One-Click Upgrade from 2D to 3D: Sandwiched RGB-D Video Compression for Stereoscopic Teleconferencing

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- This paper presents a novel approach for compressing RGB-D (color and depth) video for stereoscopic teleconferencing applications.
- The key idea is to "sandwich" the depth information between the left and right color frames, allowing for efficient encoding and transmission of the full 3D video.
- The proposed method enables a "one-click upgrade" from 2D to 3D video, without requiring specialized hardware or complex setup on the user's end.
Plain English Explanation
The paper describes a way to compress 3D video for video conferencing in a simple and efficient manner. Typical 3D video requires capturing and transmitting separate left and right camera feeds, which can be complex and bandwidth-intensive.
Instead, the researchers developed a technique to "sandwich" the depth information (which indicates how far away objects are) between the left and right color frames. This allows the full 3D video to be encoded and transmitted using less data than traditional methods.
The key benefit is that users can upgrade from a regular 2D video call to a 3D experience with just a single click, without needing specialized cameras or other equipment. The depth information is automatically extracted and combined with the color frames to create a stereoscopic 3D effect.
This "one-click upgrade" approach makes 3D video conferencing much more accessible and practical for everyday use, paving the way for more immersive remote collaboration and communication.
Technical Explanation
The paper proposes a "sandwiched RGB-D video compression" technique for efficient encoding and transmission of stereoscopic 3D video. The key innovation is to embed the depth information between the left and right color frames, rather than transmitting separate left and right video streams.
This is achieved by first extracting the depth map from the input RGB-D video using a depth estimation neural network. The depth map is then compressed and inserted between the left and right color frames.
On the receiving end, the depth information is extracted and used to reconstruct the 3D video, leveraging video super-resolution techniques to enhance the quality.
The authors show that this "sandwiched" approach outperforms traditional 3D video codecs in terms of compression efficiency and subjective 3D quality, while also enabling a "one-click upgrade" from 2D to 3D without the need for specialized hardware.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a compelling solution for making 3D video conferencing more accessible and practical. By efficiently encoding the depth information alongside the color frames, the proposed method avoids the bandwidth and complexity issues of traditional 3D video capture and transmission.
However, the paper does not address potential limitations, such as the accuracy of the depth estimation neural network or the impact of depth compression on the final 3D quality. Additionally, the authors do not discuss the computational requirements of their approach, which could be a concern for resource-constrained devices.
Further research could explore ways to improve the depth estimation or optimize the depth compression to enhance the overall 3D video quality and user experience. Conducting user studies to assess the perceived 3D quality and usability of the "one-click upgrade" feature would also be valuable.
Conclusion
This paper presents a novel approach for efficient 3D video compression and transmission, enabling a "one-click upgrade" from 2D to stereoscopic 3D for video conferencing applications. By sandwiching the depth information between the left and right color frames, the proposed method achieves high compression efficiency and quality, while also simplifying the user experience.
This research represents an important step towards making 3D video conferencing more accessible and practical for everyday use, with potential applications in remote collaboration, education, and entertainment. Further advancements in depth estimation and compression could unlock even more immersive and user-friendly 3D communication experiences in the future.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
One-Click Upgrade from 2D to 3D: Sandwiched RGB-D Video Compression for Stereoscopic Teleconferencing
Yueyu Hu, Onur G. Guleryuz, Philip A. Chou, Danhang Tang, Jonathan Taylor, Rus Maxham, Yao Wang
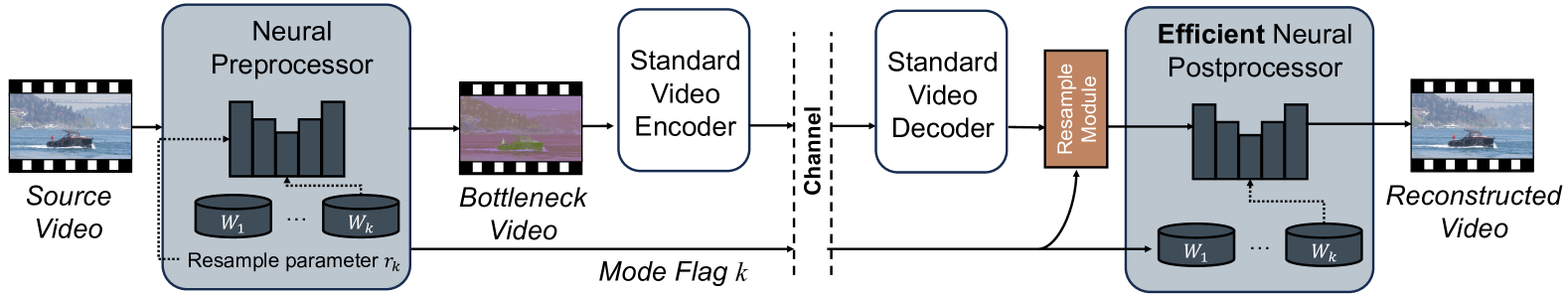
Stereoscopic video conferencing is still challenging due to the need to compress stereo RGB-D video in real-time. Though hardware implementations of standard video codecs such as H.264 / AVC and HEVC are widely available, they are not designed for stereoscopic videos and suffer from reduced quality and performance. Specific multiview or 3D extensions of these codecs are complex and lack efficient implementations. In this paper, we propose a new approach to upgrade a 2D video codec to support stereo RGB-D video compression, by wrapping it with a neural pre- and post-processor pair. The neural networks are end-to-end trained with an image codec proxy, and shown to work with a more sophisticated video codec. We also propose a geometry-aware loss function to improve rendering quality. We train the neural pre- and post-processors on a synthetic 4D people dataset, and evaluate it on both synthetic and real-captured stereo RGB-D videos. Experimental results show that the neural networks generalize well to unseen data and work out-of-box with various video codecs. Our approach saves about 30% bit-rate compared to a conventional video coding scheme and MV-HEVC at the same level of rendering quality from a novel view, without the need of a task-specific hardware upgrade.
Read more4/16/2024

0
Standard compliant video coding using low complexity, switchable neural wrappers
Yueyu Hu, Chenhao Zhang, Onur G. Guleryuz, Debargha Mukherjee, Yao Wang
The proliferation of high resolution videos posts great storage and bandwidth pressure on cloud video services, driving the development of next-generation video codecs. Despite great progress made in neural video coding, existing approaches are still far from economical deployment considering the complexity and rate-distortion performance tradeoff. To clear the roadblocks for neural video coding, in this paper we propose a new framework featuring standard compatibility, high performance, and low decoding complexity. We employ a set of jointly optimized neural pre- and post-processors, wrapping a standard video codec, to encode videos at different resolutions. The rate-distorion optimal downsampling ratio is signaled to the decoder at the per-sequence level for each target rate. We design a low complexity neural post-processor architecture that can handle different upsampling ratios. The change of resolution exploits the spatial redundancy in high-resolution videos, while the neural wrapper further achieves rate-distortion performance improvement through end-to-end optimization with a codec proxy. Our light-weight post-processor architecture has a complexity of 516 MACs / pixel, and achieves 9.3% BD-Rate reduction over VVC on the UVG dataset, and 6.4% on AOM CTC Class A1. Our approach has the potential to further advance the performance of the latest video coding standards using neural processing with minimal added complexity.
Read more7/11/2024


0
StereoCrafter: Diffusion-based Generation of Long and High-fidelity Stereoscopic 3D from Monocular Videos
Sijie Zhao, Wenbo Hu, Xiaodong Cun, Yong Zhang, Xiaoyu Li, Zhe Kong, Xiangjun Gao, Muyao Niu, Ying Shan
This paper presents a novel framework for converting 2D videos to immersive stereoscopic 3D, addressing the growing demand for 3D content in immersive experience. Leveraging foundation models as priors, our approach overcomes the limitations of traditional methods and boosts the performance to ensure the high-fidelity generation required by the display devices. The proposed system consists of two main steps: depth-based video splatting for warping and extracting occlusion mask, and stereo video inpainting. We utilize pre-trained stable video diffusion as the backbone and introduce a fine-tuning protocol for the stereo video inpainting task. To handle input video with varying lengths and resolutions, we explore auto-regressive strategies and tiled processing. Finally, a sophisticated data processing pipeline has been developed to reconstruct a large-scale and high-quality dataset to support our training. Our framework demonstrates significant improvements in 2D-to-3D video conversion, offering a practical solution for creating immersive content for 3D devices like Apple Vision Pro and 3D displays. In summary, this work contributes to the field by presenting an effective method for generating high-quality stereoscopic videos from monocular input, potentially transforming how we experience digital media.
Read more9/12/2024


0
SVG: 3D Stereoscopic Video Generation via Denoising Frame Matrix
Peng Dai, Feitong Tan, Qiangeng Xu, David Futschik, Ruofei Du, Sean Fanello, Xiaojuan Qi, Yinda Zhang
Video generation models have demonstrated great capabilities of producing impressive monocular videos, however, the generation of 3D stereoscopic video remains under-explored. We propose a pose-free and training-free approach for generating 3D stereoscopic videos using an off-the-shelf monocular video generation model. Our method warps a generated monocular video into camera views on stereoscopic baseline using estimated video depth, and employs a novel frame matrix video inpainting framework. The framework leverages the video generation model to inpaint frames observed from different timestamps and views. This effective approach generates consistent and semantically coherent stereoscopic videos without scene optimization or model fine-tuning. Moreover, we develop a disocclusion boundary re-injection scheme that further improves the quality of video inpainting by alleviating the negative effects propagated from disoccluded areas in the latent space. We validate the efficacy of our proposed method by conducting experiments on videos from various generative models, including Sora [4 ], Lumiere [2], WALT [8 ], and Zeroscope [ 42]. The experiments demonstrate that our method has a significant improvement over previous methods. The code will be released at url{https://daipengwa.github.io/SVG_ProjectPage}.
Read more7/2/2024