Low Layer Functional Split Management in 5G and Beyond: Architecture and Self-adaptation

0
👨🏫
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- Radio Access Network (RAN) disaggregation is a key trend in beyond 5G networks
- It offers new opportunities for flexible deployments and intelligent network management
- A relevant problem is functional split selection - deciding which baseband functions are kept close to radio units and which are centralized
Plain English Explanation
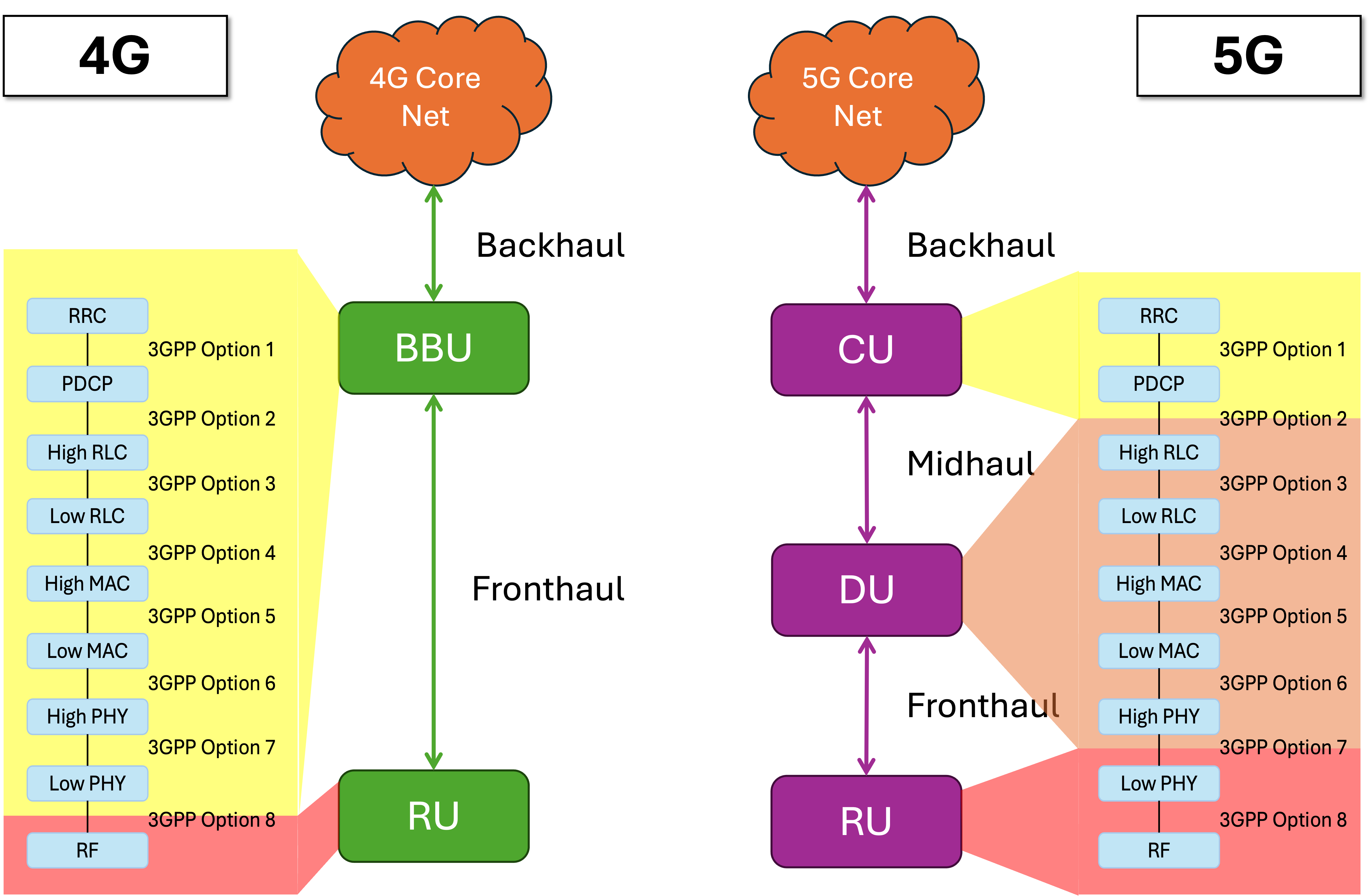
Radio Access Network (RAN) disaggregation is an emerging approach in developing future 5G and beyond networks. Traditionally, a cellular base station combines both radio and computing functions in a single unit. RAN disaggregation separates these functions, allowing the computing parts to be located separately from the radio equipment.
This flexibility can bring benefits like more efficient use of resources and better network management. However, it also introduces new challenges, such as deciding which base station functions should remain close to the radios and which can be moved to a central location. This is known as the functional split selection problem.
The paper examines how this functional split can be optimized to adapt to changing network conditions while minimizing energy costs. It proposes an architectural framework based on the O-RAN standard to support this flexibility.
Technical Explanation
The paper first presents an architectural framework for supporting RAN disaggregation based on the O-RAN reference architecture. This allows dynamic selection of the functional split between the radio units and the centralized baseband processing.
The key technical contribution is an analysis of how to optimize this functional split. The authors model the energy consumption of different split options and use this to develop an algorithm that can dynamically adjust the split based on factors like network load.
Simulations are used to evaluate the performance of this approach. The results show it can reduce energy costs compared to static split configurations, while still meeting requirements for throughput and latency.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a thoughtful analysis of the functional split selection problem in disaggregated RANs. It offers a practical solution based on the emerging O-RAN standard, which is important as this standard gains traction in the industry.
However, the paper only considers a single metric of energy efficiency. In real networks, there may be other important factors to balance, such as cost, reliability, or coverage. Further research could explore multi-objective optimization of the functional split.
Additionally, the simulations are performed in a simplified scenario. Evaluating the approach in more realistic network conditions, with factors like mobility and interference, would help validate its real-world applicability.
Conclusion
This paper presents a promising approach for optimizing the functional split in disaggregated RANs to improve energy efficiency. The proposed framework leverages the flexibility of the O-RAN architecture to dynamically adjust the split based on network conditions.
While further research is needed to extend the analysis, this work contributes valuable insights into managing the trade-offs inherent in RAN disaggregation. As 5G and beyond networks become more complex, intelligent and adaptive solutions like this will be crucial for maximizing the benefits of this emerging technology.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
👨🏫

0
Low Layer Functional Split Management in 5G and Beyond: Architecture and Self-adaptation
Jordi P'erez-Romero, Oriol Sallent, David Campoy, Antoni Gelonch, Xavier Gelabert, Bleron Klaiqi
Radio Access Network (RAN) disaggregation is emerging as a key trend in beyond 5G, as it offers new opportunities for more flexible deployments and intelligent network management. A relevant problem in disaggregated RAN is the functional split selection, which dynamically decides which baseband (BB) functions of a base station are kept close to the radio units and which ones are centralized. In this context, this paper firstly presents an architectural framework for supporting this concept relying on the O-RAN architecture. Then, the paper analyzes how the functional split can be optimized to adapt to the different load conditions while minimizing energy costs.
Read more9/4/2024


0
Throughput Requirements for RAN Functional Splits in 3D-Networks
MohammadAmin Vakilifard, Tim Due, Mohammad Rihan, Maik Roper, Dirk Wubben, Carsten Bockelmann, Armin Dekorsy
The rapid growth of non-terrestrial communication necessitates its integration with existing terrestrial networks, as highlighted in 3GPP Releases 16 and 17. This paper analyses the concept of functional splits in 3D-Networks. To manage this complex structure effectively, the adoption of a Radio Access Network (RAN) architecture with Functional Split (FS) offers advantages in flexibility, scalability, and cost-efficiency. RAN achieves this by disaggregating functionalities into three separate units. Analogous to the terrestrial network approach, 3GPP is extending this concept to non-terrestrial platforms as well. This work presents a general analysis of the requested Fronthaul (FH) data rate on feeder link between a non-terrestrial platform and the ground-station. Each split option is a trade-of between FH data rate and the respected complexity. Since flying nodes face more limitations regarding power consumption and complexity on board in comparison to terrestrial ones, we are investigating the split options between lower and higher physical layer.
Read more5/27/2024


0
Energy-efficient Functional Split in Non-terrestrial Open Radio Access Networks
S. M. Mahdi Shahabi, Xiaonan Deng, Ahmad Qidan, Taisir Elgorashi, Jaafar Elmirghani
This paper investigates the integration of Open Radio Access Network (O-RAN) within non-terrestrial networks (NTN), and optimizing the dynamic functional split between Centralized Units (CU) and Distributed Units (DU) for enhanced energy efficiency in the network. We introduce a novel framework utilizing a Deep Q-Network (DQN)-based reinforcement learning approach to dynamically find the optimal RAN functional split option and the best NTN-based RAN network out of the available NTN-platforms according to real-time conditions, traffic demands, and limited energy resources in NTN platforms. This approach supports capability of adapting to various NTN-based RANs across different platforms such as LEO satellites and high-altitude platform stations (HAPS), enabling adaptive network reconfiguration to ensure optimal service quality and energy utilization. Simulation results validate the effectiveness of our method, offering significant improvements in energy efficiency and sustainability under diverse NTN scenarios.
Read more9/4/2024

0
Shaping Radio Access to Match Variable Wireless Fronthaul Quality in Next-Generation Networks
Marcello Morini, Eugenio Moro, Ilario Filippini, Danilo De Donno, Antonio Capone
The emergence of Centralized-RAN (C-RAN) has revolutionized mobile network infrastructure, offering streamlined cell-site engineering and enhanced network management capabilities. As C-RAN gains momentum, the focus shifts to optimizing fronthaul links. While fiber fronthaul guarantees performance, wireless alternatives provide cost efficiency and scalability, making them preferable in densely urbanized areas. However, wireless fronthaul often requires expensive over-dimensioning to overcome the challenging atmospheric attenuation typical of high frequencies. We propose a framework designed to continuously align radio access capacity with fronthaul link quality to overcome this rigidity. By gradually adapting radio access capacity to available fronthaul capacity, the framework ensures smooth degradation rather than complete service loss. Various strategies are proposed, considering factors like functional split and beamforming technology and exploring the tradeoff between adaptation strategy complexity and end-to-end system performance. Numerical evaluations using experimental rain attenuation data illustrate the framework's effectiveness in optimizing radio access capacity under realistically variable fronthaul link quality, ultimately proving the importance of adaptive capacity management in maximizing C-RAN efficiency.
Read more6/26/2024