LLM-Augmented Agent-Based Modelling for Social Simulations: Challenges and Opportunities
2405.06700

0
0
✨
Abstract
As large language models (LLMs) continue to make significant strides, their better integration into agent-based simulations offers a transformational potential for understanding complex social systems. However, such integration is not trivial and poses numerous challenges. Based on this observation, in this paper, we explore architectures and methods to systematically develop LLM-augmented social simulations and discuss potential research directions in this field. We conclude that integrating LLMs with agent-based simulations offers a powerful toolset for researchers and scientists, allowing for more nuanced, realistic, and comprehensive models of complex systems and human behaviours.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- As large language models (LLMs) continue to advance, integrating them with agent-based simulations could have transformative potential for understanding complex social systems.
- However, this integration poses significant challenges that require systematic exploration of architectures and methods.
- The paper examines ways to develop LLM-augmented social simulations and discusses potential research directions in this field.
- Integrating LLMs with agent-based simulations could provide researchers and scientists with a powerful toolset for creating more nuanced, realistic, and comprehensive models of complex systems and human behaviors.
Plain English Explanation
Large language models (LLMs) are advanced artificial intelligence systems that can generate human-like text. As these models continue to improve, researchers are exploring how to better integrate them with agent-based simulations - computer programs that simulate the behavior of individual "agents" within complex social systems.
Combining LLMs with agent-based simulations could be a game-changer for understanding how societies and human behavior work. LLMs could help make these simulations more realistic and comprehensive, allowing researchers to model nuanced social interactions and complex decision-making processes.
However, integrating LLMs into agent-based simulations is not straightforward. There are numerous technical and conceptual challenges that need to be addressed. This paper explores different ways to tackle these challenges and outlines promising research directions in this emerging field.
By leveraging the capabilities of LLMs within agent-based simulations, researchers and scientists could gain a powerful new toolset for studying complex social systems and human behaviors in a more realistic and comprehensive way. This could lead to important insights and breakthroughs in fields ranging from sociology and psychology to economics and political science.
Technical Explanation
The paper examines the potential of integrating large language models (LLMs) with agent-based simulations to advance the understanding of complex social systems. LLMs have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in natural language processing and generation, which could enhance the realism and nuance of agent-based simulations.
The authors propose a systematic approach to developing LLM-augmented social simulations. This involves exploring different architectural designs and methods for seamlessly incorporating LLMs into agent-based models. One key challenge is ensuring that the LLM-powered agents exhibit coherent and consistent behaviors across simulations.
The paper discusses several potential research directions, such as:
- Developing techniques to align LLM-based agents' behaviors with the simulation's underlying rules and dynamics
- Investigating methods for training LLMs to effectively capture and reproduce complex social interactions
- Exploring ways to maintain the interpretability and explainability of LLM-augmented agent-based models
Through these research efforts, the authors aim to unlock the transformative potential of integrating LLMs with agent-based simulations, leading to more realistic and comprehensive models of complex social systems and human behaviors.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a compelling vision for the integration of large language models (LLMs) and agent-based simulations, but it also acknowledges the significant challenges involved in realizing this vision.
One key limitation highlighted in the paper is the need to ensure that LLM-powered agents exhibit coherent and consistent behaviors across simulations. Maintaining this consistency is crucial for the validity and interpretability of the models, but it may require complex training and alignment techniques that are not yet fully developed.
Additionally, the paper does not delve deeply into the potential biases and limitations of LLMs, which could be amplified or manifested in the agent-based simulations. Researchers will need to carefully consider how to mitigate these issues and ensure that the LLM-augmented models are as unbiased and representative as possible.
Another area for further exploration is the interpretability and explainability of the LLM-augmented agent-based models. As these systems become more complex, it may become increasingly difficult to understand the underlying mechanisms and decision-making processes, which could limit their usefulness for scientific research and policy applications.
Despite these challenges, the potential benefits of integrating LLMs with agent-based simulations are substantial. By leveraging the rich language capabilities of LLMs, researchers can create more nuanced and realistic models of complex social systems, potentially leading to important insights and breakthroughs in various fields.
Conclusion
This paper explores the transformative potential of integrating large language models (LLMs) with agent-based simulations to advance the understanding of complex social systems. While the challenges of such integration are significant, the authors outline a systematic approach to developing LLM-augmented social simulations and discuss promising research directions in this emerging field.
By combining the power of LLMs with the flexibility and complexity of agent-based models, researchers and scientists could gain a valuable new toolset for creating more nuanced, realistic, and comprehensive representations of human behavior and social dynamics. This could lead to important insights and breakthroughs in fields ranging from sociology and psychology to economics and political science.
As the paper suggests, the successful integration of LLMs and agent-based simulations offers an exciting opportunity to push the boundaries of our understanding of complex social systems and the human condition.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
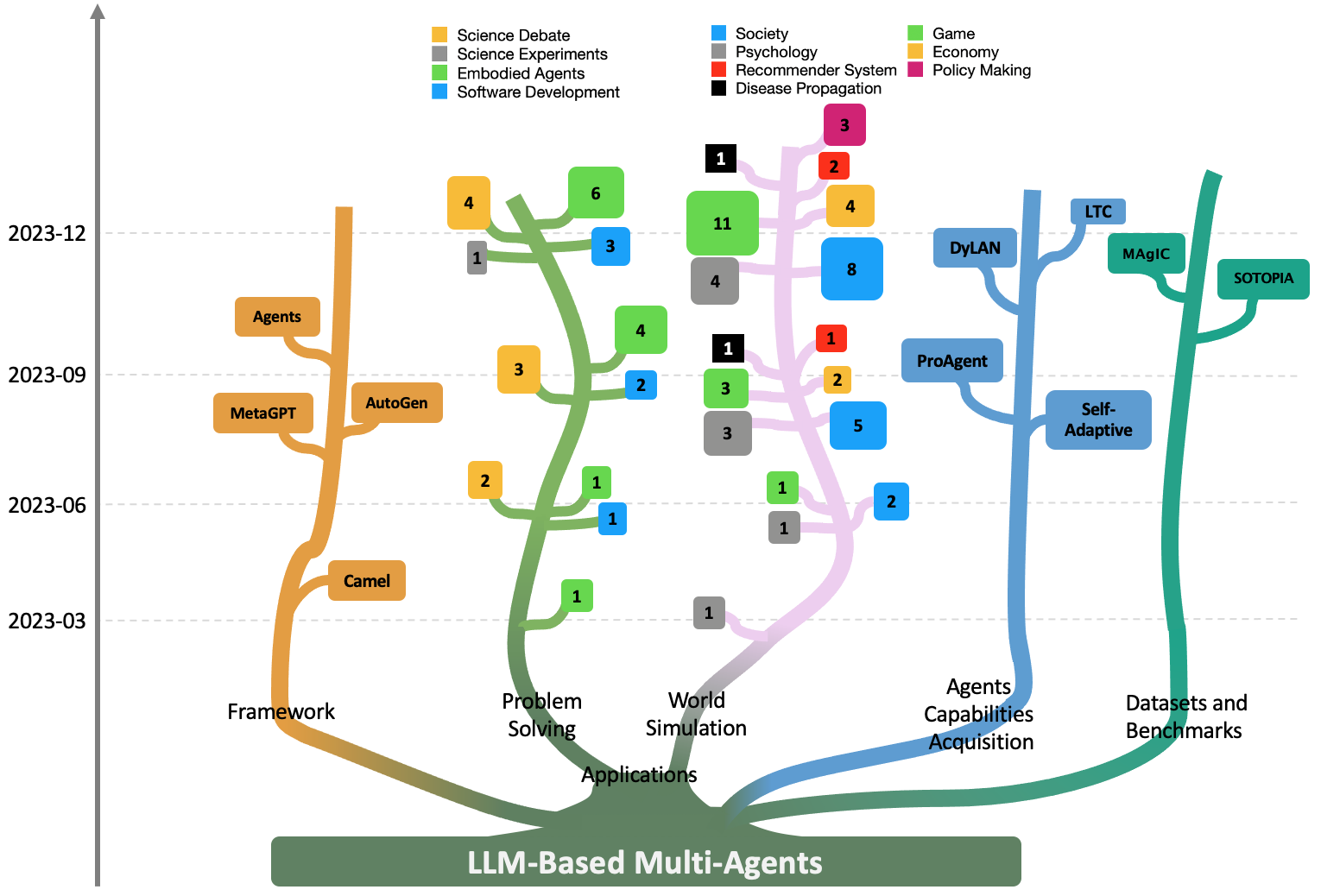
Large Language Model based Multi-Agents: A Survey of Progress and Challenges
Taicheng Guo, Xiuying Chen, Yaqi Wang, Ruidi Chang, Shichao Pei, Nitesh V. Chawla, Olaf Wiest, Xiangliang Zhang

0
0
Large Language Models (LLMs) have achieved remarkable success across a wide array of tasks. Due to the impressive planning and reasoning abilities of LLMs, they have been used as autonomous agents to do many tasks automatically. Recently, based on the development of using one LLM as a single planning or decision-making agent, LLM-based multi-agent systems have achieved considerable progress in complex problem-solving and world simulation. To provide the community with an overview of this dynamic field, we present this survey to offer an in-depth discussion on the essential aspects of multi-agent systems based on LLMs, as well as the challenges. Our goal is for readers to gain substantial insights on the following questions: What domains and environments do LLM-based multi-agents simulate? How are these agents profiled and how do they communicate? What mechanisms contribute to the growth of agents' capacities? For those interested in delving into this field of study, we also summarize the commonly used datasets or benchmarks for them to have convenient access. To keep researchers updated on the latest studies, we maintain an open-source GitHub repository, dedicated to outlining the research on LLM-based multi-agent systems.
4/22/2024
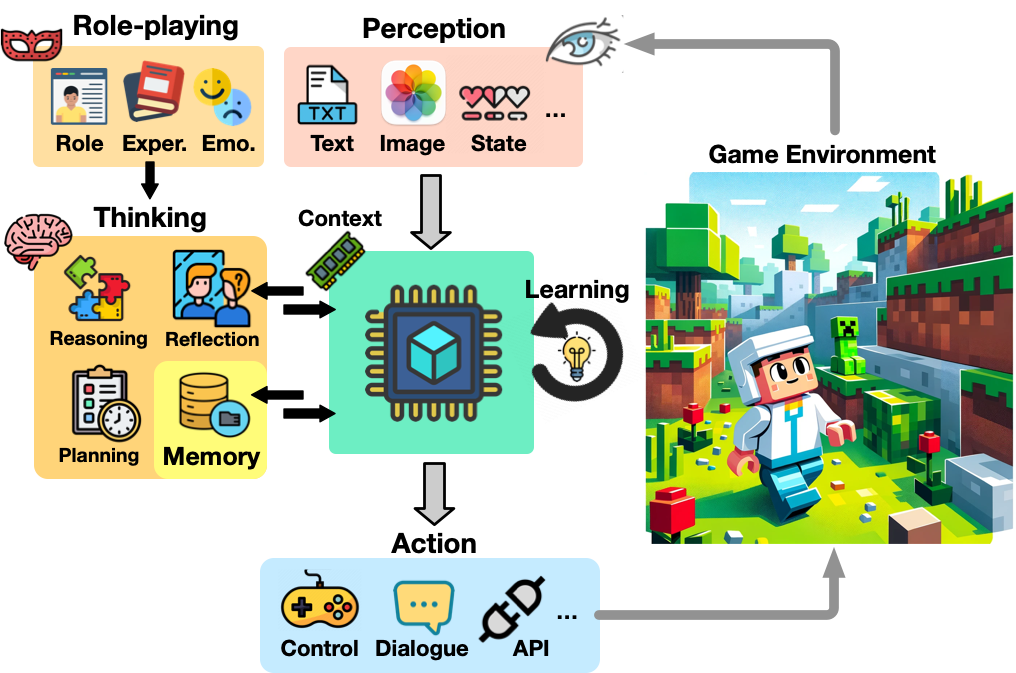
A Survey on Large Language Model-Based Game Agents
Sihao Hu, Tiansheng Huang, Fatih Ilhan, Selim Tekin, Gaowen Liu, Ramana Kompella, Ling Liu

0
0
The development of game agents holds a critical role in advancing towards Artificial General Intelligence (AGI). The progress of LLMs and their multimodal counterparts (MLLMs) offers an unprecedented opportunity to evolve and empower game agents with human-like decision-making capabilities in complex computer game environments. This paper provides a comprehensive overview of LLM-based game agents from a holistic viewpoint. First, we introduce the conceptual architecture of LLM-based game agents, centered around six essential functional components: perception, memory, thinking, role-playing, action, and learning. Second, we survey existing representative LLM-based game agents documented in the literature with respect to methodologies and adaptation agility across six genres of games, including adventure, communication, competition, cooperation, simulation, and crafting & exploration games. Finally, we present an outlook of future research and development directions in this burgeoning field. A curated list of relevant papers is maintained and made accessible at: https://github.com/git-disl/awesome-LLM-game-agent-papers.
4/3/2024
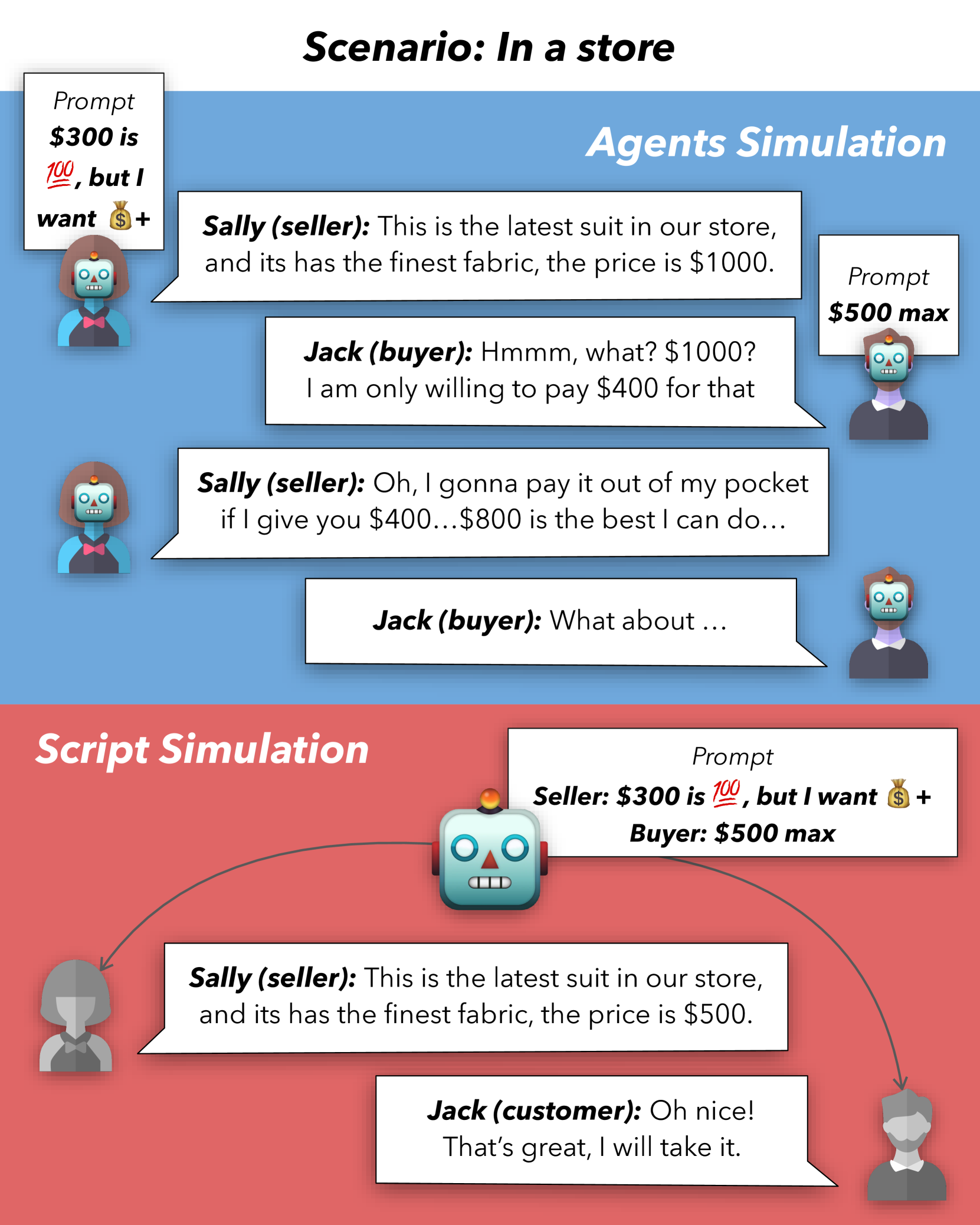
Is this the real life? Is this just fantasy? The Misleading Success of Simulating Social Interactions With LLMs
Xuhui Zhou, Zhe Su, Tiwalayo Eisape, Hyunwoo Kim, Maarten Sap

0
0
Recent advances in large language models (LLM) have enabled richer social simulations, allowing for the study of various social phenomena. However, most recent work has used a more omniscient perspective on these simulations (e.g., single LLM to generate all interlocutors), which is fundamentally at odds with the non-omniscient, information asymmetric interactions that involve humans and AI agents in the real world. To examine these differences, we develop an evaluation framework to simulate social interactions with LLMs in various settings (omniscient, non-omniscient). Our experiments show that LLMs perform better in unrealistic, omniscient simulation settings but struggle in ones that more accurately reflect real-world conditions with information asymmetry. Our findings indicate that addressing information asymmetry remains a fundamental challenge for LLM-based agents.
4/22/2024
Exploring Autonomous Agents through the Lens of Large Language Models: A Review
Saikat Barua

0
0
Large Language Models (LLMs) are transforming artificial intelligence, enabling autonomous agents to perform diverse tasks across various domains. These agents, proficient in human-like text comprehension and generation, have the potential to revolutionize sectors from customer service to healthcare. However, they face challenges such as multimodality, human value alignment, hallucinations, and evaluation. Techniques like prompting, reasoning, tool utilization, and in-context learning are being explored to enhance their capabilities. Evaluation platforms like AgentBench, WebArena, and ToolLLM provide robust methods for assessing these agents in complex scenarios. These advancements are leading to the development of more resilient and capable autonomous agents, anticipated to become integral in our digital lives, assisting in tasks from email responses to disease diagnosis. The future of AI, with LLMs at the forefront, is promising.
4/9/2024