Optimizing 4D Lookup Table for Low-light Video Enhancement via Wavelet Priori

0
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- Low-light video enhancement using a 4D lookup table and wavelet prior
- Multimodal approach for better performance in low-light conditions
- Optimized 4D lookup table for efficient video enhancement
Plain English Explanation
Low-light conditions can make it difficult to see details in videos. This research paper presents a method to enhance low-light videos using a 4D lookup table and a "wavelet prior."
The 4D lookup table is a way to efficiently store and apply image processing adjustments. By optimizing this lookup table, the researchers were able to make the video enhancement more effective and efficient.
They also used a "wavelet prior," which is a mathematical technique that helps preserve important details in the video, even in low-light conditions. This multimodal approach (using multiple methods together) resulted in better performance compared to previous low-light video enhancement techniques.
Technical Explanation
The key elements of this research include:
-
4D Lookup Table: The authors used a 4D lookup table to efficiently store and apply image processing adjustments. By optimizing the parameters of this lookup table, they were able to enhance low-light videos more effectively.
-
Wavelet Prior: The researchers incorporated a "wavelet prior" into their approach. This is a mathematical technique that helps preserve important details in the video, even in challenging low-light conditions.
-
Multimodal Approach: By combining the 4D lookup table and wavelet prior, the authors developed a multimodal method for low-light video enhancement. This combination of techniques resulted in improved performance compared to previous state-of-the-art approaches.
Critical Analysis
The paper acknowledges some limitations of the proposed method, such as the need for careful parameter tuning and the potential for artifacts in certain low-light scenarios. Additionally, the authors note that the method may not be as effective for extremely dark scenes where the wavelet prior is less effective.
While the multimodal approach showed promising results, further research could explore alternative techniques or combinations of methods to address the remaining challenges in low-light video enhancement. Evaluating the method's performance on a wider range of real-world low-light video data could also provide valuable insights.
Conclusion
This research presents an optimized 4D lookup table approach combined with a wavelet prior for effective low-light video enhancement. The multimodal nature of the method allows it to outperform previous techniques, making it a valuable contribution to the field of image and video processing. As low-light video enhancement continues to be an important challenge, this work demonstrates the potential of combining multiple complementary techniques to improve the quality and visibility of videos captured in challenging lighting conditions.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Optimizing 4D Lookup Table for Low-light Video Enhancement via Wavelet Priori
Jinhong He, Minglong Xue, Wenhai Wang, Mingliang Zhou
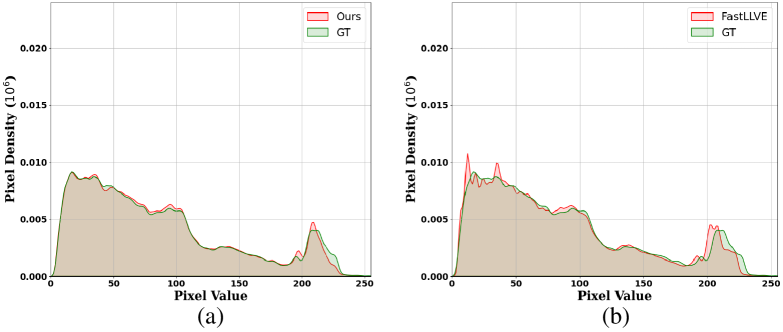
Low-light video enhancement is highly demanding in maintaining spatiotemporal color consistency. Therefore, improving the accuracy of color mapping and keeping the latency low is challenging. Based on this, we propose incorporating Wavelet-priori for 4D Lookup Table (WaveLUT), which effectively enhances the color coherence between video frames and the accuracy of color mapping while maintaining low latency. Specifically, we use the wavelet low-frequency domain to construct an optimized lookup prior and achieve an adaptive enhancement effect through a designed Wavelet-prior 4D lookup table. To effectively compensate the a priori loss in the low light region, we further explore a dynamic fusion strategy that adaptively determines the spatial weights based on the correlation between the wavelet lighting prior and the target intensity structure. In addition, during the training phase, we devise a text-driven appearance reconstruction method that dynamically balances brightness and content through multimodal semantics-driven Fourier spectra. Extensive experiments on a wide range of benchmark datasets show that this method effectively enhances the previous method's ability to perceive the color space and achieves metric-favorable and perceptually oriented real-time enhancement while maintaining high efficiency.
Read more9/16/2024

0
Taming Lookup Tables for Efficient Image Retouching
Sidi Yang, Binxiao Huang, Mingdeng Cao, Yatai Ji, Hanzhong Guo, Ngai Wong, Yujiu Yang
The widespread use of high-definition screens in edge devices, such as end-user cameras, smartphones, and televisions, is spurring a significant demand for image enhancement. Existing enhancement models often optimize for high performance while falling short of reducing hardware inference time and power consumption, especially on edge devices with constrained computing and storage resources. To this end, we propose Image Color Enhancement Lookup Table (ICELUT) that adopts LUTs for extremely efficient edge inference, without any convolutional neural network (CNN). During training, we leverage pointwise (1x1) convolution to extract color information, alongside a split fully connected layer to incorporate global information. Both components are then seamlessly converted into LUTs for hardware-agnostic deployment. ICELUT achieves near-state-of-the-art performance and remarkably low power consumption. We observe that the pointwise network structure exhibits robust scalability, upkeeping the performance even with a heavily downsampled 32x32 input image. These enable ICELUT, the first-ever purely LUT-based image enhancer, to reach an unprecedented speed of 0.4ms on GPU and 7ms on CPU, at least one order faster than any CNN solution. Codes are available at https://github.com/Stephen0808/ICELUT.
Read more7/16/2024


0
WB LUTs: Contrastive Learning for White Balancing Lookup Tables
Sai Kumar Reddy Manne, Michael Wan
Automatic white balancing (AWB), one of the first steps in an integrated signal processing (ISP) pipeline, aims to correct the color cast induced by the scene illuminant. An incorrect white balance (WB) setting or AWB failure can lead to an undesired blue or red tint in the rendered sRGB image. To address this, recent methods pose the post-capture WB correction problem as an image-to-image translation task and train deep neural networks to learn the necessary color adjustments at a lower resolution. These low resolution outputs are post-processed to generate high resolution WB corrected images, forming a bottleneck in the end-to-end run time. In this paper we present a 3D Lookup Table (LUT) based WB correction model called WB LUTs that can generate high resolution outputs in real time. We introduce a contrastive learning framework with a novel hard sample mining strategy, which improves the WB correction quality of baseline 3D LUTs by 25.5%. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed WB LUTs perform competitively against state-of-the-art models on two benchmark datasets while being 300 times faster using 12.7 times less memory. Our model and code are available at https://github.com/skrmanne/3DLUT_sRGB_WB.
Read more4/17/2024


0
Online Video Quality Enhancement with Spatial-Temporal Look-up Tables
Zefan Qu, Xinyang Jiang, Yifan Yang, Dongsheng Li, Cairong Zhao
Low latency rates are crucial for online video-based applications, such as video conferencing and cloud gaming, which make improving video quality in online scenarios increasingly important. However, existing quality enhancement methods are limited by slow inference speed and the requirement for temporal information contained in future frames, making it challenging to deploy them directly in online tasks. In this paper, we propose a novel method, STLVQE, specifically designed to address the rarely studied online video quality enhancement (Online-VQE) problem. Our STLVQE designs a new VQE framework which contains a Module-Agnostic Feature Extractor that greatly reduces the redundant computations and redesign the propagation, alignment, and enhancement module of the network. A Spatial-Temporal Look-up Tables (STL) is proposed, which extracts spatial-temporal information in videos while saving substantial inference time. To the best of our knowledge, we are the first to exploit the LUT structure to extract temporal information in video tasks. Extensive experiments on the MFQE 2.0 dataset demonstrate that our STLVQE achieves a satisfactory performance-speed trade-off.
Read more7/11/2024