Maximization of Communication Network Throughput using Dynamic Traffic Allocation Scheme

0
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- Focuses on maximizing communication network throughput using a dynamic traffic allocation scheme
- Proposes an approach to intelligently allocate network resources to improve overall performance and quality of service (QoS)
- Aims to enhance bandwidth utilization and network throughput while maintaining QoS requirements
Plain English Explanation
In modern communication networks, effectively managing the flow of data traffic is crucial for optimizing network performance. The paper presents a dynamic traffic allocation scheme that aims to maximize the overall throughput of the communication network.
The key idea is to dynamically adjust the allocation of network resources, such as bandwidth, to different types of traffic based on their QoS requirements. This allows the network to adapt to changing traffic patterns and prioritize critical data, ultimately enhancing the overall throughput and efficiency of the communication system.
By intelligently distributing the available resources, the proposed approach helps to maximize the network's throughput while ensuring that the QoS needs of various applications and services are met. This can be particularly beneficial in scenarios where the network faces fluctuating or unpredictable traffic demands, as the dynamic allocation scheme can respond and adapt accordingly.
Technical Explanation
The paper presents a dynamic traffic allocation scheme that aims to maximize the throughput of a communication network while maintaining the required quality of service (QoS) for different types of traffic.
The proposed approach involves continuously monitoring the network's traffic patterns and dynamically adjusting the allocation of bandwidth to different traffic classes based on their QoS requirements. This allows the network to adapt to changes in traffic demands and prioritize critical data, leading to enhanced overall throughput and efficient utilization of network resources.
The researchers developed a mathematical model to represent the dynamic traffic allocation problem and formulated an optimization problem to find the optimal allocation of resources. They then designed and implemented a practical algorithm to solve this optimization problem in real-time, enabling the network to continuously adapt and optimize its performance.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a promising approach to maximizing communication network throughput through a dynamic traffic allocation scheme. However, the researchers acknowledge that the proposed method may have some limitations in handling highly volatile or unpredictable traffic patterns, which could impact the effectiveness of the dynamic allocation algorithm.
Additionally, the paper does not provide a comprehensive evaluation of the scheme's performance under various network conditions, such as different traffic loads, network topologies, or QoS requirements. Further research and experimentation may be needed to fully understand the impact of the dynamic traffic allocation approach and its applicability in diverse real-world communication network scenarios.
It would also be valuable to explore the computational complexity and scalability of the proposed algorithm, as the ability to handle large-scale networks and make real-time decisions is crucial for practical deployment.
Conclusion
The paper presents a dynamic traffic allocation scheme that aims to maximize the throughput of communication networks by intelligently distributing network resources based on QoS requirements. This approach has the potential to enhance overall network performance, improve bandwidth utilization, and ensure that critical data is prioritized, leading to better service quality for end-users.
While the proposed method shows promise, further research and evaluation are needed to fully understand its practical implications and limitations. Exploring the scheme's performance in diverse network scenarios and addressing scalability concerns could help solidify its viability for real-world deployment in modern communication networks.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Maximization of Communication Network Throughput using Dynamic Traffic Allocation Scheme
Md. Arquam, Suchi Kumari
Optimizing network throughput in real-world dynamic systems is critical, especially for diverse and delay-sensitive multimedia data types such as VoIP and video streaming. Traditional routing protocols, which rely on static metrics and single shortest-path algorithms, were unable in managing this complex information. To address these challenges, we propose a novel approach that enhances resource utilization while maintaining Quality of Service (QoS). Our dynamic traffic allocation model prioritizes different data types based on their delay sensitivity and allocates traffic by considering factors such as bandwidth, latency, and network failures. This approach is shown to significantly improve network throughput compared to static load balancing, especially for multimedia applications. Simulation results confirm the effectiveness of this dynamic method in maximizing network throughput and maintaining QoS across various data types.
Read more9/10/2024

0
Distributed Scheduling for Throughput Maximization under Deadline Constraint in Wireless Mesh Networks
Xin Wang, Xudong Wang
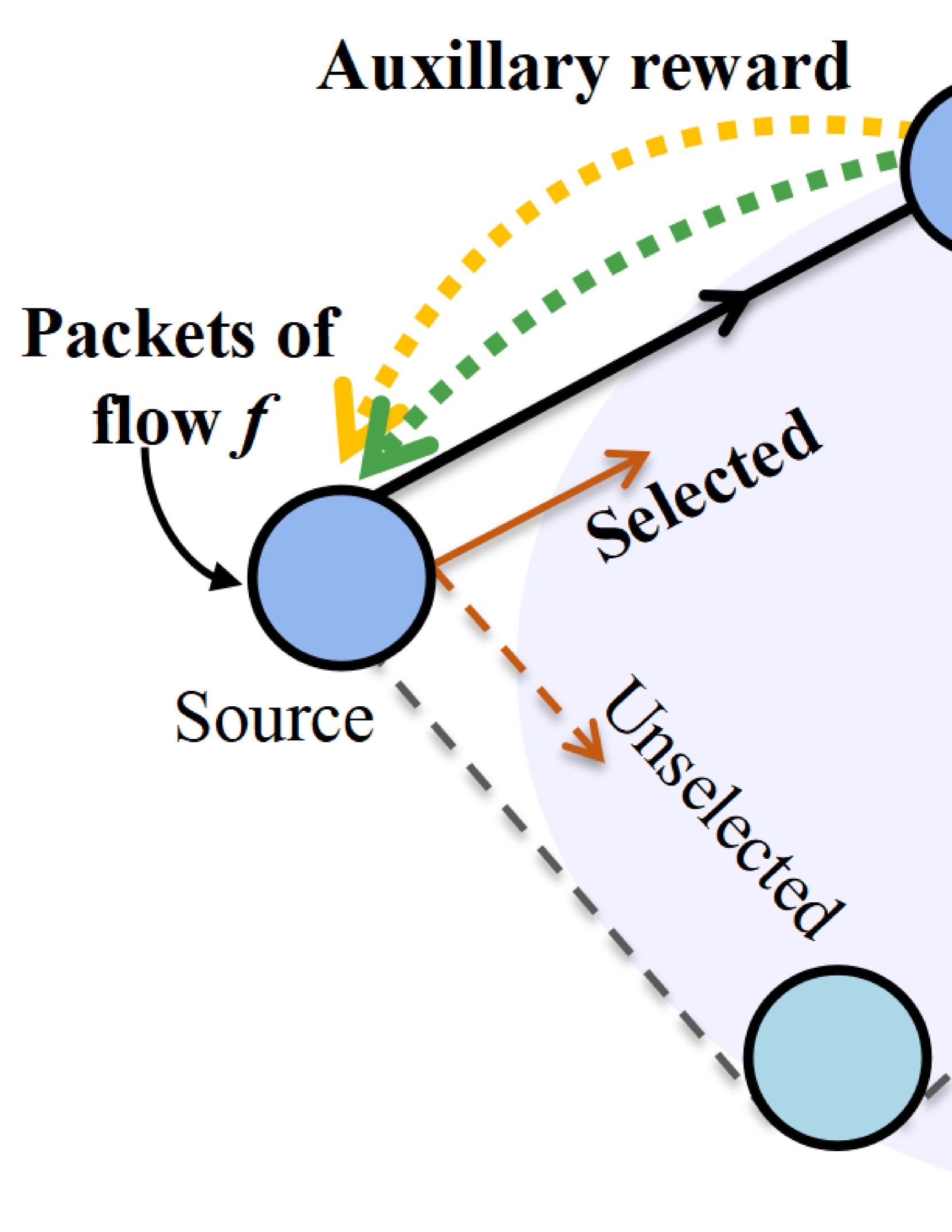
This paper studies the distributed scheduling of traffic flows with arbitrary deadlines that arrive at their source nodes and are transmitted to different destination nodes via multiple intermediate nodes in a wireless mesh network. When a flow is successfully delivered to its destination, a reward will be obtained, which is the embodiment of network performance and can be expressed by metrics such as throughput or network utility. The objective is to maximize the aggregate reward of all the deadline-constrained flows, which can be transformed into the constrained Markov decision process (CMDP). According to the transformation, a policy gradient-based distributed scheduling (PGDS) method is first proposed, where a primary reward and an auxiliary reward are designed to incentivize each node to independently schedule network resources such as power and subcarriers. The primary reward is generated when flows are successfully delivered to their destinations. The auxiliary reward, designed based on potential-based reward shaping (PBRS) using local information of data transmission, aims to accelerate the convergence speed. Inside this method, a reward feedback scheme is designed to let each node obtain the primary reward. Noting that each node selecting resources independently may cause interference and collision which leads to instability of data transmission, a policy gradient-based resource determination algorithm is proposed. Moreover, the optimality and convergence of the PGDS method are derived. Especially, when a policy obtained by the algorithm is not matched with the optimal policy but can better deal with the interference, an asymptotic optimum still exists and is further derived.
Read more7/16/2024


0
Quality of Service-Constrained Online Routing in High Throughput Satellites
Olivier B'elanger, Olfa Ben Yahia, St'ephane Martel, Antoine Lesage-Landry, Gunes Karabulut Kurt
High throughput satellites (HTSs) outpace traditional satellites due to their multi-beam transmission. The rise of low Earth orbit mega constellations amplifies HTS data rate demands to terabits/second with acceptable latency. This surge in data rate necessitates multiple modems, often exceeding single device capabilities. Consequently, satellites employ several processors, forming a complex packet-switch network. This can lead to potential internal congestion and challenges in adhering to strict quality of service (QoS) constraints. While significant research exists on constellation-level routing, a literature gap remains on the internal routing within a single HTS. The intricacy of this internal network architecture presents a significant challenge to achieve high data rates. This paper introduces an online optimal flow allocation and scheduling method for HTSs. The problem is presented as a multi-commodity flow instance with different priority data streams. An initial full time horizon model is proposed as a benchmark. We apply a model predictive control (MPC) approach to enable adaptive routing based on current information and the forecast within the prediction time horizon while allowing for deviation of the latter. Importantly, MPC is inherently suited to handle uncertainty in incoming flows. Our approach minimizes the packet loss by optimally and adaptively managing the priority queue schedulers and flow exchanges between satellite processing modules. Central to our method is a routing model focusing on optimal priority scheduling to enhance data rates and maintain QoS. The model's stages are critically evaluated, and results are compared to traditional methods via numerical simulations. Through simulations, our method demonstrates performance nearly on par with the hindsight optimum, showcasing its efficiency and adaptability in addressing satellite communication challenges.
Read more6/3/2024
🛠️

0
Dynamic Optimization of Video Streaming Quality Using Network Digital Twin Technology
Zurh Farus, Betty Searcy, Tina Nassisid, Kevin Muhammad
This paper introduces a novel dynamic optimization framework for video streaming that leverages Network Digital Twin (NDT) technology to address the challenges posed by fluctuating wireless network conditions. Traditional adaptive streaming methods often struggle with rapid changes in network bandwidth, latency, and packet loss, leading to suboptimal user experiences characterized by frequent buffering and reduced video quality. Our proposed framework integrates a sophisticated NDT that models the wireless network in real-time and employs predictive analytics to forecast near-future network states. Utilizing machine learning techniques, specifically Random Forest and Neural Networks, the NDT predicts bandwidth availability, latency trends, and potential packet losses before they impact video transmission. Based on these predictions, our adaptive streaming algorithm dynamically adjusts video bitrates, resolution, and buffering strategies, thus ensuring an uninterrupted and high-quality viewing experience. Experimental validations demonstrate that our approach significantly enhances the Quality of Experience (QoE) by reducing buffering times by up to 50% and improving resolution in varied network conditions compared to conventional streaming methods. This paper underscores the potential of integrating digital twin technology into multimedia transmission, paving the way for more resilient and user-centric video streaming solutions.
Read more7/2/2024