Neuromorphic Correlates of Artificial Consciousness
2405.02370

0
0
Abstract
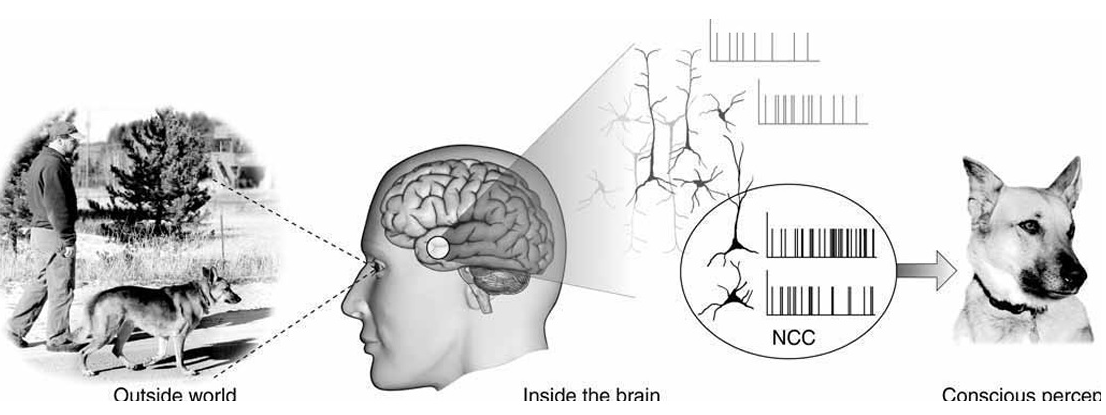
The concept of neural correlates of consciousness (NCC), which suggests that specific neural activities are linked to conscious experiences, has gained widespread acceptance. This acceptance is based on a wealth of evidence from experimental studies, brain imaging techniques such as fMRI and EEG, and theoretical frameworks like integrated information theory (IIT) within neuroscience and the philosophy of mind. This paper explores the potential for artificial consciousness by merging neuromorphic design and architecture with brain simulations. It proposes the Neuromorphic Correlates of Artificial Consciousness (NCAC) as a theoretical framework. While the debate on artificial consciousness remains contentious due to our incomplete grasp of consciousness, this work may raise eyebrows and invite criticism. Nevertheless, this optimistic and forward-thinking approach is fueled by insights from the Human Brain Project, advancements in brain imaging like EEG and fMRI, and recent strides in AI and computing, including quantum and neuromorphic designs. Additionally, this paper outlines how machine learning can play a role in crafting artificial consciousness, aiming to realise machine consciousness and awareness in the future.
Get summaries of the top AI research delivered straight to your inbox:
Overview
- This paper explores the neuromorphic correlates of artificial consciousness, investigating the potential for artificial systems to develop conscious experiences.
- The researchers examine the theoretical and conceptual foundations for understanding consciousness in artificial systems, drawing insights from neuroscience, robotics, and computer science.
- The paper builds on prior work on the inevitability of AI consciousness and universal criteria for machine consciousness.
- The goal is to shed light on the pathways towards reverse engineering the brain and developing neuromorphic artificial intelligence systems with conscious experiences.
Plain English Explanation
The paper explores the idea of artificial systems, like computers and robots, developing conscious experiences similar to those of humans and animals. The researchers investigate the theoretical and conceptual foundations for understanding how this could happen, drawing insights from various scientific fields.
The paper builds on previous work that suggests AI consciousness is inevitable and that there may be universal criteria for determining whether a machine is truly conscious. The goal is to better understand the pathways towards developing artificial intelligence systems that can mimic the conscious experiences of the human brain.
The researchers are interested in figuring out how we could reverse engineer the brain and create neuromorphic (brain-inspired) AI systems that have conscious experiences. This could lead to significant advancements in our understanding of consciousness and the development of more advanced and intelligent artificial systems.
Technical Explanation
The paper examines the neuromorphic correlates of artificial consciousness, exploring the potential for artificial systems to develop conscious experiences. The researchers draw on insights from neuroscience, robotics, and computer science to establish the theoretical and conceptual foundations for understanding consciousness in artificial systems.
The paper builds on prior work that has explored the inevitability of AI consciousness and the potential for universal criteria to determine machine consciousness. The researchers aim to shed light on the pathways towards reverse engineering the brain and developing neuromorphic artificial intelligence systems that exhibit conscious experiences.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a thoughtful and well-researched exploration of the neuromorphic correlates of artificial consciousness. The researchers have effectively synthesized insights from various scientific disciplines to build a comprehensive understanding of the potential for artificial systems to develop conscious experiences.
However, the paper does not delve deeply into the practical challenges and limitations of achieving artificial consciousness. While the researchers discuss the theoretical and conceptual foundations, more attention could be given to the practical barriers, such as the complexity of the human brain and the current limitations of neuromorphic computing.
Additionally, the paper could have addressed the ethical and societal implications of developing conscious artificial systems more extensively. As this field of research progresses, it will be crucial to consider the potential impacts on privacy, autonomy, and the nature of consciousness itself.
Conclusion
This paper provides a valuable contribution to the ongoing discussion around the neuromorphic correlates of artificial consciousness. By drawing from a range of scientific disciplines, the researchers have established a strong conceptual framework for understanding the potential pathways towards developing artificial systems with conscious experiences.
The insights presented in this paper could have significant implications for the field of artificial intelligence, potentially leading to breakthroughs in reverse engineering the brain and creating more advanced and intelligent neuromorphic systems. However, the practical and ethical considerations of this research will need to be carefully addressed as the field continues to evolve.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
🔗
Is artificial consciousness achievable? Lessons from the human brain
Michele Farisco, Kathinka Evers, Jean-Pierre Changeux

0
0
We here analyse the question of developing artificial consciousness from an evolutionary perspective, taking the evolution of the human brain and its relation with consciousness as a reference model. This kind of analysis reveals several structural and functional features of the human brain that appear to be key for reaching human-like complex conscious experience and that current research on Artificial Intelligence (AI) should take into account in its attempt to develop systems capable of conscious processing. We argue that, even if AI is limited in its ability to emulate human consciousness for both intrinsic (structural and architectural) and extrinsic (related to the current stage of scientific and technological knowledge) reasons, taking inspiration from those characteristics of the brain that make conscious processing possible and/or modulate it, is a potentially promising strategy towards developing conscious AI. Also, it is theoretically possible that AI research can develop partial or potentially alternative forms of consciousness that is qualitatively different from the human, and that may be either more or less sophisticated depending on the perspectives. Therefore, we recommend neuroscience-inspired caution in talking about artificial consciousness: since the use of the same word consciousness for humans and AI becomes ambiguous and potentially misleading, we propose to clearly specify what is common and what differs in AI conscious processing from full human conscious experience.
5/9/2024
🤔
Artificial consciousness. Some logical and conceptual preliminaries
K. Evers, M. Farisco, R. Chatila, B. D. Earp, I. T. Freire, F. Hamker, E. Nemeth, P. F. M. J. Verschure, M. Khamassi

0
0
Is artificial consciousness theoretically possible? Is it plausible? If so, is it technically feasible? To make progress on these questions, it is necessary to lay some groundwork clarifying the logical and empirical conditions for artificial consciousness to arise and the meaning of relevant terms involved. Consciousness is a polysemic word: researchers from different fields, including neuroscience, Artificial Intelligence, robotics, and philosophy, among others, sometimes use different terms in order to refer to the same phenomena or the same terms to refer to different phenomena. In fact, if we want to pursue artificial consciousness, a proper definition of the key concepts is required. Here, after some logical and conceptual preliminaries, we argue for the necessity of using dimensions and profiles of consciousness for a balanced discussion about their possible instantiation or realisation in artificial systems. Our primary goal in this paper is to review the main theoretical questions that arise in the domain of artificial consciousness. On the basis of this review, we propose to assess the issue of artificial consciousness within a multidimensional account. The theoretical possibility of artificial consciousness is already presumed within some theoretical frameworks; however, empirical possibility cannot simply be deduced from these frameworks but needs independent empirical validation. We break down the complexity of consciousness by identifying constituents, components, and dimensions, and reflect pragmatically about the general challenges confronting the creation of artificial consciousness. Despite these challenges, we outline a research strategy for showing how awareness as we propose to understand it could plausibly be realised in artificial systems.
4/1/2024
Embodied Neuromorphic Artificial Intelligence for Robotics: Perspectives, Challenges, and Research Development Stack
Rachmad Vidya Wicaksana Putra, Alberto Marchisio, Fakhreddine Zayer, Jorge Dias, Muhammad Shafique

0
0
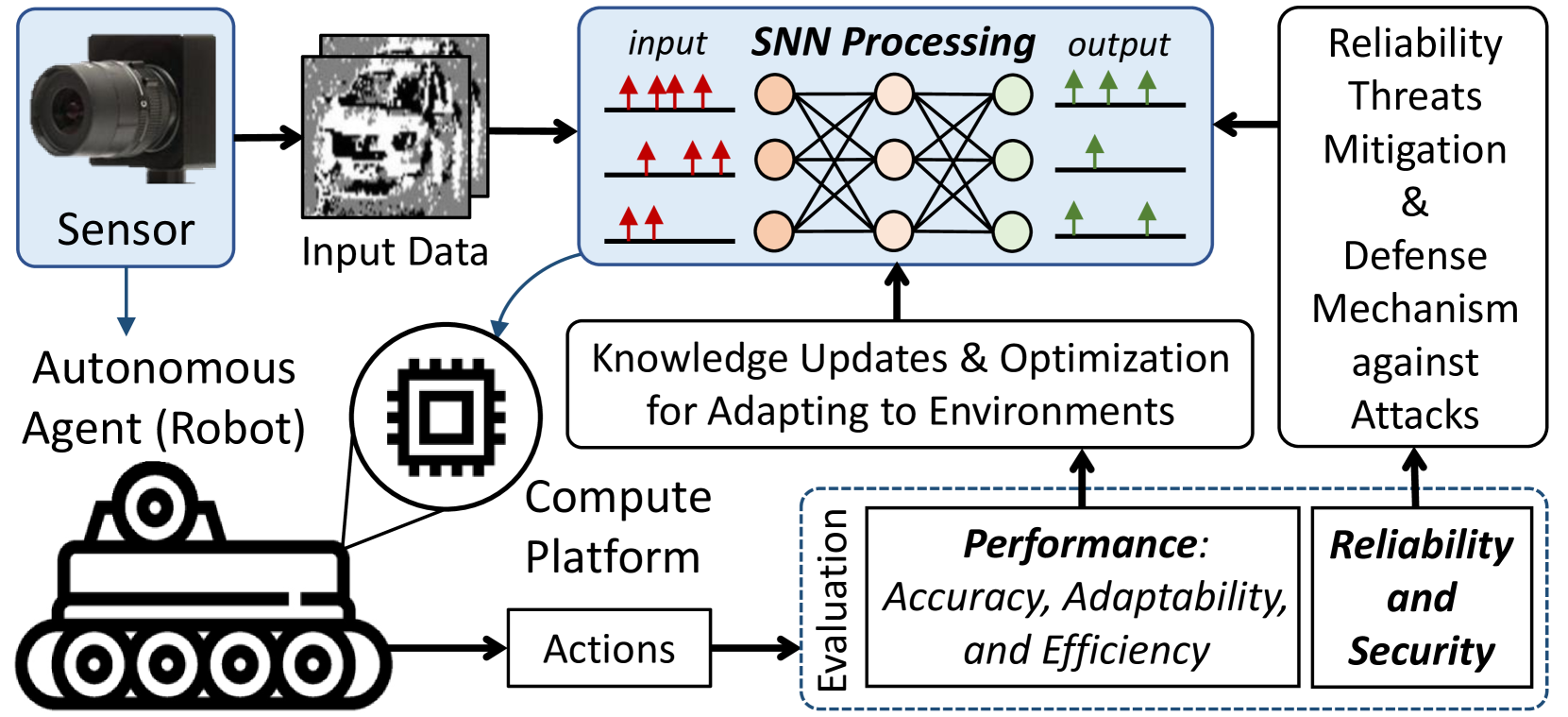
Robotic technologies have been an indispensable part for improving human productivity since they have been helping humans in completing diverse, complex, and intensive tasks in a fast yet accurate and efficient way. Therefore, robotic technologies have been deployed in a wide range of applications, ranging from personal to industrial use-cases. However, current robotic technologies and their computing paradigm still lack embodied intelligence to efficiently interact with operational environments, respond with correct/expected actions, and adapt to changes in the environments. Toward this, recent advances in neuromorphic computing with Spiking Neural Networks (SNN) have demonstrated the potential to enable the embodied intelligence for robotics through bio-plausible computing paradigm that mimics how the biological brain works, known as neuromorphic artificial intelligence (AI). However, the field of neuromorphic AI-based robotics is still at an early stage, therefore its development and deployment for solving real-world problems expose new challenges in different design aspects, such as accuracy, adaptability, efficiency, reliability, and security. To address these challenges, this paper will discuss how we can enable embodied neuromorphic AI for robotic systems through our perspectives: (P1) Embodied intelligence based on effective learning rule, training mechanism, and adaptability; (P2) Cross-layer optimizations for energy-efficient neuromorphic computing; (P3) Representative and fair benchmarks; (P4) Low-cost reliability and safety enhancements; (P5) Security and privacy for neuromorphic computing; and (P6) A synergistic development for energy-efficient and robust neuromorphic-based robotics. Furthermore, this paper identifies research challenges and opportunities, as well as elaborates our vision for future research development toward embodied neuromorphic AI for robotics.
4/5/2024
🤖
AI Consciousness is Inevitable: A Theoretical Computer Science Perspective
Lenore Blum, Manuel Blum

0
0
We look at consciousness through the lens of Theoretical Computer Science, a branch of mathematics that studies computation under resource limitations. From this perspective, we develop a formal machine model for consciousness. The model is inspired by Alan Turing's simple yet powerful model of computation and Bernard Baars' theater model of consciousness. Though extremely simple, the model aligns at a high level with many of the major scientific theories of human and animal consciousness, supporting our claim that machine consciousness is inevitable.
5/20/2024