Leveraging Digital Twin Technologies for Public Space Protection and Vulnerability Assessment

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- This research paper explores how digital twin technologies can be leveraged to protect public spaces and assess their vulnerabilities.
- The study was funded by the European Commission under the Ceasefire project.
- Key topics covered include public space protection, digital twins, artificial intelligence, security, and vulnerability assessment.
Plain English Explanation
Leveraging Digital Twin Technologies for Public Space Protection and Vulnerability Assessment investigates how digital twin technologies can be used to enhance security and safety in public areas.
A digital twin is a virtual replica of a physical system or environment. By creating digital twins of public spaces, researchers can analyze them in detail to identify potential vulnerabilities and test security measures without disrupting the actual location. This allows for more thorough vulnerability assessments and the development of advanced AI-powered security systems.
The key idea is to leverage the capabilities of digital twins to enhance public space protection in a more comprehensive and proactive manner. This could help prevent or mitigate threats such as terrorist attacks, civil unrest, or other security incidents in crowded public areas.
Technical Explanation
The paper outlines a framework for utilizing digital twin technologies to safeguard public spaces. The researchers describe how digital twins can be created to faithfully replicate the physical attributes, environmental conditions, and human activity patterns of a given public area.
By analyzing these digital representations, AI-based vulnerability assessment models can be developed to identify potential security weaknesses, such as blind spots, choke points, or areas susceptible to cyberattacks. The digital twins also enable the testing of various security interventions and the optimization of protective measures without disrupting the actual public space.
The researchers highlight how this approach can improve public space protection by providing a comprehensive, data-driven understanding of the environment and allowing for more effective security planning and response strategies.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a compelling case for leveraging digital twin technologies to enhance public space protection. However, some potential limitations and areas for further research are worth considering:
- The feasibility and scalability of creating high-fidelity digital twins for large, complex public spaces may be challenging and resource-intensive.
- The accuracy and reliability of the vulnerability assessment models are crucial, and their performance in real-world scenarios needs to be thoroughly evaluated.
- The integration of digital twin data with existing security systems and decision-making processes may require significant organizational and technological changes.
- Privacy and ethical concerns around the collection and use of data for digital twin modeling should be carefully addressed.
Conclusion
This research paper presents a compelling vision for the use of digital twin technologies to improve public space protection and vulnerability assessment. By creating detailed digital replicas of public areas, researchers can develop advanced AI-powered security systems and test interventions without disrupting the actual environment.
While the approach holds significant promise, careful consideration of the technical, organizational, and ethical challenges will be crucial for successful implementation. As digital twin technologies continue to evolve, this research highlights their potential to transform how we safeguard and secure our public spaces.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Leveraging Digital Twin Technologies for Public Space Protection and Vulnerability Assessment
Artemis Stefanidou, Jorgen Cani, Thomas Papadopoulos, Panagiotis Radoglou-Grammatikis, Panagiotis Sarigiannidis, Iraklis Varlamis, Georgios Th. Papadopoulos
Over the recent years, the protection of the so-called `soft-targets', i.e. locations easily accessible by the general public with relatively low, though, security measures, has emerged as a rather challenging and increasingly important issue. The complexity and seriousness of this security threat growths nowadays exponentially, due to the emergence of new advanced technologies (e.g. Artificial Intelligence (AI), Autonomous Vehicles (AVs), 3D printing, etc.); especially when it comes to large-scale, popular and diverse public spaces. In this paper, a novel Digital Twin-as-a-Security-Service (DTaaSS) architecture is introduced for holistically and significantly enhancing the protection of public spaces (e.g. metro stations, leisure sites, urban squares, etc.). The proposed framework combines a Digital Twin (DT) conceptualization with additional cutting-edge technologies, including Internet of Things (IoT), cloud computing, Big Data analytics and AI. In particular, DTaaSS comprises a holistic, real-time, large-scale, comprehensive and data-driven security solution for the efficient/robust protection of public spaces, supporting: a) data collection and analytics, b) area monitoring/control and proactive threat detection, c) incident/attack prediction, and d) quantitative and data-driven vulnerability assessment. Overall, the designed architecture exhibits increased potential in handling complex, hybrid and combined threats over large, critical and popular soft-targets. The applicability and robustness of DTaaSS is discussed in detail against representative and diverse real-world application scenarios, including complex attacks to: a) a metro station, b) a leisure site, and c) a cathedral square.
Read more9/2/2024
🤖

0
The Role and Applications of Airport Digital Twin in Cyberattack Protection during the Generative AI Era
Abraham Itzhak Weinberg
In recent years, the threat facing airports from growing and increasingly sophisticated cyberattacks has become evident. Airports are considered a strategic national asset, so protecting them from attacks, specifically cyberattacks, is a crucial mission. One way to increase airports' security is by using Digital Twins (DTs). This paper shows and demonstrates how DTs can enhance the security mission. The integration of DTs with Generative AI (GenAI) algorithms can lead to synergy and new frontiers in fighting cyberattacks. The paper exemplifies ways to model cyberattack scenarios using simulations and generate synthetic data for testing defenses. It also discusses how DTs can be used as a crucial tool for vulnerability assessment by identifying weaknesses, prioritizing, and accelerating remediations in case of cyberattacks. Moreover, the paper demonstrates approaches for anomaly detection and threat hunting using Machine Learning (ML) and GenAI algorithms. Additionally, the paper provides impact prediction and recovery coordination methods that can be used by DT operators and stakeholders. It also introduces ways to harness the human factor by integrating training and simulation algorithms with Explainable AI (XAI) into the DT platforms. Lastly, the paper offers future applications and technologies that can be utilized in DT environments.
Read more8/13/2024
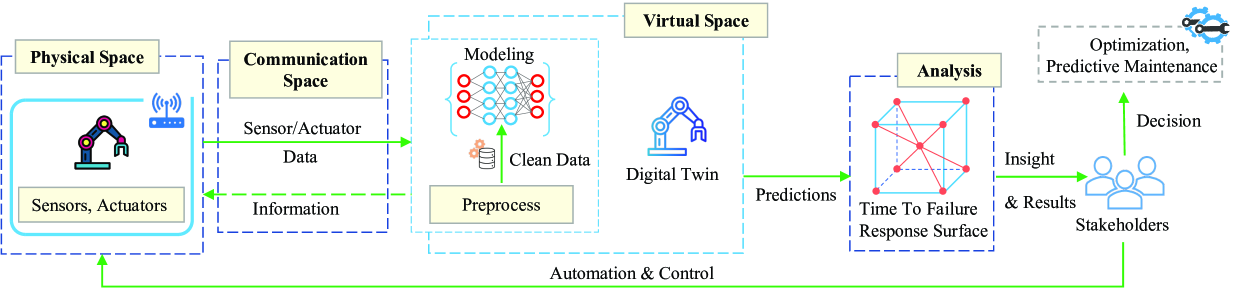

0
A Survey on Privacy Attacks Against Digital Twin Systems in AI-Robotics
Ivan A. Fernandez, Subash Neupane, Trisha Chakraborty, Shaswata Mitra, Sudip Mittal, Nisha Pillai, Jingdao Chen, Shahram Rahimi
Industry 4.0 has witnessed the rise of complex robots fueled by the integration of Artificial Intelligence/Machine Learning (AI/ML) and Digital Twin (DT) technologies. While these technologies offer numerous benefits, they also introduce potential privacy and security risks. This paper surveys privacy attacks targeting robots enabled by AI and DT models. Exfiltration and data leakage of ML models are discussed in addition to the potential extraction of models derived from first-principles (e.g., physics-based). We also discuss design considerations with DT-integrated robotics touching on the impact of ML model training, responsible AI and DT safeguards, data governance and ethical considerations on the effectiveness of these attacks. We advocate for a trusted autonomy approach, emphasizing the need to combine robotics, AI, and DT technologies with robust ethical frameworks and trustworthiness principles for secure and reliable AI robotic systems.
Read more6/28/2024

0
Digital Twins and Testbeds for Supporting AI Research with Autonomous Vehicle Networks
An{i}l Gurses, Gautham Reddy, Saad Masrur, Ozgur Ozdemir, .Ismail Guvenc{c}, Mihail L. Sichitiu, Alphan c{S}ahin, Ahmed Alkhateeb, Magreth Mushi, Rudra Dutta
Digital twins (DTs), which are virtual environments that simulate, predict, and optimize the performance of their physical counterparts, hold great promise in revolutionizing next-generation wireless networks. While DTs have been extensively studied for wireless networks, their use in conjunction with autonomous vehicles featuring programmable mobility remains relatively under-explored. In this paper, we study DTs used as a development environment to design, deploy, and test artificial intelligence (AI) techniques that utilize real-world (RW) observations, e.g. radio key performance indicators, for vehicle trajectory and network optimization decisions in autonomous vehicle networks (AVN). We first compare and contrast the use of simulation, digital twin (software in the loop (SITL)), sandbox (hardware-in-the-loop (HITL)), and physical testbed (PT) environments for their suitability in developing and testing AI algorithms for AVNs. We then review various representative use cases of DTs for AVN scenarios. Finally, we provide an example from the NSF AERPAW platform where a DT is used to develop and test AI-aided solutions for autonomous unmanned aerial vehicles for localizing a signal source based solely on link quality measurements. Our results in the physical testbed show that SITL DTs, when supplemented with data from RW measurements and simulations, can serve as an ideal environment for developing and testing innovative AI solutions for AVNs.
Read more8/9/2024