An Open Knowledge Graph-Based Approach for Mapping Concepts and Requirements between the EU AI Act and International Standards

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- Provides a method for mapping concepts and requirements between the EU AI Act and international standards using an open knowledge graph.
- Aims to support compliance with the EU AI Act and enable interoperability between AI systems and international standards.
- Demonstrates the approach through a case study mapping concepts from the EU AI Act to the ISO/IEC 27001 information security management standard.
Plain English Explanation
The paper presents an approach for creating an open knowledge graph to map the concepts and requirements between the European Union's AI Act and various international standards. This is important because the EU AI Act is a new regulation that will require companies developing or using AI systems in the EU to comply with certain rules and standards.
By building a knowledge graph that connects the concepts and requirements in the AI Act to those in other widely used standards, such as the ISO/IEC 27001 information security standard, the researchers aim to help organizations more easily understand how to align their AI systems with the EU regulation. This could support compliance and also enable better interoperability between AI systems and international standards.
The paper demonstrates this approach through a case study that maps concepts from the EU AI Act to the ISO/IEC 27001 standard. This shows how the knowledge graph can be used to identify overlaps, gaps, and connections between the regulatory requirements and established security practices.
Technical Explanation
The paper proposes an open knowledge graph-based approach for mapping concepts and requirements between the EU AI Act and international standards. The key steps of the approach are:
- Extracting and formalizing the concepts and requirements from the EU AI Act and relevant international standards (such as ISO/IEC 27001) into a machine-readable format.
- Building a knowledge graph that represents the relationships between the extracted concepts and requirements from the different sources.
- Querying and analyzing the knowledge graph to identify overlaps, gaps, and connections between the regulatory requirements and standards.
The researchers demonstrate this approach through a case study that maps concepts from the EU AI Act to the ISO/IEC 27001 information security management standard. They extract the relevant concepts from the documents, model them in an ontology, and build a knowledge graph to enable semantic querying and analysis.
The results of the case study show how the knowledge graph can be used to identify alignments and misalignments between the regulatory requirements and the security standard, supporting compliance efforts and interoperability between AI systems and international standards.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a promising approach for bridging the gap between AI regulation and international standards, but there are a few potential limitations and areas for further research:
- The case study focuses on only one international standard (ISO/IEC 27001), and it would be valuable to expand the approach to cover a broader range of standards relevant to AI systems.
- The knowledge graph construction and querying processes are not fully automated in the current approach, which could limit its scalability as the number of standards and regulatory documents grows.
- The paper does not address how the knowledge graph might be maintained and updated as the EU AI Act and international standards evolve over time, which is an important consideration for long-term usability.
Additionally, while the proposed approach aims to support compliance and interoperability, it does not directly address other important considerations, such as the ethical implications of AI systems or the societal impact of their deployment. Further research could explore how this knowledge graph-based approach might be extended to incorporate these broader perspectives.
Conclusion
This paper presents a novel open knowledge graph-based approach for mapping concepts and requirements between the EU AI Act and international standards. By formalizing the regulatory and standards-based knowledge into a machine-readable format and building a semantic knowledge graph, the researchers demonstrate how this approach can support compliance efforts and enable better interoperability between AI systems and established international standards.
The case study focusing on the ISO/IEC 27001 standard provides a proof of concept, but the researchers acknowledge the need to expand the approach to cover a wider range of international standards and address challenges around scalability and maintainability over time. Further research could also explore how this knowledge graph-based approach might incorporate broader considerations around the ethical and societal implications of AI systems.
Overall, this paper presents a promising step towards bridging the gap between AI regulation and international standards, which could have significant implications for the responsible development and deployment of AI technologies.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
An Open Knowledge Graph-Based Approach for Mapping Concepts and Requirements between the EU AI Act and International Standards
Julio Hernandez, Delaram Golpayegani, Dave Lewis
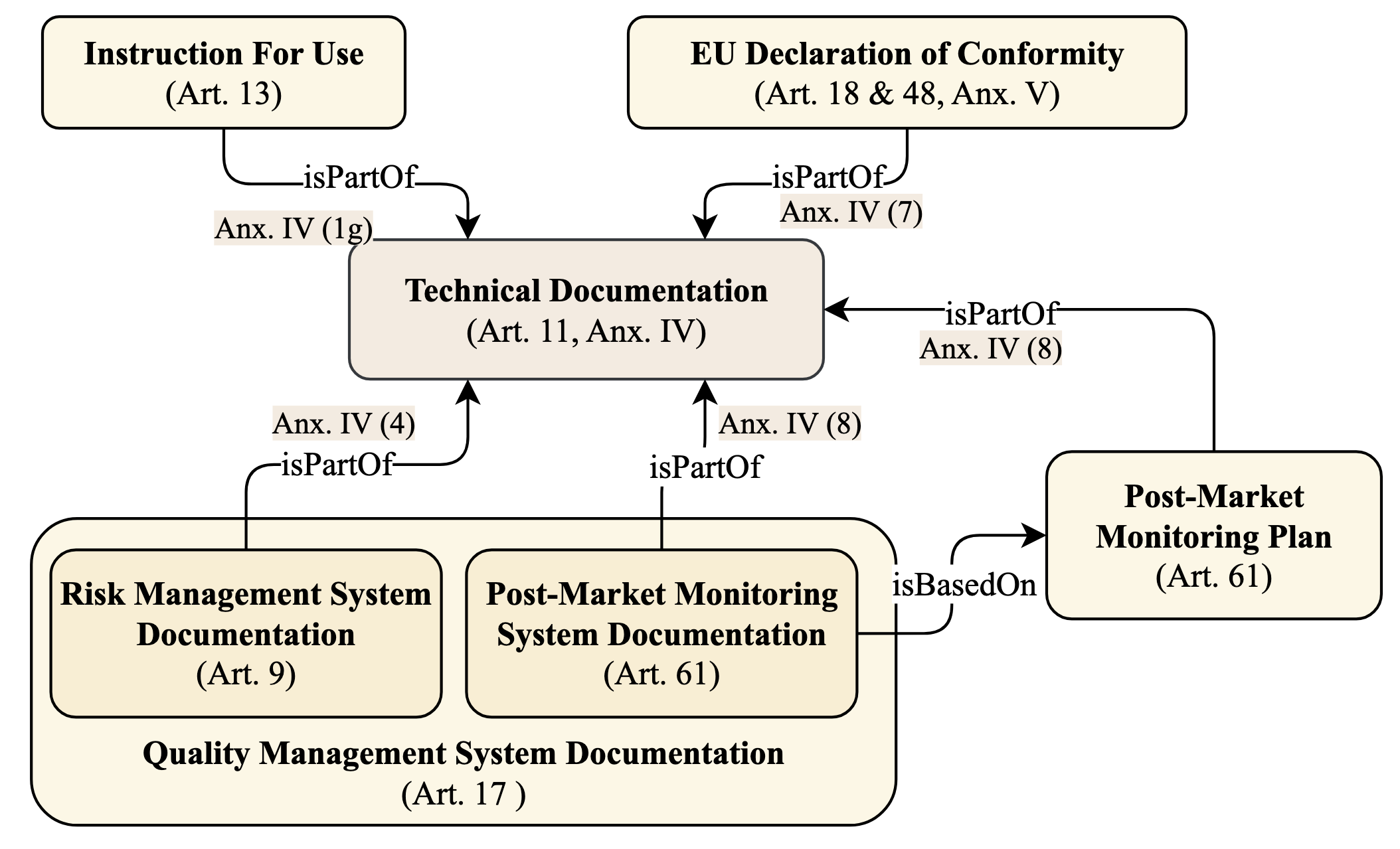
The many initiatives on trustworthy AI result in a confusing and multipolar landscape that organizations operating within the fluid and complex international value chains must navigate in pursuing trustworthy AI. The EU's AI Act will now shift the focus of such organizations toward conformance with the technical requirements for regulatory compliance, for which the Act relies on Harmonized Standards. Though a high-level mapping to the Act's requirements will be part of such harmonization, determining the degree to which standards conformity delivers regulatory compliance with the AI Act remains a complex challenge. Variance and gaps in the definitions of concepts and how they are used in requirements between the Act and harmonized standards may impact the consistency of compliance claims across organizations, sectors, and applications. This may present regulatory uncertainty, especially for SMEs and public sector bodies relying on standards conformance rather than proprietary equivalents for developing and deploying compliant high-risk AI systems. To address this challenge, this paper offers a simple and repeatable mechanism for mapping the terms and requirements relevant to normative statements in regulations and standards, e.g., AI Act and ISO management system standards, texts into open knowledge graphs. This representation is used to assess the adequacy of standards conformance to regulatory compliance and thereby provide a basis for identifying areas where further technical consensus development in trustworthy AI value chains is required to achieve regulatory compliance.
Read more8/23/2024

0
AI Cards: Towards an Applied Framework for Machine-Readable AI and Risk Documentation Inspired by the EU AI Act
Delaram Golpayegani, Isabelle Hupont, Cecilia Panigutti, Harshvardhan J. Pandit, Sven Schade, Declan O'Sullivan, Dave Lewis
With the upcoming enforcement of the EU AI Act, documentation of high-risk AI systems and their risk management information will become a legal requirement playing a pivotal role in demonstration of compliance. Despite its importance, there is a lack of standards and guidelines to assist with drawing up AI and risk documentation aligned with the AI Act. This paper aims to address this gap by providing an in-depth analysis of the AI Act's provisions regarding technical documentation, wherein we particularly focus on AI risk management. On the basis of this analysis, we propose AI Cards as a novel holistic framework for representing a given intended use of an AI system by encompassing information regarding technical specifications, context of use, and risk management, both in human- and machine-readable formats. While the human-readable representation of AI Cards provides AI stakeholders with a transparent and comprehensible overview of the AI use case, its machine-readable specification leverages on state of the art Semantic Web technologies to embody the interoperability needed for exchanging documentation within the AI value chain. This brings the flexibility required for reflecting changes applied to the AI system and its context, provides the scalability needed to accommodate potential amendments to legal requirements, and enables development of automated tools to assist with legal compliance and conformity assessment tasks. To solidify the benefits, we provide an exemplar AI Card for an AI-based student proctoring system and further discuss its potential applications within and beyond the context of the AI Act.
Read more6/27/2024
🔎

0
First Analysis of the EU Artifical Intelligence Act: Towards a Global Standard for Trustworthy AI?
Marion Ho-Dac (UA, CDEP)
The EU Artificial Intelligence Act (AI Act) came into force in the European Union (EU) on 1 August 2024. It is a key piece of legislation both for the citizens at the heart of AI technologies and for the industry active in the internal market. The AI Act imposes progressive compliance on organisations - both private and public - involved in the global value chain of AI systems and models marketed and used in the EU. While the Act is unprecedented on an international scale in terms of its horizontal and binding regulatory scope, its global appeal in support of trustworthy AI is one of its major challenges.
Read more8/19/2024
🤖

0
Catalog of General Ethical Requirements for AI Certification
Nicholas Kluge Corr^ea, Julia Maria Monig
This whitepaper offers normative and practical guidance for developers of artificial intelligence (AI) systems to achieve Trustworthy AI. In it, we present overall ethical requirements and six ethical principles with value-specific recommendations for tools to implement these principles into technology. Our value-specific recommendations address the principles of fairness, privacy and data protection, safety and robustness, sustainability, transparency and explainability and truthfulness. For each principle, we also present examples of criteria for risk assessment and categorization of AI systems and applications in line with the categories of the European Union (EU) AI Act. Our work is aimed at stakeholders who can take it as a potential blueprint to fulfill minimum ethical requirements for trustworthy AI and AI Certification.
Read more8/23/2024