The Meta Distribution of the SIR in Joint Communication and Sensing Networks
2404.01672

0
0

Abstract
In this paper, we introduce a novel mathematical framework for assessing the performance of joint communication and sensing (JCAS) in wireless networks, employing stochastic geometry as an analytical tool. We focus on deriving the meta distribution of the signal-to-interference ratio (SIR) for JCAS networks. This approach enables a fine-grained quantification of individual user or radar performance intrinsic to these networks. Our work involves the modeling of JCAS networks and the derivation of mathematical expressions for the JCAS SIR meta distribution. Through simulations, we validate both our theoretical analysis and illustrate how the JCAS SIR meta distribution varies with the network deployment density.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper examines the meta distribution of the signal-to-interference ratio (SIR) in joint communication and sensing networks.
- It develops a mathematical model to analyze the performance of these networks, which are used for both wireless communication and sensing applications.
- The research provides insights into how the meta distribution of the SIR, which captures the distribution of the SIR across the network, is affected by different system parameters.
Plain English Explanation
The paper looks at a type of wireless network that is used for both communication and sensing purposes. In these networks, devices need to be able to transmit data to each other while also detecting and measuring things in their environment.
The key metric the researchers focus on is the signal-to-interference ratio (SIR). This measures how strong the desired signal is compared to any unwanted interference. The researchers develop a mathematical model to understand the distribution of SIR values across the entire network, known as the "meta distribution" of SIR.
By analyzing this meta distribution, the researchers can see how factors like the number of devices, their locations, and the frequencies they use impact the overall performance of the joint communication and sensing network. This provides insights that can help engineers design these types of networks more effectively.
Technical Explanation
The paper presents a model for the meta distribution of the signal-to-interference ratio (SIR) in a joint communication and sensing network. The network is modeled as a Poisson point process, with devices randomly distributed in space.
Each device acts as both a transmitter for communication and a sensor for monitoring the environment. The researchers derive an expression for the meta distribution of the SIR, which captures the full statistical characterization of the SIR experienced across the network.
The meta distribution is shown to depend on key system parameters, including the device density, the communication and sensing ranges, and the target SIR thresholds. The researchers analyze how changes in these parameters affect the meta distribution, providing insights into the tradeoffs involved in designing these joint networks.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a rigorous mathematical framework for analyzing the performance of joint communication and sensing networks. The meta distribution metric offers a comprehensive way to evaluate network-wide SIR performance, going beyond just looking at average or aggregate measures.
However, the analysis assumes an idealized scenario with Poisson-distributed devices and does not consider practical issues like fading, shadowing, or imperfect sensing/communication modules. Accounting for these real-world factors could introduce additional complexities that are not captured in the current model.
Additionally, the paper does not discuss potential use cases or applications for these joint networks. Understanding the specific requirements and constraints of different application domains would be important for translating the theoretical insights into practical system designs.
Further research could explore extending the model to more complex network topologies, validating the results through simulations or experiments, and investigating how the meta distribution analysis could inform the development of adaptive resource allocation algorithms.
Conclusion
This paper presents a mathematical framework for analyzing the meta distribution of the signal-to-interference ratio in joint communication and sensing networks. By capturing the full statistical characterization of SIR performance across the network, the research provides valuable insights that can inform the design of these types of versatile wireless systems.
The insights from this work could help engineers strike the right balance between communication and sensing capabilities, leading to more efficient and effective joint networks that can support a wide range of emerging applications.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
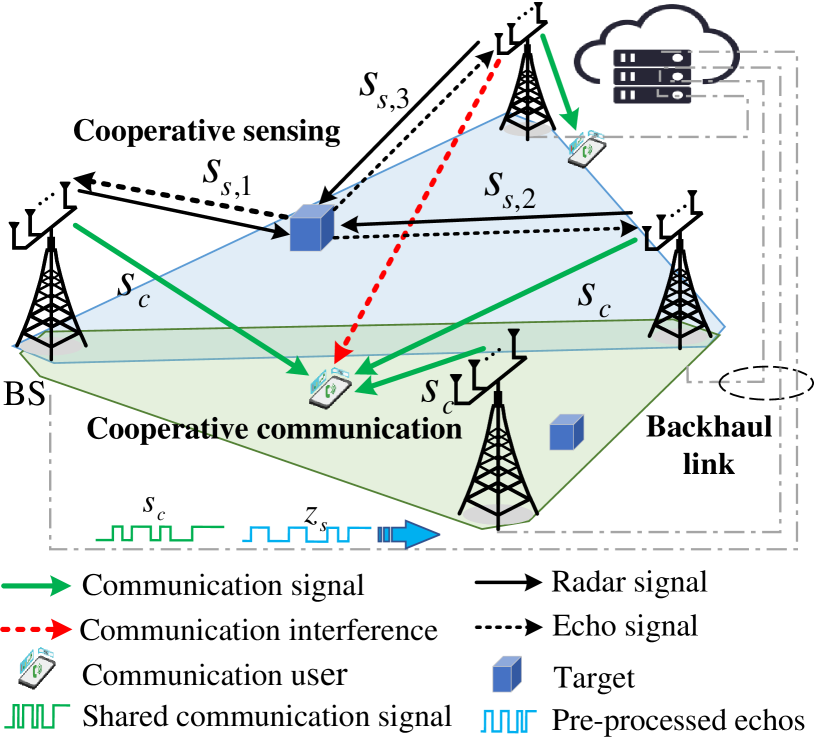
Cooperative Sensing and Communication for ISAC Networks: Performance Analysis and Optimization
Kaitao Meng, Christos Masouros

0
0
In this work, we study integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) networks intending to effectively balance sensing and communication (S&C) performance at the network level. Through the simultaneous utilization of multi-point (CoMP) coordinated joint transmission and distributed multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) radar techniques, we propose a cooperative networked ISAC scheme to enhance both S&C services. Then, the tool of stochastic geometry is exploited to capture the S&C performance, which allows us to illuminate key cooperative dependencies in the ISAC network. Remarkably, the derived expression of the Cramer-Rao lower bound (CRLB) of the localization accuracy unveils a significant finding: Deploying $N$ ISAC transceivers yields an enhanced sensing performance across the entire network, in accordance with the $ln^2N$ scaling law. Simulation results demonstrate that compared to the time-sharing scheme, the proposed cooperative ISAC scheme can effectively improve the average data rate and reduce the CRLB.
4/1/2024

Network-Level Analysis of Integrated Sensing and Communication Using Stochastic Geometry
Ruibo Wang, Baha Eddine Youcef Belmekki, Xue Zhang, Mohamed-Slim Alouini

0
0
To meet the demands of densely deploying communication and sensing devices in the next generation of wireless networks, integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) technology is employed to alleviate spectrum scarcity, while stochastic geometry (SG) serves as a tool for low-complexity performance evaluation. To assess network-level performance, there is a natural interaction between ISAC technology and the SG method. From ISAC network perspective, we illustrate how to leverage SG analytical framework to evaluate ISAC network performance by introducing point process distributions and stochastic fading channel models. From SG framework perspective, we summarize the unique performance metrics and research objectives of ISAC networks, thereby extending the scope of SG research in the field of wireless communications. Additionally, considering the limited discussion in the existing SG-based ISAC works in terms of distribution and channel modeling, a case study is designed to exploit topology and channel fading awareness to provide relevant network insights.
4/23/2024

Addressing Privacy Concerns in Joint Communication and Sensing for 6G Networks: Challenges and Prospects
Prajnamaya Dass, Sonika Ujjwal, Jiri Novotny, Yevhen Zolotavkin, Zakaria Laaroussi, Stefan Kopsell

0
0
The vision for 6G extends beyond mere communication, incorporating sensing capabilities to facilitate a diverse array of novel applications and services. However, the advent of joint communication and sensing (JCAS) technology introduces concerns regarding the handling of sensitive personally identifiable information (PII) pertaining to individuals and objects, along with external third-party data and disclosure. Consequently, JCAS-based applications are susceptible to privacy breaches, including location tracking, identity disclosure, profiling, and misuse of sensor data, raising significant implications under the European Union's general data protection regulation (GDPR) as well as other applicable standards. This paper critically examines emergent JCAS architectures and underscores the necessity for network functions to enable privacy-specific features in the 6G systems. We propose an enhanced JCAS architecture with additional network functions and interfaces, facilitating the management of sensing policies, consent information, and transparency guidelines, alongside the integration of sensing-specific functions and storage for sensing processing sessions. Furthermore, we conduct a comprehensive threat analysis for all interfaces, employing security threat model STRIDE and privacy threat model LINDDUN. We also summarise the identified threats using standard common weakness enumeration (CWE). Finally, we suggest the security and privacy controls as the mitigating strategies to counter the identified threats stemming from the JCAS architecture.
6/18/2024
✨
Joint Spectrum Partitioning and Power Allocation for Energy Efficient Semi-Integrated Sensing and Communications
Ammar Mohamed Abouelmaati, Sylvester Aboagye, Hina Tabassum

0
0
With spectrum resources becoming congested and the emergence of sensing-enabled wireless applications, conventional resource allocation methods need a revamp to support communications-only, sensing-only, and integrated sensing and communication (ISaC) services together. In this letter, we propose two joint spectrum partitioning (SP) and power allocation (PA) schemes to maximize the aggregate sensing and communication performance as well as corresponding energy efficiency (EE) of a semi-ISaC system that supports all three services in a unified manner. The proposed framework captures the priority of the distinct services, impact of target clutters, power budget and bandwidth constraints, and sensing and communication quality-of-service (QoS) requirements. We reveal that the former problem is jointly convex and the latter is a non-convex problem that can be solved optimally by exploiting fractional and parametric programming techniques. Numerical results verify the effectiveness of proposed schemes and extract novel insights related to the impact of the priority and QoS requirements of distinct services on the performance of semi-ISaC networks.
4/30/2024