Middle Fusion and Multi-Stage, Multi-Form Prompts for Robust RGB-T Tracking

0
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- This paper proposes a novel RGB-T (RGB and Thermal) tracking approach called "Middle Fusion and Multi-Stage, Multi-Form Prompts for Robust RGB-T Tracking".
- The key ideas are to use a middle fusion strategy that combines RGB and thermal features at an intermediate stage, and to leverage multi-stage and multi-form prompts to improve the tracking performance.
- The proposed method is evaluated on several RGB-T tracking benchmarks and shows superior performance compared to existing approaches.
Plain English Explanation
The paper describes a new way to track objects using both color (RGB) and heat (thermal) cameras. Tracking objects is an important task in computer vision, with applications in surveillance, robotics, and self-driving cars. Combining information from RGB and thermal cameras can improve tracking accuracy, as the thermal camera can detect objects that are hard to see in regular color images.
The researchers developed a middle fusion and multi-stage, multi-form prompts for robust RGB-T tracking. The "middle fusion" means they combine the features from the RGB and thermal cameras at an intermediate stage of the tracking algorithm, rather than at the beginning or end. This allows the algorithm to take advantage of information from both modalities.
The "multi-stage, multi-form prompts" refer to using multiple steps and input formats to guide the tracking process. The algorithm generates "prompts" or hints about the object's location and appearance, and uses these in different ways across multiple stages of processing. This helps the tracker be more robust to changes in the object's appearance or the environment.
The researchers tested their method on several benchmark datasets for RGB-T tracking, and found it outperformed existing approaches. This suggests their technique is a promising way to improve object tracking using both color and thermal cameras.
Technical Explanation
The paper proposes a novel RGB-T tracking approach called "Middle Fusion and Multi-Stage, Multi-Form Prompts for Robust RGB-T Tracking". The key contributions are:
-
Middle Fusion: The method uses a middle fusion strategy to combine RGB and thermal features at an intermediate stage of the tracking pipeline, rather than early or late fusion approaches. This allows the model to better leverage the complementary information from the two modalities.
-
Multi-Stage, Multi-Form Prompts: The tracker employs a multi-stage processing pipeline, where each stage generates and uses "prompts" or guiding signals about the target's location and appearance. These prompts can take different forms, such as bounding boxes, segmentation masks, or keypoints, and are used in different ways across the stages to improve robustness.
-
Robust RGB-T Tracking: The proposed method is evaluated on several RGB-T tracking benchmarks, including Revisiting RGBT Tracking Benchmarks: From Perspective of Modality, Transformer-based RGB-T Tracking: Channel-Spatial Interaction Matters, and Multi-Prompt Depth-Partitioned Cross-Modal Learning. The results demonstrate that the method outperforms existing state-of-the-art RGB-T trackers.
The paper first reviews related work on RGB-T tracking, including From Two-Stream to One-Stream: Efficient RGB-T Tracking with Channel and Spatial Interactions and TENET: Targetness Entanglement Incorporating Multi-Scale Pooling. It then presents the details of the proposed Middle Fusion and Multi-Stage, Multi-Form Prompts approach.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a well-designed and thorough evaluation of the proposed RGB-T tracking method. The authors explore multiple benchmark datasets and compare their approach to state-of-the-art techniques, demonstrating its superior performance.
One potential limitation is that the method may be computationally more expensive than simpler fusion approaches, due to the multi-stage processing and generation of multiple prompts. The paper does not provide detailed runtime or efficiency analysis, which would be helpful for understanding the practical applicability of the method.
Additionally, the paper does not discuss potential biases or failure cases of the proposed tracker. It would be valuable to understand in which scenarios the method may struggle, and how it could be further improved to address these limitations.
Overall, the paper makes a compelling case for the effectiveness of middle fusion and multi-stage, multi-form prompts for RGB-T tracking. The technical details and experimental results suggest this is a promising direction for further research and development in this area.
Conclusion
This paper presents a novel RGB-T tracking approach called "Middle Fusion and Multi-Stage, Multi-Form Prompts for Robust RGB-T Tracking". The key ideas are to use a middle fusion strategy to combine RGB and thermal features, and to leverage multi-stage and multi-form prompts to improve tracking performance.
The proposed method is shown to outperform existing state-of-the-art RGB-T trackers on several benchmark datasets. This suggests the technique is a promising way to improve object tracking by effectively combining information from color and thermal cameras.
The paper makes a meaningful contribution to the field of RGB-T tracking, and the insights and techniques it presents could inspire further advancements in this important computer vision problem.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers

0
Middle Fusion and Multi-Stage, Multi-Form Prompts for Robust RGB-T Tracking
Qiming Wang, Yongqiang Bai, Hongxing Song
RGB-T tracking, a vital downstream task of object tracking, has made remarkable progress in recent years. Yet, it remains hindered by two major challenges: 1) the trade-off between performance and efficiency; 2) the scarcity of training data. To address the latter challenge, some recent methods employ prompts to fine-tune pre-trained RGB tracking models and leverage upstream knowledge in a parameter-efficient manner. However, these methods inadequately explore modality-independent patterns and disregard the dynamic reliability of different modalities in open scenarios. We propose M3PT, a novel RGB-T prompt tracking method that leverages middle fusion and multi-modal and multi-stage visual prompts to overcome these challenges. We pioneer the use of the adjustable middle fusion meta-framework for RGB-T tracking, which could help the tracker balance the performance with efficiency, to meet various demands of application. Furthermore, based on the meta-framework, we utilize multiple flexible prompt strategies to adapt the pre-trained model to comprehensive exploration of uni-modal patterns and improved modeling of fusion-modal features in diverse modality-priority scenarios, harnessing the potential of prompt learning in RGB-T tracking. Evaluating on 6 existing challenging benchmarks, our method surpasses previous state-of-the-art prompt fine-tuning methods while maintaining great competitiveness against excellent full-parameter fine-tuning methods, with only 0.34M fine-tuned parameters.
Read more5/13/2024
🔮

0
From Two-Stream to One-Stream: Efficient RGB-T Tracking via Mutual Prompt Learning and Knowledge Distillation
Yang Luo, Xiqing Guo, Hao Li
Due to the complementary nature of visible light and thermal infrared modalities, object tracking based on the fusion of visible light images and thermal images (referred to as RGB-T tracking) has received increasing attention from researchers in recent years. How to achieve more comprehensive fusion of information from the two modalities at a lower cost has been an issue that researchers have been exploring. Inspired by visual prompt learning, we designed a novel two-stream RGB-T tracking architecture based on cross-modal mutual prompt learning, and used this model as a teacher to guide a one-stream student model for rapid learning through knowledge distillation techniques. Extensive experiments have shown that, compared to similar RGB-T trackers, our designed teacher model achieved the highest precision rate, while the student model, with comparable precision rate to the teacher model, realized an inference speed more than three times faster than the teacher model.(Codes will be available if accepted.)
Read more4/9/2024

0
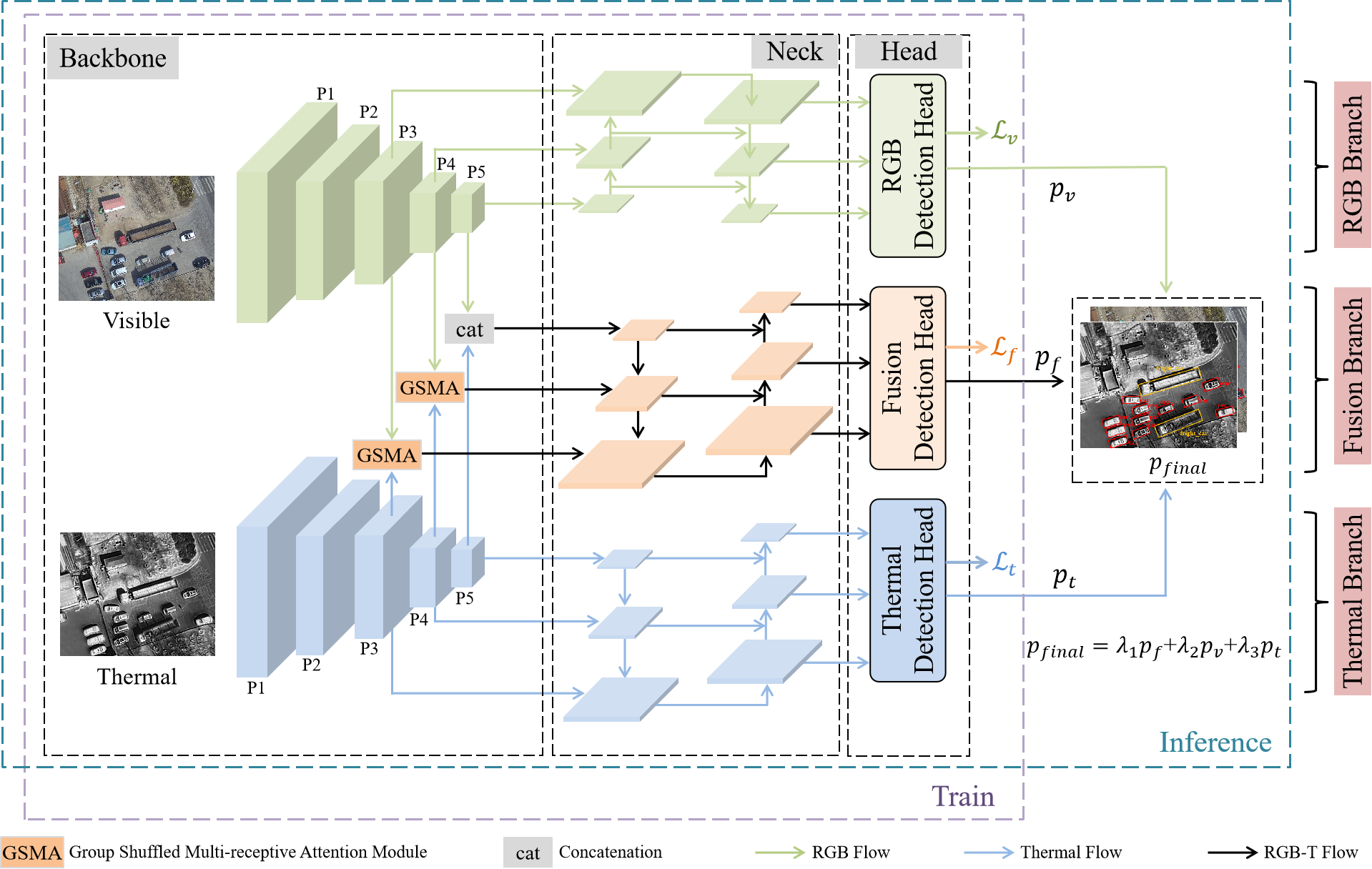
RGB-T Object Detection via Group Shuffled Multi-receptive Attention and Multi-modal Supervision
Jinzhong Wang, Xuetao Tian, Shun Dai, Tao Zhuo, Haorui Zeng, Hongjuan Liu, Jiaqi Liu, Xiuwei Zhang, Yanning Zhang
Multispectral object detection, utilizing both visible (RGB) and thermal infrared (T) modals, has garnered significant attention for its robust performance across diverse weather and lighting conditions. However, effectively exploiting the complementarity between RGB-T modals while maintaining efficiency remains a critical challenge. In this paper, a very simple Group Shuffled Multi-receptive Attention (GSMA) module is proposed to extract and combine multi-scale RGB and thermal features. Then, the extracted multi-modal features are directly integrated with a multi-level path aggregation neck, which significantly improves the fusion effect and efficiency. Meanwhile, multi-modal object detection often adopts union annotations for both modals. This kind of supervision is not sufficient and unfair, since objects observed in one modal may not be seen in the other modal. To solve this issue, Multi-modal Supervision (MS) is proposed to sufficiently supervise RGB-T object detection. Comprehensive experiments on two challenging benchmarks, KAIST and DroneVehicle, demonstrate the proposed model achieves the state-of-the-art accuracy while maintaining competitive efficiency.
Read more5/30/2024


0
Cross Fusion RGB-T Tracking with Bi-directional Adapter
Zhirong Zeng, Xiaotao Liu, Meng Sun, Hongyu Wang, Jing Liu
Many state-of-the-art RGB-T trackers have achieved remarkable results through modality fusion. However, these trackers often either overlook temporal information or fail to fully utilize it, resulting in an ineffective balance between multi-modal and temporal information. To address this issue, we propose a novel Cross Fusion RGB-T Tracking architecture (CFBT) that ensures the full participation of multiple modalities in tracking while dynamically fusing temporal information. The effectiveness of CFBT relies on three newly designed cross spatio-temporal information fusion modules: Cross Spatio-Temporal Augmentation Fusion (CSTAF), Cross Spatio-Temporal Complementarity Fusion (CSTCF), and Dual-Stream Spatio-Temporal Adapter (DSTA). CSTAF employs a cross-attention mechanism to enhance the feature representation of the template comprehensively. CSTCF utilizes complementary information between different branches to enhance target features and suppress background features. DSTA adopts the adapter concept to adaptively fuse complementary information from multiple branches within the transformer layer, using the RGB modality as a medium. These ingenious fusions of multiple perspectives introduce only less than 0.3% of the total modal parameters, but they indeed enable an efficient balance between multi-modal and temporal information. Extensive experiments on three popular RGB-T tracking benchmarks demonstrate that our method achieves new state-of-the-art performance.
Read more9/2/2024