Optimizing Quantile-based Trading Strategies in Electricity Arbitrage
2406.13851

0
0
Abstract
Efficiently integrating renewable resources into electricity markets is vital for addressing the challenges of matching real-time supply and demand while reducing the significant energy wastage resulting from curtailments. To address this challenge effectively, the incorporation of storage devices can enhance the reliability and efficiency of the grid, improving market liquidity and reducing price volatility. In short-term electricity markets, participants navigate numerous options, each presenting unique challenges and opportunities, underscoring the critical role of the trading strategy in maximizing profits. This study delves into the optimization of day-ahead and balancing market trading, leveraging quantile-based forecasts. Employing three trading approaches with practical constraints, our research enhances forecast assessment, increases trading frequency, and employs flexible timestamp orders. Our findings underscore the profit potential of simultaneous participation in both day-ahead and balancing markets, especially with larger battery storage systems; despite increased costs and narrower profit margins associated with higher-volume trading, the implementation of high-frequency strategies plays a significant role in maximizing profits and addressing market challenges. Finally, we modelled four commercial battery storage systems and evaluated their economic viability through a scenario analysis, with larger batteries showing a shorter return on investment.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper explores the optimization of quantile-based trading strategies for electricity arbitrage, which involves buying and selling electricity at different times to take advantage of price differences.
- The researchers propose a novel approach to optimize these trading strategies using quantile regression, which can capture the full probability distribution of electricity prices rather than just the mean.
- The paper evaluates the performance of the quantile-based trading strategies on real-world electricity market data and compares them to traditional mean-based strategies.
Plain English Explanation
The paper is about finding the best ways to buy and sell electricity to make a profit, known as "electricity arbitrage." Electricity prices can fluctuate a lot, so traders try to take advantage of these price differences by buying electricity when it's cheap and selling it when it's more expensive.
The researchers in this paper tried a new approach to optimize these trading strategies. Instead of just looking at the average electricity price, they used a statistical technique called "quantile regression" to capture the full range of possible prices. This allows them to better understand the risks and potential rewards of different trading strategies.
By testing their quantile-based strategies on real-world electricity market data, the researchers found that they performed better than traditional strategies that only focus on the average price. This suggests that considering the full distribution of prices, not just the average, can lead to more successful electricity trading.
Technical Explanation
The paper proposes a novel approach to optimizing quantile-based trading strategies in electricity arbitrage. The researchers use quantile regression, a statistical technique that can model the entire probability distribution of electricity prices, rather than just the mean or average price.
This allows them to develop trading strategies that consider the full range of possible prices, rather than just targeting the expected or "average" price. The paper evaluates the performance of these quantile-based trading strategies on real-world electricity market data and compares them to traditional mean-based strategies.
The key insight is that by capturing the full probability distribution of prices, the quantile-based strategies can better navigate the risks and uncertainties inherent in electricity arbitrage. This allows them to outperform strategies that only focus on the average price.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a well-designed and thorough evaluation of the quantile-based trading strategies. However, the researchers acknowledge some limitations, such as the need to further investigate the impact of market liquidity and transaction costs on the strategies' performance.
Additionally, the paper does not address the potential for the strategies to be gamed or exploited by larger market participants. There may be concerns about the scalability and robustness of the approaches, especially in the face of changing market conditions or regulatory changes.
Further research could explore the generalizability of the findings to other energy trading markets or the potential for integrating the quantile-based strategies into sequential market clearing processes.
Conclusion
This paper presents a novel approach to optimizing quantile-based trading strategies for electricity arbitrage. By capturing the full probability distribution of electricity prices, rather than just the average, the researchers demonstrate that their strategies can outperform traditional mean-based approaches.
The findings suggest that considering the risks and uncertainties inherent in electricity markets can lead to more successful trading strategies. This has important implications for energy trading and market design, as well as for the broader field of quantitative finance and risk management.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
Energy Storage Arbitrage in Two-settlement Markets: A Transformer-Based Approach
Saud Alghumayjan, Jiajun Han, Ningkun Zheng, Ming Yi, Bolun Xu

0
0
This paper presents an integrated model for bidding energy storage in day-ahead and real-time markets to maximize profits. We show that in integrated two-stage bidding, the real-time bids are independent of day-ahead settlements, while the day-ahead bids should be based on predicted real-time prices. We utilize a transformer-based model for real-time price prediction, which captures complex dynamical patterns of real-time prices, and use the result for day-ahead bidding design. For real-time bidding, we utilize a long short-term memory-dynamic programming hybrid real-time bidding model. We train and test our model with historical data from New York State, and our results showed that the integrated system achieved promising results of almost a 20% increase in profit compared to only bidding in real-time markets, and at the same time reducing the risk in terms of the number of days with negative profits.
4/30/2024
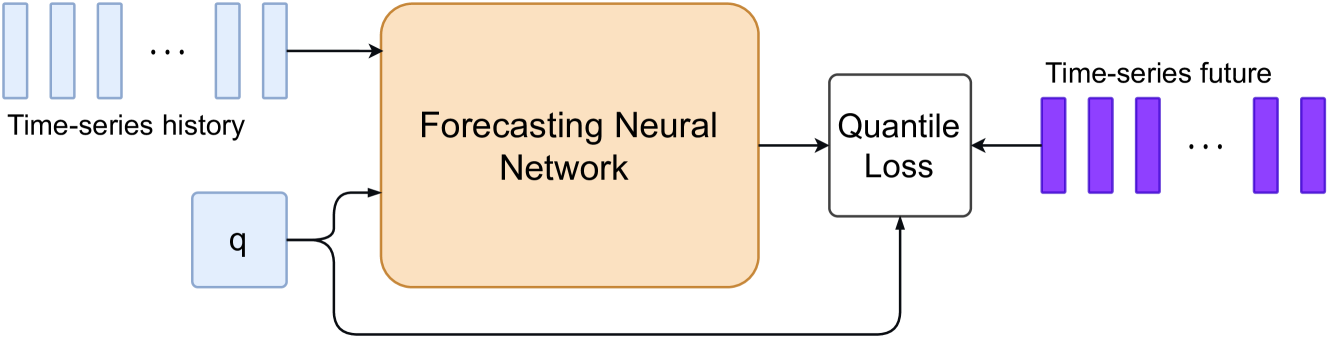
Any-Quantile Probabilistic Forecasting of Short-Term Electricity Demand
Slawek Smyl, Boris N. Oreshkin, Pawe{l} Pe{l}ka, Grzegorz Dudek

0
0
Power systems operate under uncertainty originating from multiple factors that are impossible to account for deterministically. Distributional forecasting is used to control and mitigate risks associated with this uncertainty. Recent progress in deep learning has helped to significantly improve the accuracy of point forecasts, while accurate distributional forecasting still presents a significant challenge. In this paper, we propose a novel general approach for distributional forecasting capable of predicting arbitrary quantiles. We show that our general approach can be seamlessly applied to two distinct neural architectures leading to the state-of-the-art distributional forecasting results in the context of short-term electricity demand forecasting task. We empirically validate our method on 35 hourly electricity demand time-series for European countries. Our code is available here: https://github.com/boreshkinai/any-quantile.
4/29/2024
⚙️
An adaptive standardisation methodology for Day-Ahead electricity price forecasting
Carlos Sebasti'an, Carlos E. Gonz'alez-Guill'en, Jes'us Juan

0
0
The study of Day-Ahead prices in the electricity market is one of the most popular problems in time series forecasting. Previous research has focused on employing increasingly complex learning algorithms to capture the sophisticated dynamics of the market. However, there is a threshold where increased complexity fails to yield substantial improvements. In this work, we propose an alternative approach by introducing an adaptive standardisation to mitigate the effects of dataset shifts that commonly occur in the market. By doing so, learning algorithms can prioritize uncovering the true relationship between the target variable and the explanatory variables. We investigate five distinct markets, including two novel datasets, previously unexplored in the literature. These datasets provide a more realistic representation of the current market context, that conventional datasets do not show. The results demonstrate a significant improvement across all five markets using the widely accepted learning algorithms in the literature (LEAR and DNN). In particular, the combination of the proposed methodology with the methodology previously presented in the literature obtains the best results. This significant advancement unveils new lines of research in this field, highlighting the potential of adaptive transformations in enhancing the performance of forecasting models.
4/29/2024
🌐
Feature-Driven Strategies for Trading Wind Power and Hydrogen
Emil Helgren, Jalal Kazempour, Lesia Mitridati

0
0
This paper develops a feature-driven model for hybrid power plants, enabling them to exploit available contextual information such as historical forecasts of wind power, and make optimal wind power and hydrogen trading decisions in the day-ahead stage. For that, we develop different variations of feature-driven linear policies, including a variation where policies depend on price domains, resulting in a price-quantity bidding curve. In addition, we propose a real-time adjustment strategy for hydrogen production. Our numerical results show that the final profit obtained from our proposed feature-driven trading mechanism in the day-ahead stage together with the real-time adjustment strategy is very close to that in an ideal benchmark with perfect information.
4/1/2024