Leveraging Large Language Models for Patient Engagement: The Power of Conversational AI in Digital Health

0
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- This paper explores the use of large language models (LLMs) in digital health for improved patient engagement.
- The authors discuss the potential of conversational AI powered by LLMs to enhance the patient experience and support healthcare providers.
- Key topics include language model applications in digital health, opportunities for patient-centered care, and challenges or limitations to consider.
Plain English Explanation
Large language models (LLMs) are advanced AI systems that can understand and generate human-like text. This paper examines how these powerful language models can be leveraged in digital healthcare to improve patient engagement and experience.
The researchers explain how LLMs can enable more natural, conversational interactions between patients and digital healthcare tools. This could allow patients to ask questions, share concerns, and receive personalized guidance in a user-friendly way, rather than navigating rigid, menu-driven interfaces. Link to "Survey of Large Language Models in Healthcare"
By harnessing the natural language capabilities of LLMs, digital health apps and chatbots could become more responsive to individual patient needs and preferences. This could foster stronger patient-provider relationships and encourage patients to be more actively involved in managing their own health. Link to "Large Language Models in Medicine: A Comprehensive Survey"
However, the authors also caution that implementing LLMs in healthcare comes with important considerations around data privacy, model reliability, and ethical use. Careful design and rigorous testing will be crucial to ensuring these conversational AI systems deliver value to patients without compromising safety or trust. Link to "Evaluating Large Language Models for Medical Applications: A Survey"
Overall, this paper highlights the promising potential of LLMs to humanize digital healthcare and empower patients, while urging caution and responsibility in how these advanced language technologies are applied in sensitive medical contexts.
Technical Explanation
The paper first provides an overview of how large language models (LLMs) - powerful AI systems trained on vast amounts of text data - can be leveraged to enhance patient engagement in digital healthcare environments. Link to "Survey of Large Language Models from General-Purpose to Specialized"
The authors discuss key opportunities enabled by the natural language understanding and generation capabilities of LLMs, such as:
- Developing more conversational, user-friendly digital health interfaces
- Providing personalized guidance and support tailored to individual patient needs
- Fostering stronger patient-provider relationships through empathetic, contextual communication
To illustrate these concepts, the paper outlines several use case scenarios, such as an AI-powered chatbot that can engage in nuanced dialogues to assess symptoms, offer advice, and connect patients to appropriate resources.
At the same time, the researchers acknowledge critical challenges and limitations that must be carefully addressed, including:
- Ensuring data privacy and security when handling sensitive healthcare information
- Verifying the reliability and accuracy of LLM-generated responses for medical advice
- Establishing ethical frameworks to govern the use of AI in sensitive healthcare contexts
The paper emphasizes that realizing the full potential of LLMs in digital health will require a thoughtful, multidisciplinary approach - one that balances innovation with robust testing, safeguards, and user-centered design principles.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a well-rounded perspective on the opportunities and considerations surrounding the use of large language models (LLMs) in digital healthcare. The authors rightly highlight the promise of LLMs to enhance patient engagement through more natural, personalized interactions. Link to "Comprehensive Survey of Large Language Models for Multimodal Applications"
However, the paper also raises important caveats that warrant further exploration. For instance, while the authors discuss the need for data privacy and model reliability, they do not delve deeply into specific technical or regulatory challenges. Additional research may be needed to fully understand the complexities of deploying LLMs in sensitive healthcare contexts.
The paper could also benefit from a more critical examination of potential biases or limitations inherent in LLM technology. As these systems are trained on large but potentially biased datasets, there is a risk of perpetuating or amplifying societal biases related to race, gender, or socioeconomic status. The authors could have explored strategies for mitigating such biases and ensuring equitable access to LLM-powered digital health tools.
Overall, the paper provides a solid foundational understanding of the opportunities and considerations around LLMs in digital health. However, further research and discussion will be necessary to fully address the nuanced technical, ethical, and practical challenges involved in realizing the transformative potential of these language models in the healthcare domain.
Conclusion
This paper explores the promising potential of leveraging large language models (LLMs) to enhance patient engagement and experience in digital healthcare. By harnessing the natural language understanding and generation capabilities of LLMs, the authors envision a future where digital health tools can engage in more conversational, personalized interactions with patients.
The researchers outline several use case scenarios that illustrate how LLM-powered chatbots and digital assistants could provide more tailored guidance, support patient-provider relationships, and empower individuals to take a more active role in managing their own health. Link to "Survey of Large Language Models in Healthcare"
At the same time, the paper underscores critical challenges and limitations that must be carefully addressed, such as data privacy, model reliability, and ethical considerations. Realizing the full transformative potential of LLMs in digital health will require a multidisciplinary, user-centric approach to ensure these advanced language technologies are deployed responsibly and equitably.
Overall, this paper offers a thought-provoking exploration of the intersection between large language models and digital healthcare, highlighting both the exciting possibilities and the complex realities that must be navigated to deliver meaningful patient-centered experiences powered by conversational AI.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Leveraging Large Language Models for Patient Engagement: The Power of Conversational AI in Digital Health
Bo Wen, Raquel Norel, Julia Liu, Thaddeus Stappenbeck, Farhana Zulkernine, Huamin Chen
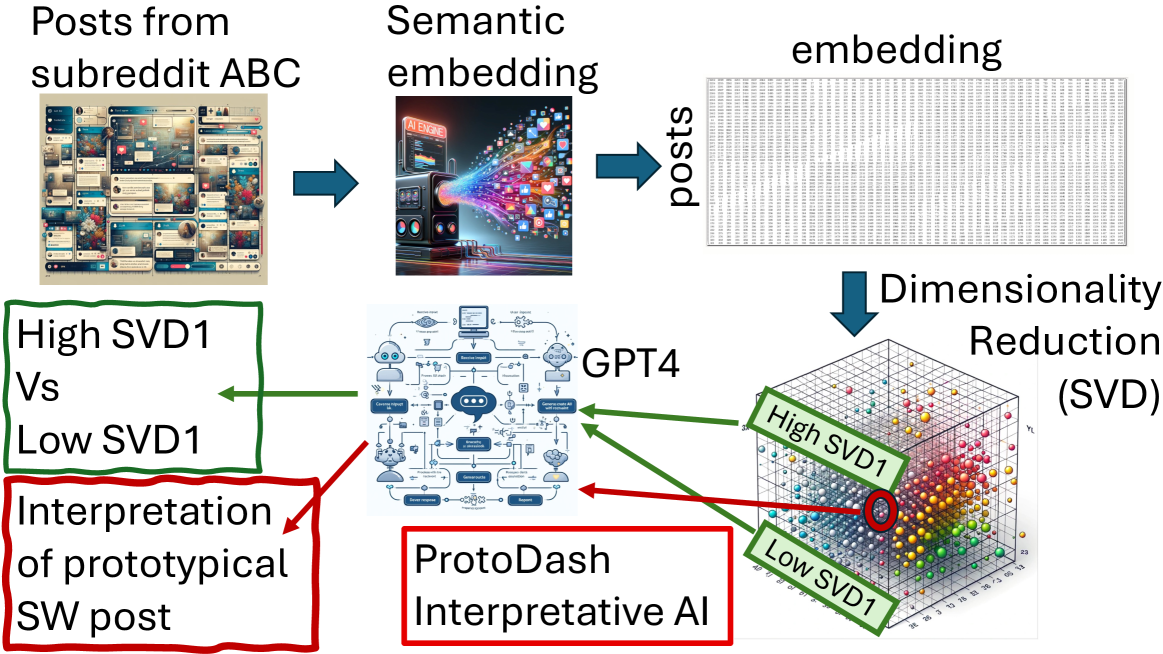
The rapid advancements in large language models (LLMs) have opened up new opportunities for transforming patient engagement in healthcare through conversational AI. This paper presents an overview of the current landscape of LLMs in healthcare, specifically focusing on their applications in analyzing and generating conversations for improved patient engagement. We showcase the power of LLMs in handling unstructured conversational data through four case studies: (1) analyzing mental health discussions on Reddit, (2) developing a personalized chatbot for cognitive engagement in seniors, (3) summarizing medical conversation datasets, and (4) designing an AI-powered patient engagement system. These case studies demonstrate how LLMs can effectively extract insights and summarizations from unstructured dialogues and engage patients in guided, goal-oriented conversations. Leveraging LLMs for conversational analysis and generation opens new doors for many patient-centered outcomes research opportunities. However, integrating LLMs into healthcare raises important ethical considerations regarding data privacy, bias, transparency, and regulatory compliance. We discuss best practices and guidelines for the responsible development and deployment of LLMs in healthcare settings. Realizing the full potential of LLMs in digital health will require close collaboration between the AI and healthcare professionals communities to address technical challenges and ensure these powerful tools' safety, efficacy, and equity.
Read more6/21/2024
💬

0
A Survey of Large Language Models for Healthcare: from Data, Technology, and Applications to Accountability and Ethics
Kai He, Rui Mao, Qika Lin, Yucheng Ruan, Xiang Lan, Mengling Feng, Erik Cambria
The utilization of large language models (LLMs) in the Healthcare domain has generated both excitement and concern due to their ability to effectively respond to freetext queries with certain professional knowledge. This survey outlines the capabilities of the currently developed LLMs for Healthcare and explicates their development process, with the aim of providing an overview of the development roadmap from traditional Pretrained Language Models (PLMs) to LLMs. Specifically, we first explore the potential of LLMs to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of various Healthcare applications highlighting both the strengths and limitations. Secondly, we conduct a comparison between the previous PLMs and the latest LLMs, as well as comparing various LLMs with each other. Then we summarize related Healthcare training data, training methods, optimization strategies, and usage. Finally, the unique concerns associated with deploying LLMs in Healthcare settings are investigated, particularly regarding fairness, accountability, transparency and ethics. Our survey provide a comprehensive investigation from perspectives of both computer science and Healthcare specialty. Besides the discussion about Healthcare concerns, we supports the computer science community by compiling a collection of open source resources, such as accessible datasets, the latest methodologies, code implementations, and evaluation benchmarks in the Github. Summarily, we contend that a significant paradigm shift is underway, transitioning from PLMs to LLMs. This shift encompasses a move from discriminative AI approaches to generative AI approaches, as well as a shift from model-centered methodologies to data-centered methodologies. Also, we determine that the biggest obstacle of using LLMs in Healthcare are fairness, accountability, transparency and ethics.
Read more6/12/2024
💬

0
The Role of Language Models in Modern Healthcare: A Comprehensive Review
Amna Khalid, Ayma Khalid, Umar Khalid
The application of large language models (LLMs) in healthcare has gained significant attention due to their ability to process complex medical data and provide insights for clinical decision-making. These models have demonstrated substantial capabilities in understanding and generating natural language, which is crucial for medical documentation, diagnostics, and patient interaction. This review examines the trajectory of language models from their early stages to the current state-of-the-art LLMs, highlighting their strengths in healthcare applications and discussing challenges such as data privacy, bias, and ethical considerations. The potential of LLMs to enhance healthcare delivery is explored, alongside the necessary steps to ensure their ethical and effective integration into medical practice.
Read more9/26/2024
💬

0
Large language models in healthcare and medical domain: A review
Zabir Al Nazi, Wei Peng
The deployment of large language models (LLMs) within the healthcare sector has sparked both enthusiasm and apprehension. These models exhibit the remarkable capability to provide proficient responses to free-text queries, demonstrating a nuanced understanding of professional medical knowledge. This comprehensive survey delves into the functionalities of existing LLMs designed for healthcare applications, elucidating the trajectory of their development, starting from traditional Pretrained Language Models (PLMs) to the present state of LLMs in healthcare sector. First, we explore the potential of LLMs to amplify the efficiency and effectiveness of diverse healthcare applications, particularly focusing on clinical language understanding tasks. These tasks encompass a wide spectrum, ranging from named entity recognition and relation extraction to natural language inference, multi-modal medical applications, document classification, and question-answering. Additionally, we conduct an extensive comparison of the most recent state-of-the-art LLMs in the healthcare domain, while also assessing the utilization of various open-source LLMs and highlighting their significance in healthcare applications. Furthermore, we present the essential performance metrics employed to evaluate LLMs in the biomedical domain, shedding light on their effectiveness and limitations. Finally, we summarize the prominent challenges and constraints faced by large language models in the healthcare sector, offering a holistic perspective on their potential benefits and shortcomings. This review provides a comprehensive exploration of the current landscape of LLMs in healthcare, addressing their role in transforming medical applications and the areas that warrant further research and development.
Read more7/9/2024