Joint Spectrum Partitioning and Power Allocation for Energy Efficient Semi-Integrated Sensing and Communications

0
✨
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- As wireless communications become more congested, conventional resource allocation methods need to be updated to support different types of wireless services together, including communications-only, sensing-only, and integrated sensing and communication (ISaC).
- This paper proposes two joint spectrum partitioning (SP) and power allocation (PA) schemes to maximize the overall sensing and communication performance as well as energy efficiency (EE) in a semi-ISaC system that supports all three service types.
- The proposed framework considers the priority of the different services, impact of target clutters, power and bandwidth constraints, and quality-of-service (QoS) requirements for sensing and communication.
Plain English Explanation
As the wireless spectrum becomes more crowded, the traditional ways of allocating resources to different wireless services need to be updated. This paper proposes new methods to efficiently divide up the available spectrum and power between three types of wireless services: communications-only, sensing-only, and integrated sensing and communication (ISaC), where both sensing and communication happen together.
The key idea is to find the best way to split up the available spectrum and power to maximize the overall performance of the sensing and communication tasks, while also making the system as energy-efficient as possible. The proposed approach takes into account the priorities of the different services, the impact of things that can interfere with the sensing (called "target clutters"), and the minimum quality-of-service (QoS) requirements for both the sensing and communication tasks.
The researchers show that one of the optimization problems they formulate is a convex problem, meaning it can be solved efficiently. The other problem is more complex and non-convex, but they are able to find an optimal solution by using specialized mathematical techniques.
Technical Explanation
The paper proposes two joint spectrum partitioning (SP) and power allocation (PA) schemes to maximize the aggregate sensing and communication performance, as well as the corresponding energy efficiency (EE), of a semi-ISaC system. This system supports communications-only, sensing-only, and integrated sensing and communication (ISaC) services in a unified manner.
The proposed framework captures the priority of the distinct services, the impact of target clutters, the power budget and bandwidth constraints, and the sensing and communication quality-of-service (QoS) requirements. The researchers reveal that the former optimization problem is jointly convex, while the latter is a non-convex problem. However, they are able to solve the non-convex problem optimally by exploiting fractional and parametric programming techniques.
Numerical results validate the effectiveness of the proposed schemes and provide novel insights into the impact of the priority and QoS requirements of the distinct services on the performance of semi-ISaC networks. For example, the analysis shows how the meta-distribution of the signal-to-interference ratio in joint communication-sensing networks is affected by the resource allocation strategies.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a comprehensive framework for optimizing the resource allocation in semi-ISaC networks, taking into account the different service priorities and QoS requirements. However, the analysis is limited to a single-cell scenario, and the extension to a multi-cell setting may introduce additional challenges.
Additionally, the paper does not consider the practical challenges of implementing the proposed schemes, such as the need for accurate channel state information and the overhead associated with coordinating the resource allocation between the sensing and communication functionalities.
Further research could explore the robustness of the proposed schemes to imperfect channel information or the integration of machine learning techniques to enhance the resource allocation process. Investigating the network-level performance and scalability of the semi-ISaC architecture would also be a valuable direction for future work.
Conclusion
This paper presents a novel framework for joint spectrum partitioning and power allocation in semi-ISaC wireless networks, which support communications-only, sensing-only, and integrated sensing and communication services. The proposed schemes are designed to maximize the aggregate sensing and communication performance, as well as the energy efficiency of the system, while considering the priority and QoS requirements of the different services.
The results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach and provide valuable insights into the impact of service prioritization on the performance of semi-ISaC networks. As wireless communications continue to evolve, this research represents an important step towards developing efficient resource management strategies for emerging integrated sensing and communication applications.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
✨

0
Joint Spectrum Partitioning and Power Allocation for Energy Efficient Semi-Integrated Sensing and Communications
Ammar Mohamed Abouelmaati, Sylvester Aboagye, Hina Tabassum
With spectrum resources becoming congested and the emergence of sensing-enabled wireless applications, conventional resource allocation methods need a revamp to support communications-only, sensing-only, and integrated sensing and communication (ISaC) services together. In this letter, we propose two joint spectrum partitioning (SP) and power allocation (PA) schemes to maximize the aggregate sensing and communication performance as well as corresponding energy efficiency (EE) of a semi-ISaC system that supports all three services in a unified manner. The proposed framework captures the priority of the distinct services, impact of target clutters, power budget and bandwidth constraints, and sensing and communication quality-of-service (QoS) requirements. We reveal that the former problem is jointly convex and the latter is a non-convex problem that can be solved optimally by exploiting fractional and parametric programming techniques. Numerical results verify the effectiveness of proposed schemes and extract novel insights related to the impact of the priority and QoS requirements of distinct services on the performance of semi-ISaC networks.
Read more4/30/2024

0
Economics of Integrated Sensing and Communication service provision in 6G networks
Luis Guijarro, Maurizio Naldi, Vicent Pla, Jose-Ramon Vidal
In Beyond5G and 6G networks, a common theme is that sensing will play a more significant role than ever before. Over this trend, Integrated Sensing and Communications (ISAC) is focused on unifying the sensing functionalities and the communications ones and to pursue direct tradeoffs between them as well as mutual performance gains. We frame the resource tradeoff between the SAC functionalities within an economic setting. We model a service provision by one operator to the users, the utility of which is derived from both SAC functionalities. The tradeoff between the resources that the operator assigns to the SAC functionalities is analyzed from the point of view of the service prices, quantities and profits. We demonstrate that equilibrium quantities and prices exist. And we provide relevant recommendations for enforcing regulatory limits of both power and bandwidth.
Read more5/17/2024

0
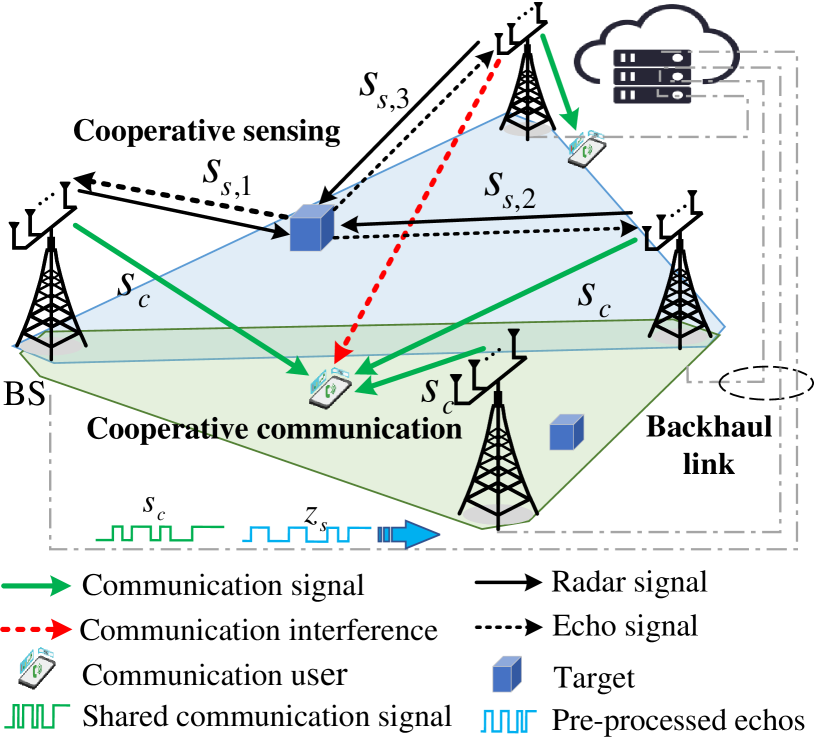
Cooperative Sensing and Communication for ISAC Networks: Performance Analysis and Optimization
Kaitao Meng, Christos Masouros
In this work, we study integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) networks intending to effectively balance sensing and communication (S&C) performance at the network level. Through the simultaneous utilization of multi-point (CoMP) coordinated joint transmission and distributed multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) radar techniques, we propose a cooperative networked ISAC scheme to enhance both S&C services. Then, the tool of stochastic geometry is exploited to capture the S&C performance, which allows us to illuminate key cooperative dependencies in the ISAC network. Remarkably, the derived expression of the Cramer-Rao lower bound (CRLB) of the localization accuracy unveils a significant finding: Deploying $N$ ISAC transceivers yields an enhanced sensing performance across the entire network, in accordance with the $ln^2N$ scaling law. Simulation results demonstrate that compared to the time-sharing scheme, the proposed cooperative ISAC scheme can effectively improve the average data rate and reduce the CRLB.
Read more4/1/2024

0
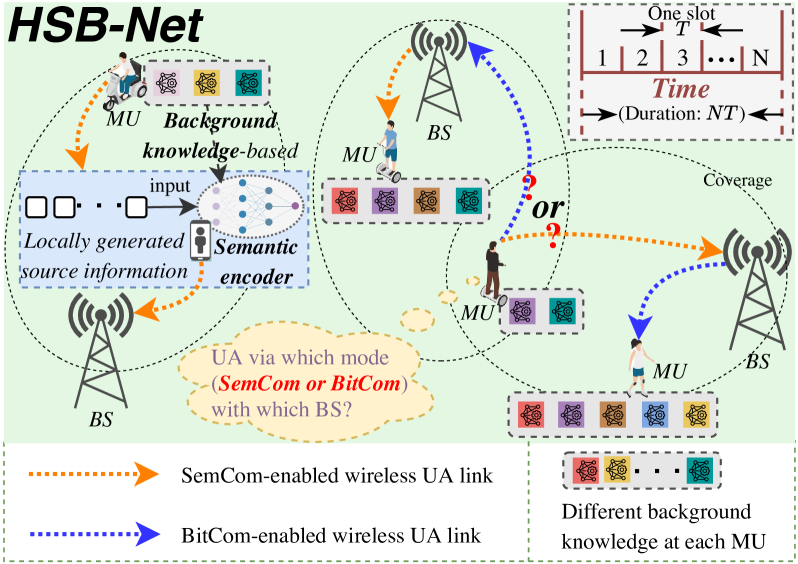
Wireless Resource Optimization in Hybrid Semantic/Bit Communication Networks
Le Xia, Yao Sun, Dusit Niyato, Lan Zhang, Muhammad Ali Imran
Recently, semantic communication (SemCom) has shown great potential in significant resource savings and efficient information exchanges, thus naturally introducing a novel and practical cellular network paradigm where two modes of SemCom and conventional bit communication (BitCom) coexist. Nevertheless, the involved wireless resource management becomes rather complicated and challenging, given the unique background knowledge matching and time-consuming semantic coding requirements in SemCom. To this end, this paper jointly investigates user association (UA), mode selection (MS), and bandwidth allocation (BA) problems in a hybrid semantic/bit communication network (HSB-Net). Concretely, we first identify a unified performance metric of message throughput for both SemCom and BitCom links. Next, we specially develop a knowledge matching-aware two-stage tandem packet queuing model and theoretically derive the average packet loss ratio and queuing latency. Combined with practical constraints, we then formulate a joint optimization problem for UA, MS, and BA to maximize the overall message throughput of HSB-Net. Afterward, we propose an optimal resource management strategy by utilizing a Lagrange primal-dual transformation method and a preference list-based heuristic algorithm with polynomial-time complexity. Numerical results not only demonstrate the accuracy of our analytical queuing model, but also validate the performance superiority of our proposed strategy compared with different benchmarks.
Read more8/21/2024