Optimizing Multicarrier Multiantenna Systems for LoS Channel Charting

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- Examines how to optimize multicarrier multiantenna systems for line-of-sight (LoS) channel charting
- Focuses on dimensionality reduction and machine learning techniques to efficiently represent the LoS channel
- Proposes an approach to jointly optimize the transmitter and receiver design for channel charting
Plain English Explanation
This research paper looks at ways to improve the performance of wireless communication systems that use multiple antennas and multiple radio frequency carriers (known as multicarrier multiantenna systems). The key goal is to effectively channel charting, which means representing the wireless channel in a compact, low-dimensional form that captures the essential information.
The researchers are particularly interested in line-of-sight (LoS) channels, where there is a direct unobstructed path between the transmitter and receiver. They propose an approach to jointly optimize the transmitter and receiver design to enable efficient channel charting for LoS scenarios.
The core idea is to use dimensionality reduction and machine learning techniques to compress the information about the wireless channel into a low-dimensional representation. This allows the system to quickly and accurately track changes in the channel, which is useful for applications like channel estimation and beamforming.
Technical Explanation
The paper formulates the problem of optimizing multicarrier multiantenna systems for LoS channel charting. It starts by describing the system and channel models, which assume a LoS scenario with a single-bounce reflection path.
The key objective is to design the transmitter and receiver to jointly minimize the dimensionality of the channel representation while preserving the essential information. This is achieved through an optimization problem that considers both the transmitter precoding matrix and the receiver combining matrix.
The proposed approach leverages a dimensionality reduction technique called principal component analysis (PCA) to extract a low-dimensional subspace that captures the dominant channel characteristics. Machine learning is then used to learn a mapping between this subspace and the physical parameters of the environment, enabling efficient channel charting.
The paper presents numerical results demonstrating the effectiveness of the joint optimization approach compared to conventional strategies. It shows that the proposed method can significantly reduce the dimension of the channel representation while maintaining accurate tracking of the LoS channel variations.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a well-designed optimization framework for multicarrier multiantenna systems targeting LoS channel charting. The authors thoroughly address the key challenges, including the need for dimensionality reduction and the joint optimization of the transmitter and receiver.
One potential limitation is the assumption of a single-bounce reflection path, which may not capture the full complexity of real-world wireless channels. Extending the approach to handle more realistic multipath scenarios could be an area for future research.
Additionally, the paper does not extensively discuss the practical implementation considerations, such as the computational complexity of the proposed algorithms or the sensitivity to imperfect channel knowledge. These aspects could be valuable to assess the feasibility of deploying such systems in real-world applications.
Overall, the research makes a compelling case for the benefits of jointly optimizing multicarrier multiantenna systems for LoS channel charting, and the findings could have important implications for a range of wireless communication and sensing applications.
Conclusion
This paper presents a novel approach to optimizing multicarrier multiantenna systems for efficient line-of-sight (LoS) channel charting. By jointly designing the transmitter and receiver to leverage dimensionality reduction and machine learning techniques, the proposed method can significantly compress the representation of the LoS channel while maintaining accurate tracking of its variations.
The findings of this research could lead to improvements in various wireless communication and sensing applications, such as channel estimation, beamforming, and localization. The techniques developed in this paper could also be extended to address more complex multipath scenarios, further expanding the potential impact of this work.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Optimizing Multicarrier Multiantenna Systems for LoS Channel Charting
Taha Yassine (IRT b-com, Hypermedia), Luc Le Magoarou (INSA Rennes, IETR), Matthieu Crussi`ere (IETR), Stephane Paquelet (IRT b-com)
Channel charting (CC) consists in learning a mapping between the space of raw channel observations, made available from pilot-based channel estimation in multicarrier multiantenna system, and a low-dimensional space where close points correspond to channels of user equipments (UEs) close spatially. Among the different methods of learning this mapping, some rely on a distance measure between channel vectors. Such a distance should reliably reflect the local spatial neighborhoods of the UEs. The recently proposed phase-insensitive (PI) distance exhibits good properties in this regards, but suffers from ambiguities due to both its periodic and oscillatory aspects, making users far away from each other appear closer in some cases. In this paper, a thorough theoretical analysis of the said distance and its limitations is provided, giving insights on how they can be mitigated. Guidelines for designing systems capable of learning quality charts are consequently derived. Experimental validation is then conducted on synthetic and realistic data in different scenarios.
Read more7/24/2024


0
Global Scale Self-Supervised Channel Charting with Sensor Fusion
Omid Esrafilian, Mohsen Ahadi, Florian Kaltenberger, David Gesbert
The sensing and positioning capabilities foreseen in 6G have great potential for technology advancements in various domains, such as future smart cities and industrial use cases. Channel charting has emerged as a promising technology in recent years for radio frequency-based sensing and localization. However, the accuracy of these techniques is yet far behind the numbers envisioned in 6G. To reduce this gap, in this paper, we propose a novel channel charting technique capitalizing on the time of arrival measurements from surrounding Transmission Reception Points (TRPs) along with their locations and leveraging sensor fusion in channel charting by incorporating laser scanner data during the training phase of our algorithm. The proposed algorithm remains self-supervised during training and test phases, requiring no geometrical models or user position ground truth. Simulation results validate the achievement of a sub-meter level localization accuracy using our algorithm 90% of the time, outperforming the state-of-the-art channel charting techniques and the traditional triangulation-based approaches.
Read more5/8/2024

0
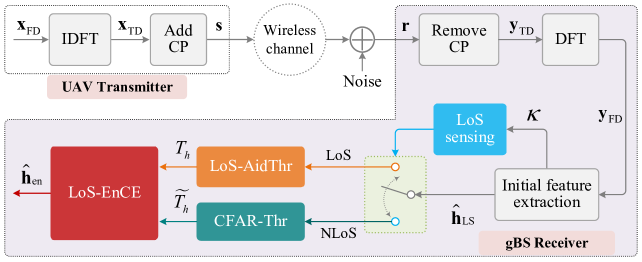
LoS Sensing-based Channel Estimation in UAV-Assisted OFDM Systems
Chaojin Qing, Zhiying Liu, Wenquan Hu, Yinjie Zhang, Xi Cai, Pengfei Du
In unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV)-assisted orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) systems, the potential advantage of the line-of-sight (LoS) path, characterized by its high probability of existence, has not been fully harnessed, thereby impeding the improvement of channel estimation (CE) accuracy. Inspired by the ideas of integrated sensing and communication (ISAC), this letter develops a LoS sensing method aimed at detecting the presence of LoS path. Leveraging the prior information obtained from LoS path detection, the detection thresholds for resolvable paths are proposed for LoS and Non-LoS (NLoS) scenarios, respectively. By employing these specifically designed detection thresholds, denoising processing is applied to classical least square (LS) CE, thereby improving the CE accuracy. Simulation results validate the effectiveness of the proposed method in enhancing CE accuracy and demonstrate its robustness against parameter variations.
Read more4/4/2024

0
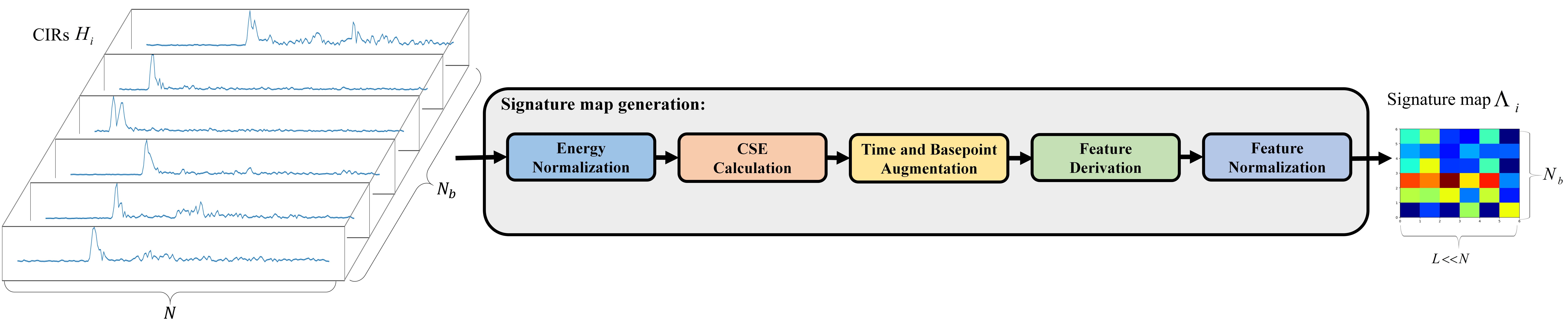
A Signature Based Approach Towards Global Channel Charting with Ultra Low Complexity
Longhai Zhao, Yunchuan Yang, Qi Xiong, He Wang, Bin Yu, Feifei Sun, Chengjun Sun
Channel charting, an unsupervised learning method that learns a low-dimensional representation from channel information to preserve geometrical property of physical space of user equipments (UEs), has drawn many attentions from both academic and industrial communities, because it can facilitate many downstream tasks, such as indoor localization, UE handover, beam management, and so on. However, many previous works mainly focus on charting that only preserves local geometry and use raw channel information to learn the chart, which do not consider the global geometry and are often computationally intensive and very time-consuming. Therefore, in this paper, a novel signature based approach for global channel charting with ultra low complexity is proposed. By using an iterated-integral based method called signature transform, a compact feature map and a novel distance metric are proposed, which enable channel charting with ultra low complexity and preserving both local and global geometry. We demonstrate the efficacy of our method using synthetic and open-source real-field datasets.
Read more4/1/2024