Open6G OTIC: A Blueprint for Programmable O-RAN and 3GPP Testing Infrastructure

0
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- This paper presents a blueprint for an Open RAN Testing and Integration Center (OTIC) to enable programmable and automated testing of O-RAN and 3GPP systems.
- The OTIC is designed to provide a flexible and scalable testing infrastructure to support the development and deployment of open and interoperable 5G networks.
- The research was partially supported by the O-RAN ALLIANCE, the National Telecommunications and Information Administration (NTIA), and the Massachusetts Technology Collaborative.
Plain English Explanation
The paper describes a plan for building a specialized testing facility called the Open RAN Testing and Integration Center (OTIC). The goal of the OTIC is to make it easier to test and validate new 5G network technologies, particularly those related to the Open RAN standard.
The OTIC would provide a flexible and automated testing environment where researchers and engineers can experiment with different 5G components and ensure they work together properly. This is important as 5G networks are becoming more open and modular, with equipment from multiple vendors needing to seamlessly integrate.
By having a centralized testing facility, the researchers hope to accelerate the development and deployment of innovative 5G technologies. The OTIC would allow for automated over-the-air testing of 5G systems, as well as provide tools for programming and configuring the network in a standardized way.
Overall, the OTIC is intended to be a critical piece of infrastructure to support the growth of open and interoperable 5G networks, which could have significant implications for the telecom industry and the wider adoption of 5G technology.
Technical Explanation
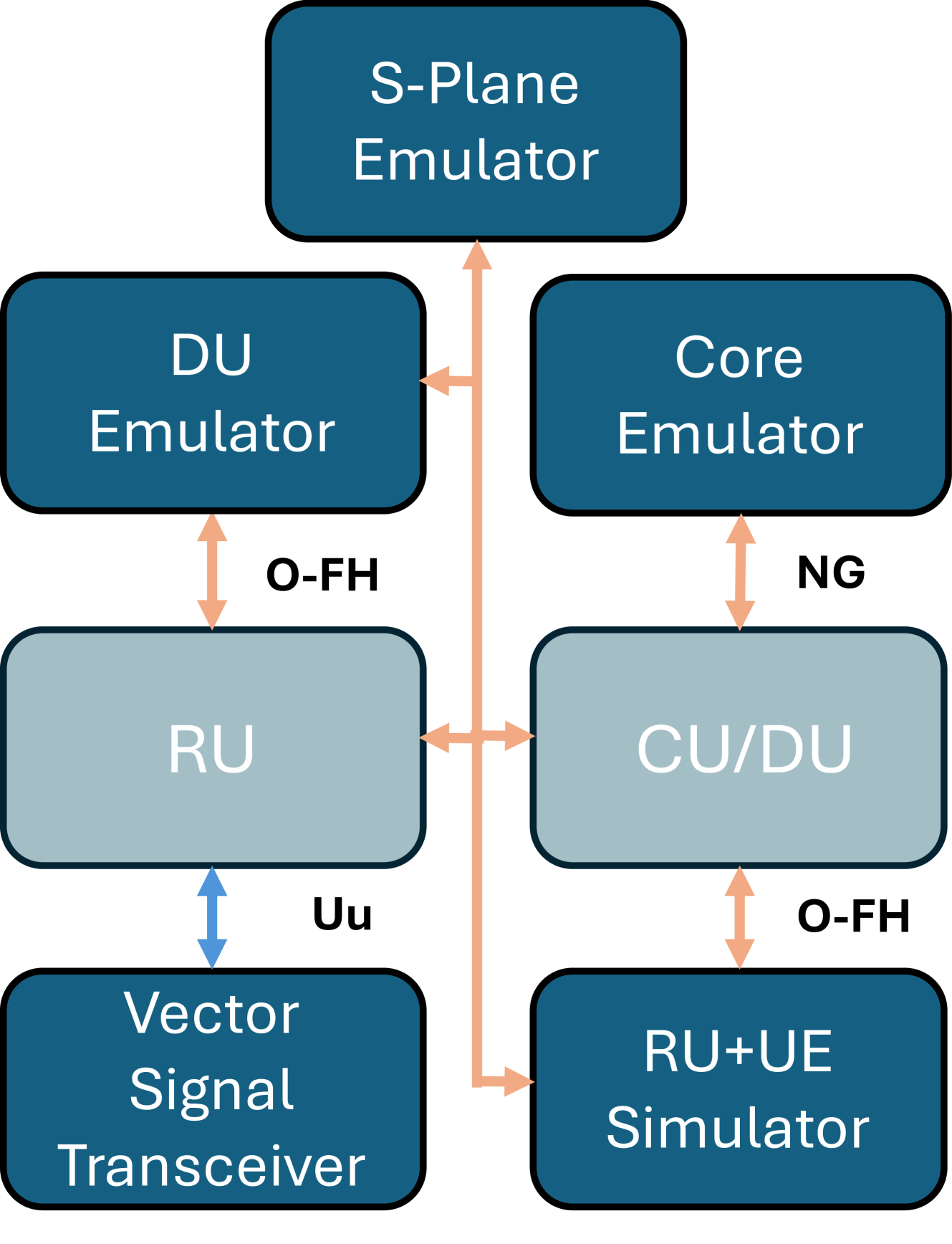
The paper outlines the design and architecture of the proposed Open6G OTIC, which is envisioned as a programmable and automated testing platform for O-RAN and 3GPP-compliant 5G systems.
The OTIC would consist of several key components:
-
Flexible Hardware Infrastructure: The OTIC would feature a modular hardware setup that can be easily reconfigured to accommodate different 5G network topologies and equipment. This includes software-defined radio (SDR) platforms, programmable network interfaces, and other customizable hardware.
-
Automated Test Orchestration: The OTIC would provide tools and workflows for automatically deploying, configuring, and executing test cases across the hardware infrastructure. This includes features for automated over-the-air testing of 5G systems.
-
Programmable Test Environments: The OTIC would allow users to programmatically define and configure test environments, such as simulating different network conditions, traffic patterns, and security attack scenarios. This enables greater flexibility and repeatability in testing.
-
Standardized Interfaces and APIs: The OTIC would implement standard interfaces and APIs to integrate with existing 5G testing and validation tools, as well as facilitate seamless integration with O-RAN and 3GPP architectures.
-
Testbed as a Service: The OTIC would provide a "testbed as a service" model, allowing remote access and utilization of the testing infrastructure by various stakeholders, including equipment vendors, network operators, and academic researchers.
The researchers envision the Open6G OTIC as a critical piece of infrastructure to support the development, testing, and deployment of open, interoperable, and secure 5G networks. By providing a flexible and programmable testing environment, the OTIC aims to accelerate innovation in the 5G ecosystem and facilitate the adoption of emerging 5G technologies.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a well-thought-out blueprint for the Open6G OTIC, addressing key requirements and challenges in building a programmable and automated testing infrastructure for 5G systems.
One potential limitation mentioned in the paper is the need to ensure the OTIC's compatibility and interoperability with a wide range of 5G equipment and technologies, as the 5G ecosystem is rapidly evolving. The researchers acknowledge the importance of developing security testing capabilities within the OTIC to address emerging security threats in the open 5G architecture.
Additionally, the paper does not delve into the specific implementation details or the timeline for the OTIC's development and deployment. The feasibility and scalability of the OTIC concept may depend on factors such as funding, technical expertise, and industry adoption, which are not extensively discussed.
Overall, the Open6G OTIC presents a promising vision for a flexible and programmable testing infrastructure to support the growth of open and interoperable 5G networks. However, the successful realization of this blueprint will require sustained collaboration and commitment from various stakeholders in the 5G ecosystem.
Conclusion
The Open6G OTIC proposed in this paper represents a significant step towards enabling a more open, flexible, and secure 5G ecosystem. By providing a centralized testing and integration platform, the OTIC aims to accelerate the development, validation, and deployment of innovative 5G technologies, including those based on the O-RAN and 3GPP standards.
The OTIC's programmable and automated testing capabilities, coupled with its ability to simulate diverse network conditions and security scenarios, could play a crucial role in fostering innovation and ensuring the interoperability of 5G systems from multiple vendors. This, in turn, could have far-reaching implications for the wider adoption and success of 5G technology, benefiting network operators, equipment manufacturers, and end-users alike.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Open6G OTIC: A Blueprint for Programmable O-RAN and 3GPP Testing Infrastructure
Gabriele Gemmi, Michele Polese, Pedram Johari, Stefano Maxenti, Michael Seltser, Tommaso Melodia
Softwarized and programmable Radio Access Networks (RANs) come with virtualized and disaggregated components, increasing the supply chain robustness and the flexibility and dynamism of the network deployments. This is a key tenet of Open RAN, with open interfaces across disaggregated components specified by the O-RAN ALLIANCE. It is mandatory, however, to validate that all components are compliant with the specifications and can successfully interoperate, without performance gaps with traditional, monolithic appliances. Open Testing & Integration Centers (OTICs) are entities that can verify such interoperability and adherence to the standard through rigorous testing. However, how to design, instrument, and deploy an OTIC which can offer testing for multiple tenants, heterogeneous devices, and is ready to support automated testing is still an open challenge. In this paper, we introduce a blueprint for a programmable OTIC testing infrastructure, based on the design and deployment of the Open6G OTIC at Northeastern University, Boston, and provide insights on technical challenges and solutions for O-RAN testing at scale.
Read more9/5/2024
✅

0
X5G: An Open, Programmable, Multi-vendor, End-to-end, Private 5G O-RAN Testbed with NVIDIA ARC and OpenAirInterface
Davide Villa, Imran Khan, Florian Kaltenberger, Nicholas Hedberg, R'uben Soares da Silva, Stefano Maxenti, Leonardo Bonati, Anupa Kelkar, Chris Dick, Eduardo Baena, Josep M. Jornet, Tommaso Melodia, Michele Polese, Dimitrios Koutsonikolas
As Fifth generation (5G) cellular systems transition to softwarized, programmable, and intelligent networks, it becomes fundamental to enable public and private 5G deployments that are (i) primarily based on software components while (ii) maintaining or exceeding the performance of traditional monolithic systems and (iii) enabling programmability through bespoke configurations and optimized deployments. This requires hardware acceleration to scale the Physical (PHY) layer performance, programmable elements in the Radio Access Network (RAN) and intelligent controllers at the edge, careful planning of the Radio Frequency (RF) environment, as well as end-to-end integration and testing. In this paper, we describe how we developed the programmable X5G testbed, addressing these challenges through the deployment of the first 8-node network based on the integration of NVIDIA Aerial RAN CoLab (ARC), OpenAirInterface (OAI), and a near-real-time RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC). The Aerial Software Development Kit (SDK) provides the PHY layer, accelerated on Graphics Processing Unit (GPU), with the higher layers from the OAI open-source project interfaced with the PHY through the Small Cell Forum (SCF) Functional Application Platform Interface (FAPI). An E2 agent provides connectivity to the O-RAN Software Community (OSC) near-real-time RIC. We discuss software integration, the network infrastructure, and a digital twin framework for RF planning. We then profile the performance with up to 4 Commercial Off-the-Shelf (COTS) smartphones for each base station with iPerf and video streaming applications, measuring a cell rate higher than 500 Mbps in downlink and 45 Mbps in uplink.
Read more6/26/2024
🧪

0
5G-CT: Automated Deployment and Over-the-Air Testing of End-to-End Open Radio Access Networks
Leonardo Bonati, Michele Polese, Salvatore D'Oro, Pietro Brach del Prever, Tommaso Melodia
Deploying and testing cellular networks is a complex task due to the multitude of components involved -- from the core to the Radio Access Network (RAN) and User Equipment (UE) -- all of which requires integration and constant monitoring. Additional challenges are posed by the nature of the wireless channel, whose inherent randomness hinders the repeatability and consistency of the testing process. Consequently, existing solutions for both private and public cellular systems still rely heavily on human intervention for operations such as network reconfiguration, performance monitoring, and end-to-end testing. This reliance significantly slows the pace of innovation in cellular systems. To address these challenges, we introduce 5G-CT, an automation framework based on OpenShift and the GitOps workflow, capable of deploying a softwarized end-to-end 5G and O-RAN-compliant system in a matter of seconds without the need for any human intervention. We have deployed 5G-CT to test the integration and performance of open-source cellular stacks, including OpenAirInterface, and have collected months of automated over-the-air testing results involving software-defined radios. 5G-CT brings cloud-native continuous integration and delivery to the RAN, effectively addressing the complexities associated with managing spectrum, radios, heterogeneous devices, and distributed components. Moreover, it endows cellular networks with much needed automation and continuous testing capabilities, providing a platform to evaluate the robustness and resiliency of Open RAN software.
Read more4/9/2024

0
ARA-O-RAN: End-to-End Programmable O-RAN Living Lab for Agriculture and Rural Communities
Tianyi Zhang, Joshua Ofori Boateng, Taimoor UI Islam, Arsalan Ahmad, Hongwei Zhang, Daji Qiao
As wireless networks evolve towards open architectures like O-RAN, testing, and integration platforms are crucial to address challenges like interoperability. This paper describes ARA-O-RAN, a novel O-RAN testbed established through the NSF Platforms for Advanced Wireless Research (PAWR) ARA platform. ARA provides an at-scale rural wireless living lab focused on technologies for digital agriculture and rural communities. As an O-RAN Alliance certified Open Testing and Integration Centre (OTIC), ARA launched ARA-O-RAN -- the first public O-RAN testbed tailored to rural and agriculture use cases, together with the end-to-end, whole-stack programmability. ARA-O-RAN uniquely combines support for outdoor testing across a university campus, surrounding farmlands, and rural communities with a 50-node indoor sandbox. The testbed facilitates vital R&D to implement open architectures that can meet rural connectivity needs. The paper outlines ARA-O-RAN's hardware system design, software architecture, and enabled research experiments. It also discusses plans aligned with national spectrum policy and rural spectrum innovation. ARA-O-RAN exemplifies the value of purpose-built wireless testbeds in accelerating impactful wireless research.
Read more7/17/2024