusion-Based Text-to-Speech Models
2402.12423

0
0
Abstract
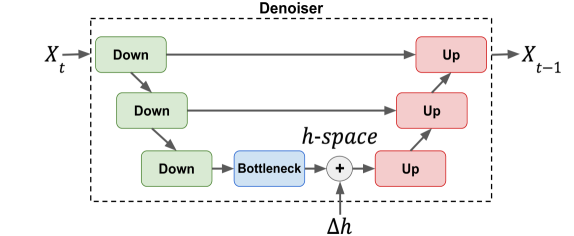
The incorporation of Denoising Diffusion Models (DDMs) in the Text-to-Speech (TTS) domain is rising, providing great value in synthesizing high quality speech. Although they exhibit impressive audio quality, the extent of their semantic capabilities is unknown, and controlling their synthesized speech's vocal properties remains a challenge. Inspired by recent advances in image synthesis, we explore the latent space of frozen TTS models, which is composed of the latent bottleneck activations of the DDM's denoiser. We identify that this space contains rich semantic information, and outline several novel methods for finding semantic directions within it, both supervised and unsupervised. We then demonstrate how these enable off-the-shelf audio editing, without any further training, architectural changes or data requirements. We present evidence of the semantic and acoustic qualities of the edited audio, and provide supplemental samples: https://latent-analysis-grad-tts.github.io/speech-samples/.
Create account to get full access
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
🔄
Discovering Interpretable Directions in the Semantic Latent Space of Diffusion Models
Ren'e Haas, Inbar Huberman-Spiegelglas, Rotem Mulayoff, Stella Gra{ss}hof, Sami S. Brandt, Tomer Michaeli

0
0
Denoising Diffusion Models (DDMs) have emerged as a strong competitor to Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs). However, despite their widespread use in image synthesis and editing applications, their latent space is still not as well understood. Recently, a semantic latent space for DDMs, coined `$h$-space', was shown to facilitate semantic image editing in a way reminiscent of GANs. The $h$-space is comprised of the bottleneck activations in the DDM's denoiser across all timesteps of the diffusion process. In this paper, we explore the properties of h-space and propose several novel methods for finding meaningful semantic directions within it. We start by studying unsupervised methods for revealing interpretable semantic directions in pretrained DDMs. Specifically, we show that global latent directions emerge as the principal components in the latent space. Additionally, we provide a novel method for discovering image-specific semantic directions by spectral analysis of the Jacobian of the denoiser w.r.t. the latent code. Next, we extend the analysis by finding directions in a supervised fashion in unconditional DDMs. We demonstrate how such directions can be found by relying on either a labeled data set of real images or by annotating generated samples with a domain-specific attribute classifier. We further show how to semantically disentangle the found direction by simple linear projection. Our approaches are applicable without requiring any architectural modifications, text-based guidance, CLIP-based optimization, or model fine-tuning.
5/30/2024

Latent Diffusion Model-Enabled Real-Time Semantic Communication Considering Semantic Ambiguities and Channel Noises
Jianhua Pei, Feng Cheng, Ping Wang, Hina Tabassum, Dongyuan Shi

0
0
Semantic communication (SemCom) has emerged as a new paradigm for communication systems, with deep learning (DL) models being one of the key drives to shift from the accuracy of bit/symbol to the semantics and pragmatics of data. Nevertheless, DL-based SemCom systems often face performance bottlenecks due to overfitting, poor generalization, and sensitivity to outliers. Furthermore, the varying-fading gains and noises with uncertain signal-to-noise ratios (SNRs) commonly present in wireless channels usually restrict the accuracy of semantic information transmission. Consequently, to address the aforementioned issues, this paper constructs a SemCom system based on the latent diffusion model, and proposes three improvements compared to existing works: i) To handle potential outliers in the source data, semantic errors obtained by projected gradient descent based on the vulnerabilities of DL models, are utilized to update the parameters and obtain an outlier-robust encoder. ii) A lightweight single-layer latent space transformation adapter completes one-shot learning at transmitter and is placed before the decoder at receiver, enabling adaptation for out-of-distribution data or enhancing human-perceptual quality. iii) An end-to-end consistency distillation (EECD) strategy is used to distill the diffusion models trained in latent space, enabling deterministic single or few-step real-time denoising in various noisy channels while maintaining high semantic quality. Extensive numerical experiments across different datasets demonstrate the superiority of the proposed SemCom system, consistently proving its robustness to outliers, the capability to transmit data with unknown distributions, and the ability to perform real-time channel denoising tasks while preserving high human perceptual quality, outperforming the existing denoising approaches in semantic metrics such as MS-SSIM and LPIPS.
6/12/2024

DiTTo-TTS: Efficient and Scalable Zero-Shot Text-to-Speech with Diffusion Transformer
Keon Lee, Dong Won Kim, Jaehyeon Kim, Jaewoong Cho

0
0
Large-scale diffusion models have shown outstanding generative abilities across multiple modalities including images, videos, and audio. However, text-to-speech (TTS) systems typically involve domain-specific modeling factors (e.g., phonemes and phoneme-level durations) to ensure precise temporal alignments between text and speech, which hinders the efficiency and scalability of diffusion models for TTS. In this work, we present an efficient and scalable Diffusion Transformer (DiT) that utilizes off-the-shelf pre-trained text and speech encoders. Our approach addresses the challenge of text-speech alignment via cross-attention mechanisms with the prediction of the total length of speech representations. To achieve this, we enhance the DiT architecture to suit TTS and improve the alignment by incorporating semantic guidance into the latent space of speech. We scale the training dataset and the model size to 82K hours and 790M parameters, respectively. Our extensive experiments demonstrate that the large-scale diffusion model for TTS without domain-specific modeling not only simplifies the training pipeline but also yields superior or comparable zero-shot performance to state-of-the-art TTS models in terms of naturalness, intelligibility, and speaker similarity. Our speech samples are available at https://ditto-tts.github.io.
6/18/2024
📈
Boosting Diffusion Model for Spectrogram Up-sampling in Text-to-speech: An Empirical Study
Chong Zhang, Yanqing Liu, Yang Zheng, Sheng Zhao

0
0
Scaling text-to-speech (TTS) with autoregressive language model (LM) to large-scale datasets by quantizing waveform into discrete speech tokens is making great progress to capture the diversity and expressiveness in human speech, but the speech reconstruction quality from discrete speech token is far from satisfaction depending on the compressed speech token compression ratio. Generative diffusion models trained with score-matching loss and continuous normalized flow trained with flow-matching loss have become prominent in generation of images as well as speech. LM based TTS systems usually quantize speech into discrete tokens and generate these tokens autoregressively, and finally use a diffusion model to up sample coarse-grained speech tokens into fine-grained codec features or mel-spectrograms before reconstructing into waveforms with vocoder, which has a high latency and is not realistic for real time speech applications. In this paper, we systematically investigate varied diffusion models for up sampling stage, which is the main bottleneck for streaming synthesis of LM and diffusion-based architecture, we present the model architecture, objective and subjective metrics to show quality and efficiency improvement.
6/10/2024