MTVQA: Benchmarking Multilingual Text-Centric Visual Question Answering
2405.11985

0
0

Abstract
Text-Centric Visual Question Answering (TEC-VQA) in its proper format not only facilitates human-machine interaction in text-centric visual environments but also serves as a de facto gold proxy to evaluate AI models in the domain of text-centric scene understanding. Nonetheless, most existing TEC-VQA benchmarks have focused on high-resource languages like English and Chinese. Despite pioneering works to expand multilingual QA pairs in non-text-centric VQA datasets through translation engines, the translation-based protocol encounters a substantial visual-textual misalignment problem when applied to TEC-VQA. Specifically, it prioritizes the text in question-answer pairs while disregarding the visual text present in images. Moreover, it fails to address complexities related to nuanced meaning, contextual distortion, language bias, and question-type diversity. In this work, we tackle multilingual TEC-VQA by introducing MTVQA, the first benchmark featuring high-quality human expert annotations across 9 diverse languages, consisting of 6,778 question-answer pairs across 2,116 images. Further, by comprehensively evaluating numerous state-of-the-art Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs), including GPT-4o, GPT-4V, Claude3, and Gemini, on the MTVQA dataset, it is evident that there is still a large room for performance improvement, underscoring the value of MTVQA. Additionally, we supply multilingual training data within the MTVQA dataset, demonstrating that straightforward fine-tuning with this data can substantially enhance multilingual TEC-VQA performance. We aspire that MTVQA will offer the research community fresh insights and stimulate further exploration in multilingual visual text comprehension. The project homepage is available at https://bytedance.github.io/MTVQA/.
Create account to get full access
Overview
• This paper introduces MTVQA, a new benchmark for Multilingual Text-Centric Visual Question Answering (VQA) that aims to evaluate the ability of models to answer questions about visual content in multiple languages.
• The benchmark includes a diverse dataset of images and multilingual questions, as well as comprehensive evaluation protocols to assess the performance of models on various aspects of this task.
Plain English Explanation
The paper presents a new dataset and benchmark called MTVQA (Multilingual Text-Centric Visual Question Answering) that is designed to evaluate how well AI models can answer questions about images in multiple languages. The key idea is to create a more challenging and realistic test of a model's ability to understand the visual content and answer related questions, not just in English, but in a variety of other languages as well.
This is important because most existing VQA datasets and benchmarks have been limited to English, which doesn't reflect the true diversity of real-world use cases where people may need to interact with visual content in many different languages. By expanding the language coverage, MTVQA aims to push the boundaries of what current AI models are capable of and encourage the development of more robust and multilingual VQA systems.
Technical Explanation
The MTVQA dataset includes a diverse collection of images paired with text-based questions in 7 different languages: English, Spanish, French, German, Italian, Portuguese, and Russian. The questions cover a wide range of topics and require an understanding of the visual content to answer correctly.
The paper also introduces comprehensive evaluation protocols to assess model performance across various dimensions, such as language-specific accuracy, zero-shot cross-lingual transfer, and the ability to handle linguistic phenomena like synonymy and paraphrasing. This goes beyond just measuring overall accuracy and provides a more nuanced view of a model's strengths and weaknesses.
To establish baseline results, the authors evaluate several state-of-the-art VQA models on the MTVQA benchmark, including ViTextVQA, TextSquare, and Open-Ended VQA. The results highlight the challenges posed by the multilingual and text-centric nature of the MTVQA task, and suggest that existing models still have significant room for improvement.
Critical Analysis
The MTVQA benchmark represents an important step forward in the field of VQA by introducing a more diverse and realistic test of model capabilities. However, the paper acknowledges some limitations, such as the relatively small size of the dataset compared to English-centric VQA benchmarks like VQAv2.
Additionally, while MTVQA covers a range of languages, it still lacks representation from other major language groups, such as those in Asia and Africa. Expanding the language diversity even further could lead to additional insights and challenges for state-of-the-art models.
Conclusion
The MTVQA benchmark offers a valuable new resource for evaluating the multilingual and text-centric capabilities of VQA models. By establishing a more comprehensive and challenging test bed, the research community can work towards developing AI systems that are truly language-agnostic and can seamlessly interact with visual content in a wide variety of real-world scenarios.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers

CVQA: Culturally-diverse Multilingual Visual Question Answering Benchmark
David Romero, Chenyang Lyu, Haryo Akbarianto Wibowo, Teresa Lynn, Injy Hamed, Aditya Nanda Kishore, Aishik Mandal, Alina Dragonetti, Artem Abzaliev, Atnafu Lambebo Tonja, Bontu Fufa Balcha, Chenxi Whitehouse, Christian Salamea, Dan John Velasco, David Ifeoluwa Adelani, David Le Meur, Emilio Villa-Cueva, Fajri Koto, Fauzan Farooqui, Frederico Belcavello, Ganzorig Batnasan, Gisela Vallejo, Grainne Caulfield, Guido Ivetta, Haiyue Song, Henok Biadglign Ademtew, Hern'an Maina, Holy Lovenia, Israel Abebe Azime, Jan Christian Blaise Cruz, Jay Gala, Jiahui Geng, Jesus-German Ortiz-Barajas, Jinheon Baek, Jocelyn Dunstan, Laura Alonso Alemany, Kumaranage Ravindu Yasas Nagasinghe, Luciana Benotti, Luis Fernando D'Haro, Marcelo Viridiano, Marcos Estecha-Garitagoitia, Maria Camila Buitrago Cabrera, Mario Rodr'iguez-Cantelar, M'elanie Jouitteau, Mihail Mihaylov, Mohamed Fazli Mohamed Imam, Muhammad Farid Adilazuarda, Munkhjargal Gochoo, Munkh-Erdene Otgonbold, Naome Etori, Olivier Niyomugisha, Paula M'onica Silva, Pranjal Chitale, Raj Dabre, Rendi Chevi, Ruochen Zhang, Ryandito Diandaru, Samuel Cahyawijaya, Santiago G'ongora, Soyeong Jeong, Sukannya Purkayastha, Tatsuki Kuribayashi, Thanmay Jayakumar, Tiago Timponi Torrent, Toqeer Ehsan, Vladimir Araujo, Yova Kementchedjhieva, Zara Burzo, Zheng Wei Lim, Zheng Xin Yong, Oana Ignat, Joan Nwatu, Rada Mihalcea, Thamar Solorio, Alham Fikri Aji

0
0
Visual Question Answering (VQA) is an important task in multimodal AI, and it is often used to test the ability of vision-language models to understand and reason on knowledge present in both visual and textual data. However, most of the current VQA models use datasets that are primarily focused on English and a few major world languages, with images that are typically Western-centric. While recent efforts have tried to increase the number of languages covered on VQA datasets, they still lack diversity in low-resource languages. More importantly, although these datasets often extend their linguistic range via translation or some other approaches, they usually keep images the same, resulting in narrow cultural representation. To address these limitations, we construct CVQA, a new Culturally-diverse multilingual Visual Question Answering benchmark, designed to cover a rich set of languages and cultures, where we engage native speakers and cultural experts in the data collection process. As a result, CVQA includes culturally-driven images and questions from across 28 countries on four continents, covering 26 languages with 11 scripts, providing a total of 9k questions. We then benchmark several Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) on CVQA, and show that the dataset is challenging for the current state-of-the-art models. This benchmark can serve as a probing evaluation suite for assessing the cultural capability and bias of multimodal models and hopefully encourage more research efforts toward increasing cultural awareness and linguistic diversity in this field.
6/11/2024
🤔
TableVQA-Bench: A Visual Question Answering Benchmark on Multiple Table Domains
Yoonsik Kim, Moonbin Yim, Ka Yeon Song

0
0
In this paper, we establish a benchmark for table visual question answering, referred to as the TableVQA-Bench, derived from pre-existing table question-answering (QA) and table structure recognition datasets. It is important to note that existing datasets have not incorporated images or QA pairs, which are two crucial components of TableVQA. As such, the primary objective of this paper is to obtain these necessary components. Specifically, images are sourced either through the application of a textit{stylesheet} or by employing the proposed table rendering system. QA pairs are generated by exploiting the large language model (LLM) where the input is a text-formatted table. Ultimately, the completed TableVQA-Bench comprises 1,500 QA pairs. We comprehensively compare the performance of various multi-modal large language models (MLLMs) on TableVQA-Bench. GPT-4V achieves the highest accuracy among commercial and open-sourced MLLMs from our experiments. Moreover, we discover that the number of vision queries plays a significant role in TableVQA performance. To further analyze the capabilities of MLLMs in comparison to their LLM backbones, we investigate by presenting image-formatted tables to MLLMs and text-formatted tables to LLMs, respectively. Our findings suggest that processing visual inputs is more challenging than text inputs, as evidenced by the lower performance of MLLMs, despite generally requiring higher computational costs than LLMs. The proposed TableVQA-Bench and evaluation codes are available at href{https://github.com/naver-ai/tablevqabench}{https://github.com/naver-ai/tablevqabench}.
5/1/2024
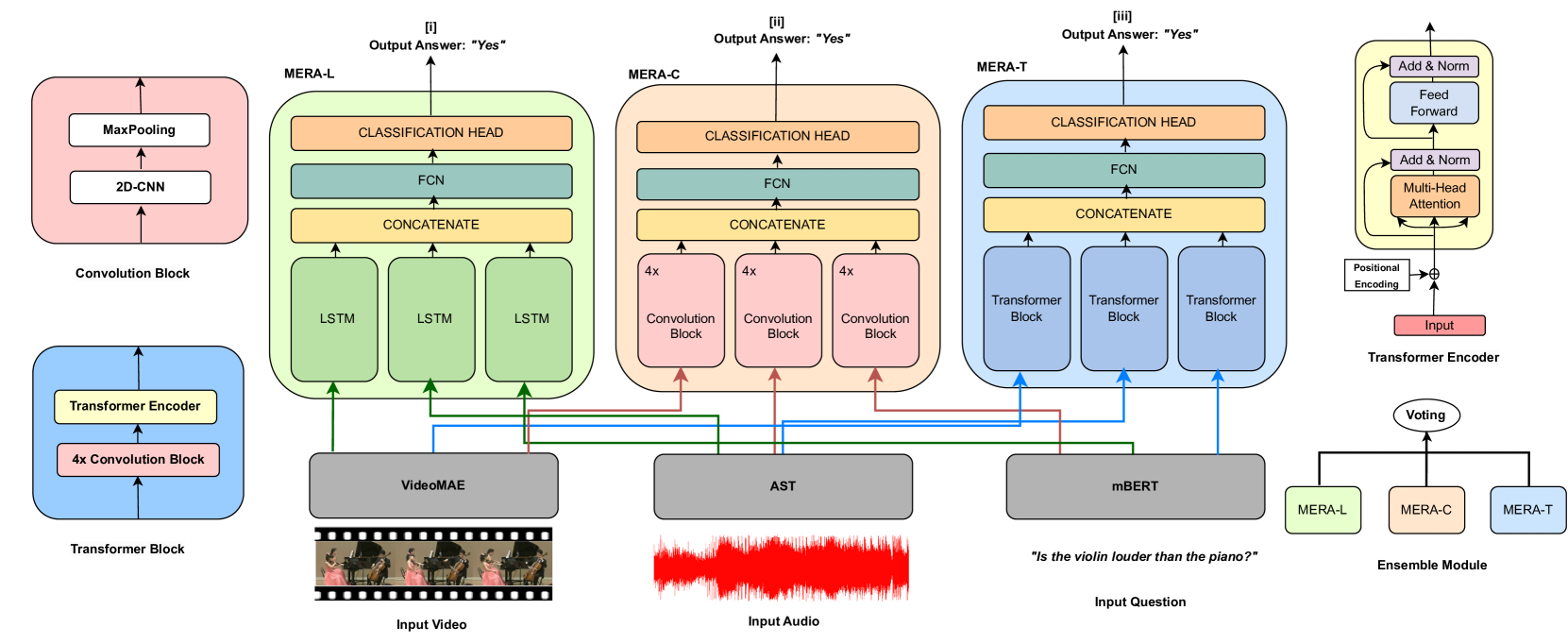
Towards Multilingual Audio-Visual Question Answering
Orchid Chetia Phukan, Priyabrata Mallick, Swarup Ranjan Behera, Aalekhya Satya Narayani, Arun Balaji Buduru, Rajesh Sharma

0
0
In this paper, we work towards extending Audio-Visual Question Answering (AVQA) to multilingual settings. Existing AVQA research has predominantly revolved around English and replicating it for addressing AVQA in other languages requires a substantial allocation of resources. As a scalable solution, we leverage machine translation and present two multilingual AVQA datasets for eight languages created from existing benchmark AVQA datasets. This prevents extra human annotation efforts of collecting questions and answers manually. To this end, we propose, MERA framework, by leveraging state-of-the-art (SOTA) video, audio, and textual foundation models for AVQA in multiple languages. We introduce a suite of models namely MERA-L, MERA-C, MERA-T with varied model architectures to benchmark the proposed datasets. We believe our work will open new research directions and act as a reference benchmark for future works in multilingual AVQA.
6/14/2024
📉
KNVQA: A Benchmark for evaluation knowledge-based VQA
Sirui Cheng, Siyu Zhang, Jiayi Wu, Muchen Lan

0
0
Within the multimodal field, large vision-language models (LVLMs) have made significant progress due to their strong perception and reasoning capabilities in the visual and language systems. However, LVLMs are still plagued by the two critical issues of object hallucination and factual accuracy, which limit the practicality of LVLMs in different scenarios. Furthermore, previous evaluation methods focus more on the comprehension and reasoning of language content but lack a comprehensive evaluation of multimodal interactions, thereby resulting in potential limitations. To this end, we propose a novel KNVQA-Eval, which is devoted to knowledge-based VQA task evaluation to reflect the factuality of multimodal LVLMs. To ensure the robustness and scalability of the evaluation, we develop a new KNVQA dataset by incorporating human judgment and perception, aiming to evaluate the accuracy of standard answers relative to AI-generated answers in knowledge-based VQA. This work not only comprehensively evaluates the contextual information of LVLMs using reliable human annotations, but also further analyzes the fine-grained capabilities of current methods to reveal potential avenues for subsequent optimization of LVLMs-based estimators. Our proposed VQA-Eval and corresponding dataset KNVQA will facilitate the development of automatic evaluation tools with the advantages of low cost, privacy protection, and reproducibility. Our code will be released upon publication.
6/14/2024