MRI Optimized Reconstruction of Simultaneous Multi-Slice Imaging Using Diffusion Model

0
📈
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- Diffusion models have been successfully used to reconstruct MRI data, including single and multi-coil acquisition.
- Simultaneous multi-slice imaging (SMS) can significantly reduce MRI scan time, but there is room for further optimization.
- This paper proposes a method to use diffusion models for SMS reconstruction, based on the slice-GRAPPA and SPIRiT techniques.
Plain English Explanation
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique that uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of the body. Diffusion models are a type of machine learning model that have been shown to be effective at reconstructing MRI data, even when the data is collected using multiple receiver coils.
Simultaneous multi-slice imaging (SMS) is a method that can significantly reduce the time it takes to collect MRI data by acquiring multiple slices of the body at the same time. This can save patients a lot of time during their MRI scans. However, the reconstruction of SMS data can be challenging and there is room for improvement.
In this paper, the researchers propose a new method that uses diffusion models to optimize the reconstruction of SMS MRI data. Their approach characterizes the prior distribution of the SMS data and the redundant information between the different coils and slices. By using this diffusion model-based approach, they were able to achieve better reconstruction results compared to other methods.
The key advantage of this approach is that it can further reduce the time required for MRI scans without compromising image quality, making it more suitable for clinical use.
Technical Explanation
The researchers' method for optimizing SMS reconstruction using diffusion models involves two main components:
-
Characterizing the prior distribution of SMS data: The researchers used a technique called "score matching" to model the underlying statistical distribution of the SMS data. This allows the diffusion model to better capture the structure and patterns in the data.
-
Characterizing the k-space redundancy between coils and slices: The researchers also modeled the redundant information between the different receiver coils and slices of the SMS data. They did this using the SPIRiT method, which enforces self-consistency in the k-space data.
By incorporating these two components, the researchers were able to develop a diffusion model-based approach that outperformed other reconstruction methods for SMS MRI data. The diffusion model was able to better capture the underlying structure of the SMS data and leverage the redundant information across coils and slices.
Critical Analysis
The researchers acknowledge that further optimization of the reconstruction results is still possible. They also note that their method relies on accurately modeling the prior distribution and k-space redundancy, which could be challenging in some cases.
Additionally, while the proposed method demonstrates improvements in reconstruction quality, the researchers do not provide a comprehensive comparison to other state-of-the-art SMS reconstruction techniques. It would be helpful to see how their approach performs relative to the latest developments in this area.
Overall, the researchers have made a valuable contribution by demonstrating the potential of diffusion models for optimizing SMS MRI reconstruction. However, there is still room for further research and refinement to fully unlock the benefits of this approach in a clinical setting.
Conclusion
This paper presents a novel method for using diffusion models to optimize the reconstruction of simultaneous multi-slice (SMS) MRI data. By characterizing the prior distribution of the SMS data and the redundant information between coils and slices, the researchers were able to achieve better reconstruction results compared to other techniques.
The key advantage of this approach is that it can further reduce the scanning time required for MRI exams without compromising image quality, making it more suitable for clinical applications. This could have a significant impact on patient experience and the efficiency of healthcare delivery.
While the researchers acknowledge that there is still room for improvement, this work represents an important step forward in the application of diffusion models to accelerate MRI acquisition and reconstruction.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
📈

0
MRI Optimized Reconstruction of Simultaneous Multi-Slice Imaging Using Diffusion Model
Ting Zhao, Zhuoxu Cui, Sen Jia, Qingyong Zhu, Congcong Liu, Yihang Zhou, Yanjie Zhu, Dong Liang, Haifeng Wang
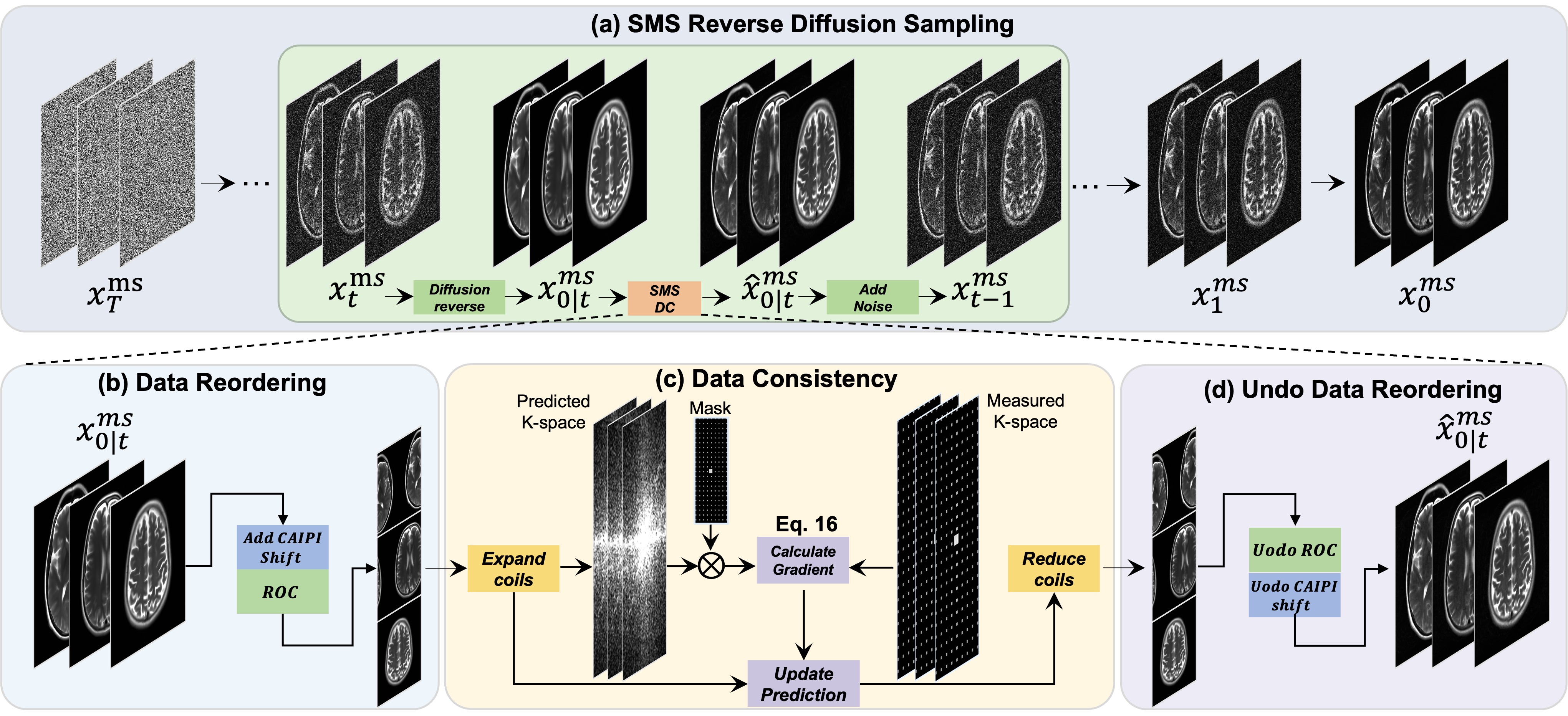
Diffusion model has been successfully applied to MRI reconstruction, including single and multi-coil acquisition of MRI data. Simultaneous multi-slice imaging (SMS), as a method for accelerating MR acquisition, can significantly reduce scanning time, but further optimization of reconstruction results is still possible. In order to optimize the reconstruction of SMS, we proposed a method to use diffusion model based on slice-GRAPPA and SPIRiT method. approach: Specifically, our method characterizes the prior distribution of SMS data by score matching and characterizes the k-space redundant prior between coils and slices based on self-consistency. With the utilization of diffusion model, we achieved better reconstruction results.The application of diffusion model can further reduce the scanning time of MRI without compromising image quality, making it more advantageous for clinical application
Read more8/22/2024

0
Robust Simultaneous Multislice MRI Reconstruction Using Deep Generative Priors
Shoujin Huang, Guanxiong Luo, Yuwan Wang, Kexin Yang, Lingyan Zhang, Jingzhe Liu, Hua Guo, Min Wang, Mengye Lyu
Simultaneous multislice (SMS) imaging is a powerful technique for accelerating magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) acquisitions. However, SMS reconstruction remains challenging due to the complex signal interactions between and within the excited slices. This study presents a robust SMS MRI reconstruction method using deep generative priors. Starting from Gaussian noise, we leverage denoising diffusion probabilistic models (DDPM) to gradually recover the individual slices through reverse diffusion iterations while imposing data consistency from the measured k-space under readout concatenation framework. The posterior sampling procedure is designed such that the DDPM training can be performed on single-slice images without special adjustments for SMS tasks. Additionally, our method integrates a low-frequency enhancement (LFE) module to address a practical issue that SMS-accelerated fast spin echo (FSE) and echo-planar imaging (EPI) sequences cannot easily embed autocalibration signals. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach consistently outperforms existing methods and generalizes well to unseen datasets. The code is available at https://github.com/Solor-pikachu/ROGER after the review process.
Read more8/1/2024
📈

0
SPIRiT-Diffusion: Self-Consistency Driven Diffusion Model for Accelerated MRI
Zhuo-Xu Cui, Chentao Cao, Yue Wang, Sen Jia, Jing Cheng, Xin Liu, Hairong Zheng, Dong Liang, Yanjie Zhu
Diffusion models have emerged as a leading methodology for image generation and have proven successful in the realm of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) reconstruction. However, existing reconstruction methods based on diffusion models are primarily formulated in the image domain, making the reconstruction quality susceptible to inaccuracies in coil sensitivity maps (CSMs). k-space interpolation methods can effectively address this issue but conventional diffusion models are not readily applicable in k-space interpolation. To overcome this challenge, we introduce a novel approach called SPIRiT-Diffusion, which is a diffusion model for k-space interpolation inspired by the iterative self-consistent SPIRiT method. Specifically, we utilize the iterative solver of the self-consistent term (i.e., k-space physical prior) in SPIRiT to formulate a novel stochastic differential equation (SDE) governing the diffusion process. Subsequently, k-space data can be interpolated by executing the diffusion process. This innovative approach highlights the optimization model's role in designing the SDE in diffusion models, enabling the diffusion process to align closely with the physics inherent in the optimization model, a concept referred to as model-driven diffusion. We evaluated the proposed SPIRiT-Diffusion method using a 3D joint intracranial and carotid vessel wall imaging dataset. The results convincingly demonstrate its superiority over image-domain reconstruction methods, achieving high reconstruction quality even at a substantial acceleration rate of 10.
Read more4/23/2024
📉

0
Simultaneous Multi-Slice Diffusion Imaging using Navigator-free Multishot Spiral Acquisition
Yuancheng Jiang, Guangqi Li, Xin Shao, Hua Guo
Purpose: This work aims to raise a novel design for navigator-free multiband (MB) multishot uniform-density spiral (UDS) acquisition and reconstruction, and to demonstrate its utility for high-efficiency, high-resolution diffusion imaging. Theory and Methods: Our design focuses on the acquisition and reconstruction of navigator-free MB multishot UDS diffusion imaging. For acquisition, radiofrequency (RF) pulse encoding was employed to achieve Controlled Aliasing in Parallel Imaging (CAIPI) in MB imaging. For reconstruction, a new algorithm named slice-POCS-enhanced Inherent Correction of phase Errors (slice-POCS-ICE) was proposed to simultaneously estimate diffusion-weighted images and inter-shot phase variations for each slice. The efficacy of the proposed methods was evaluated in both numerical simulation and in vivo experiments. Results: In both numerical simulation and in vivo experiments, slice-POCS-ICE estimated phase variations more precisely and provided results with better image quality than other methods. The inter-shot phase variations and MB slice aliasing artifacts were simultaneously resolved using the proposed slice-POCS-ICE algorithm. Conclusion: The proposed navigator-free MB multishot UDS acquisition and reconstruction method is an effective solution for high-efficiency, high-resolution diffusion imaging.
Read more7/31/2024