MTDNS: Moving Target Defense for Resilient DNS Infrastructure

0
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- This paper presents MTDNS, a Moving Target Defense (MTD) system for improving the resilience of Domain Name System (DNS) infrastructure.
- MTDNS uses Software-Defined Networking (SDN) and Network Function Virtualization (NFV) to dynamically change the mapping between domain names and IP addresses, making it harder for attackers to target DNS servers.
- The key idea is to frequently update the location and configuration of DNS servers to create a "moving target" that is difficult for attackers to pinpoint and disrupt.
Plain English Explanation
MTDNS: Moving Target Defense for Resilient DNS Infrastructure is a system that aims to make the Domain Name System (DNS) more resilient to attacks. DNS is the system that translates human-readable domain names (like "example.com") into the numerical IP addresses that computers use to communicate.
The researchers realized that DNS is a critical piece of internet infrastructure, but it can be vulnerable to Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks that try to overwhelm and disrupt DNS servers. To address this, they developed MTDNS, which uses cutting-edge networking technologies like Software-Defined Networking (SDN) and Network Function Virtualization (NFV) to constantly change, or "move," the location and configuration of DNS servers.
The key insight is that if DNS servers are always moving around and changing, it becomes much harder for attackers to target and disrupt them. It's like playing a game of "whack-a-mole" where the targets keep popping up in new locations. This "moving target defense" approach makes the DNS infrastructure more resilient and less vulnerable to large-scale attacks.
Technical Explanation
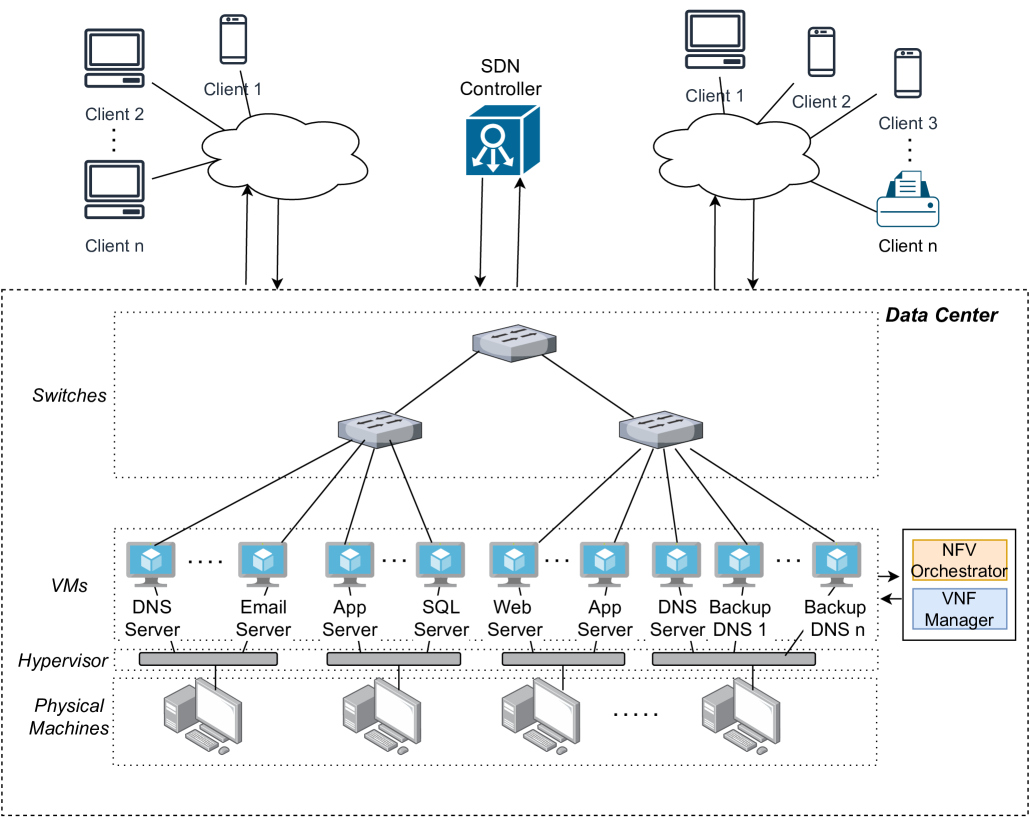
MTDNS leverages SDN and NFV to dynamically update the mapping between domain names and IP addresses, creating a "moving target" that is difficult for attackers to track and disrupt.
The architecture includes several components:
- SDN controller: Manages the network and dynamically updates routing rules to change the location of DNS servers.
- NFV orchestrator: Provisions and configures virtual DNS servers as needed to create the "moving target."
- Monitoring module: Detects potential attacks and triggers adjustments to the DNS infrastructure.
The key innovation is the ability to frequently update the DNS server mappings without disrupting normal operations. This is achieved by decoupling the DNS update timing from the traditional Time-To-Live (TTL) values, allowing for rapid changes.
The paper presents experiments comparing MTDNS to a static DNS setup, demonstrating its effectiveness in mitigating DDoS attacks and maintaining service availability. The results show that MTDNS can significantly improve the resilience of the DNS infrastructure.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a comprehensive and technically sound approach to improving DNS resilience using MTD techniques. The authors have addressed important practical considerations, such as minimizing disruption to normal DNS operations during the updates.
However, the paper does not explicitly discuss the potential performance overhead or latency implications of the frequent DNS server changes. This could be an important consideration, as users expect fast and reliable DNS lookups.
Additionally, the paper does not explore the potential security implications or vulnerabilities that might arise from the dynamic DNS infrastructure. For example, if the attacker can predict or influence the DNS server changes, they may still be able to target the system effectively.
Further research could investigate these aspects in more depth, as well as explore the scalability and deployability of the MTDNS approach in large-scale, real-world DNS environments.
Conclusion
MTDNS presents a promising approach to improving the resilience of DNS infrastructure by leveraging SDN and NFV to create a "moving target" that is difficult for attackers to disrupt. The dynamic updates to DNS server locations and configurations make it harder for large-scale DDoS attacks to succeed.
This research highlights the potential of MTD techniques to enhance the security and reliability of critical internet infrastructure. As DNS continues to play a crucial role in the modern web, solutions like MTDNS may become increasingly important for maintaining a stable and resilient online ecosystem.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
New!MTDNS: Moving Target Defense for Resilient DNS Infrastructure
Abdullah Aydeger, Pei Zhou, Sanzida Hoque, Marco Carvalho, Engin Zeydan
One of the most critical components of the Internet that an attacker could exploit is the DNS (Domain Name System) protocol and infrastructure. Researchers have been constantly developing methods to detect and defend against the attacks against DNS, specifically DNS flooding attacks. However, most solutions discard packets for defensive approaches, which can cause legitimate packets to be dropped, making them highly dependable on detection strategies. In this paper, we propose MTDNS, a resilient MTD-based approach that employs Moving Target Defense techniques through Software Defined Networking (SDN) switches to redirect traffic to alternate DNS servers that are dynamically created and run under the Network Function Virtualization (NFV) framework. The proposed approach is implemented in a testbed environment by running our DNS servers as separate Virtual Network Functions, NFV Manager, SDN switches, and an SDN Controller. The experimental result shows that the MTDNS approach achieves a much higher success rate in resolving DNS queries and significantly reduces average latency even if there is a DNS flooding attack.
Read more10/4/2024


0
MTDSense: AI-Based Fingerprinting of Moving Target Defense Techniques in Software-Defined Networking
Tina Moghaddam, Guowei Yang, Chandra Thapa, Seyit Camtepe, Dan Dongseong Kim
Moving target defenses (MTD) are proactive security techniques that enhance network security by confusing the attacker and limiting their attack window. MTDs have been shown to have significant benefits when evaluated against traditional network attacks, most of which are automated and untargeted. However, little has been done to address an attacker who is aware the network uses an MTD. In this work, we propose a novel approach named MTDSense, which can determine when the MTD has been triggered using the footprints the MTD operation leaves in the network traffic. MTDSense uses unsupervised clustering to identify traffic following an MTD trigger and extract the MTD interval. An attacker can use this information to maximize their attack window and tailor their attacks, which has been shown to significantly reduce the effectiveness of MTD. Through analyzing the attacker's approach, we propose and evaluate two new MTD update algorithms that aim to reduce the information leaked into the network by the MTD. We present an extensive experimental evaluation by creating, to our knowledge, the first dataset of the operation of an IP-shuffling MTD in a software-defined network. Our work reveals that despite previous results showing the effectiveness of MTD as a defense, traditional implementations of MTD are highly susceptible to a targeted attacker.
Read more8/9/2024

0
New!Leveraging MTD to Mitigate Poisoning Attacks in Decentralized FL with Non-IID Data
Chao Feng, Alberto Huertas Celdr'an, Zien Zeng, Zi Ye, Jan von der Assen, Gerome Bovet, Burkhard Stiller
Decentralized Federated Learning (DFL), a paradigm for managing big data in a privacy-preserved manner, is still vulnerable to poisoning attacks where malicious clients tamper with data or models. Current defense methods often assume Independently and Identically Distributed (IID) data, which is unrealistic in real-world applications. In non-IID contexts, existing defensive strategies face challenges in distinguishing between models that have been compromised and those that have been trained on heterogeneous data distributions, leading to diminished efficacy. In response, this paper proposes a framework that employs the Moving Target Defense (MTD) approach to bolster the robustness of DFL models. By continuously modifying the attack surface of the DFL system, this framework aims to mitigate poisoning attacks effectively. The proposed MTD framework includes both proactive and reactive modes, utilizing a reputation system that combines metrics of model similarity and loss, alongside various defensive techniques. Comprehensive experimental evaluations indicate that the MTD-based mechanism significantly mitigates a range of poisoning attack types across multiple datasets with different topologies.
Read more10/3/2024


0
A Factored MDP Approach To Moving Target Defense With Dynamic Threat Modeling and Cost Efficiency
Megha Bose, Praveen Paruchuri, Akshat Kumar
Moving Target Defense (MTD) has emerged as a proactive and dynamic framework to counteract evolving cyber threats. Traditional MTD approaches often rely on assumptions about the attackers knowledge and behavior. However, real-world scenarios are inherently more complex, with adaptive attackers and limited prior knowledge of their payoffs and intentions. This paper introduces a novel approach to MTD using a Markov Decision Process (MDP) model that does not rely on predefined attacker payoffs. Our framework integrates the attackers real-time responses into the defenders MDP using a dynamic Bayesian Network. By employing a factored MDP model, we provide a comprehensive and realistic system representation. We also incorporate incremental updates to an attack response predictor as new data emerges. This ensures an adaptive and robust defense mechanism. Additionally, we consider the costs of switching configurations in MTD, integrating them into the reward structure to balance execution and defense costs. We first highlight the challenges of the problem through a theoretical negative result on regret. However, empirical evaluations demonstrate the frameworks effectiveness in scenarios marked by high uncertainty and dynamically changing attack landscapes.
Read more8/20/2024