OREO: O-RAN intElligence Orchestration of xApp-based network services

0
🌐
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- The paper introduces OREO, an O-RAN xApp orchestrator designed to efficiently manage the deployment of third-party applications (xApps) in Open Radio Access Network (O-RAN) architectures.
- O-RAN aims to support various network services, such as beam management and network slicing, through the use of xApps.
- Effectively orchestrating the deployment of these xApps is crucial for providing efficient network services at the radio interface.
Plain English Explanation
The paper presents a solution called OREO, which is designed to help manage the deployment of third-party applications (called xApps) in Open Radio Access Network (O-RAN) architectures. O-RAN is a new network architecture that aims to provide a wide range of network services, such as managing network signals (beam management) and creating separate network slices for different users or applications (network slicing).
To offer these services, O-RAN relies on xApps, which are like mini-programs that can be added to the network. However, efficiently deploying and managing these xApps is a complex challenge. The OREO system addresses this by using a multi-layer graph model to understand how the various components of the network (services, xApps, resources) are connected. This allows OREO to select the best combination of xApps to deploy, maximize the sharing of xApps between different services, and efficiently allocate computing resources to the xApps.
By doing this, OREO is able to deploy more network services (up to 35% more) using fewer xApps (around 30% fewer) and less computing resources, compared to other approaches. This helps make the O-RAN network more efficient and cost-effective.
Technical Explanation
The key idea behind OREO is that network services can share xApps whenever the xApps provide semantically equivalent functions and their output quality is sufficient to meet the service requirements. OREO leverages a multi-layer graph model to capture the relationships between all the system components, from services to xApps to computing resources.
Using this graph model, OREO implements an algorithmic solution that selects the optimal service configuration, maximizes the sharing of xApps, and efficiently allocates resources to the deployed xApps. The authors demonstrate through numerical results and experiments using a proof-of-concept implementation that OREO closely matches the performance of an optimal, but computationally complex, solution to this problem.
Compared to the state of the art, OREO is able to deploy up to 35% more services while using around 30% fewer xApps and a similar reduction in resource consumption. This improvement in efficiency and resource utilization is particularly important in the context of security concerns and potential issues with AI/ML-based configurations in O-RAN networks.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a comprehensive solution for orchestrating the deployment of xApps in O-RAN architectures, addressing a crucial challenge in realizing the benefits of this new network paradigm. The authors have thoughtfully designed OREO to maximize the sharing of xApps and optimize resource allocation, which are important for improving the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of O-RAN networks.
However, the paper does not discuss the potential impact of network traffic dynamics and patterns on the performance of OREO. Additionally, while the authors mention the importance of security and AI/ML-related concerns in O-RAN, they do not provide a deeper analysis of how OREO might address these issues.
Further research could explore the robustness of OREO's orchestration strategies under varying network conditions and investigate how the system could be enhanced to better manage security and AI/ML-related risks in O-RAN deployments.
Conclusion
The OREO xApp orchestrator presented in this paper is a significant contribution to the efficient management of O-RAN architectures. By leveraging a multi-layer graph model and optimizing the deployment of xApps, OREO demonstrates the ability to provide more network services using fewer resources, which is crucial for the successful adoption and operation of O-RAN networks. While the paper does not address all potential challenges, it lays the foundation for further research and development in this important area of network orchestration.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
🌐

0
OREO: O-RAN intElligence Orchestration of xApp-based network services
Federico Mungari, Corrado Puligheddu, Andres Garcia-Saavedra, Carla Fabiana Chiasserini
The Open Radio Access Network (O-RAN) architecture aims to support a plethora of network services, such as beam management and network slicing, through the use of third-party applications called xApps. To efficiently provide network services at the radio interface, it is thus essential that the deployment of the xApps is carefully orchestrated. In this paper, we introduce OREO, an O-RAN xApp orchestrator, designed to maximize the offered services. OREO's key idea is that services can share xApps whenever they correspond to semantically equivalent functions, and the xApp output is of sufficient quality to fulfill the service requirements. By leveraging a multi-layer graph model that captures all the system components, from services to xApps, OREO implements an algorithmic solution that selects the best service configuration, maximizes the number of shared xApps, and efficiently and dynamically allocates resources to them. Numerical results as well as experimental tests performed using our proof-of-concept implementation, demonstrate that OREO closely matches the optimum, obtained by solving an NP-hard problem. Further, it outperforms the state of the art, deploying up to 35% more services with an average of 30% fewer xApps and a similar reduction in the resource consumption.
Read more5/31/2024
🤔

0
Managing O-RAN Networks: xApp Development from Zero to Hero
Joao F. Santos, Alexandre Huff, Daniel Campos, Kleber V. Cardoso, Cristiano B. Both, Luiz A. DaSilva
The Open Radio Access Network (O-RAN) Alliance proposes an open architecture that disaggregates the RAN and supports executing custom control logic in near-real time from third-party applications, the xApps. Despite O-RAN's efforts, the creation of xApps remains a complex and time-consuming endeavor, aggravated by the sometimes fragmented, outdated, or deprecated documentation from the O-RAN Software Community (OSC). These challenges hinder academia and industry from developing and validating solutions and algorithms on O-RAN networks. This tutorial addresses this gap by providing the first comprehensive guide for developing xApps to manage the O-RAN ecosystem from theory to practice. We provide a thorough theoretical foundation of the O-RAN architecture and detail the functionality offered by Near Real-Time RAN Intelligent Controller (Near-RT RIC) components. We examine the xApp design and configuration. We explore the xApp lifecycle and demonstrate how to deploy and manage xApps on a Near-RT RIC. We address the xApps' interfaces and capabilities, accompanied by practical examples. We provide comprehensive details on how xApps can control the RAN. We discuss debugging strategies and good practices to aid the xApp developers in testing their xApps. Finally, we review the current landscape and open challenges for creating xApps.
Read more8/6/2024
👀

0
A Comprehensive Overview and Survey of O-RAN: Exploring Slicing-aware Architecture, Deployment Options, and Use Cases
Khurshid Alam, Mohammad Asif Habibi, Matthias Tammen, Dennis Krummacker, Walid Saad, Marco Di Renzo, Tommaso Melodia, Xavier Costa-P'erez, M'erouane Debbah, Ashutosh Dutta, Hans D. Schotten
Open-radio access network (O-RAN) seeks to establish principles of openness, programmability, automation, intelligence, and hardware-software disaggregation with interoperable interfaces. It advocates for multi-vendorism and multi-stakeholderism within a cloudified and virtualized wireless infrastructure, aimed at enhancing the deployment, operation, and maintenance of RAN architecture. This enhancement promises increased flexibility, performance optimization, service innovation, energy efficiency, and cost efficiency in fifth-generation (5G), sixth-generation (6G), and future networks. One of the key features of the O-RAN architecture is its support for network slicing, which entails interaction with other slicing domains within a mobile network, notably the transport network (TN) domain and the core network (CN) domain, to realize end-to-end (E2E) network slicing. The study of this feature requires exploring the stances and contributions of diverse standards development organizations (SDOs). In this context, we note that despite the ongoing industrial deployments and standardization efforts, the research and standardization communities have yet to comprehensively address network slicing in O-RAN. To address this gap, this survey paper provides a comprehensive exploration of network slicing in O-RAN through an in-depth review of specification documents from O-RAN Alliance and research papers from leading industry and academic institutions. The paper commences with an overview of the ongoing standardization efforts and open-source contributions associated with O-RAN, subsequently delving into the latest O-RAN architecture with an emphasis on its slicing aspects. Further, the paper explores deployment scenarios for network slicing within O-RAN, examining options for the deployment and orchestration of O-RAN and TN network slice subnets...
Read more5/9/2024
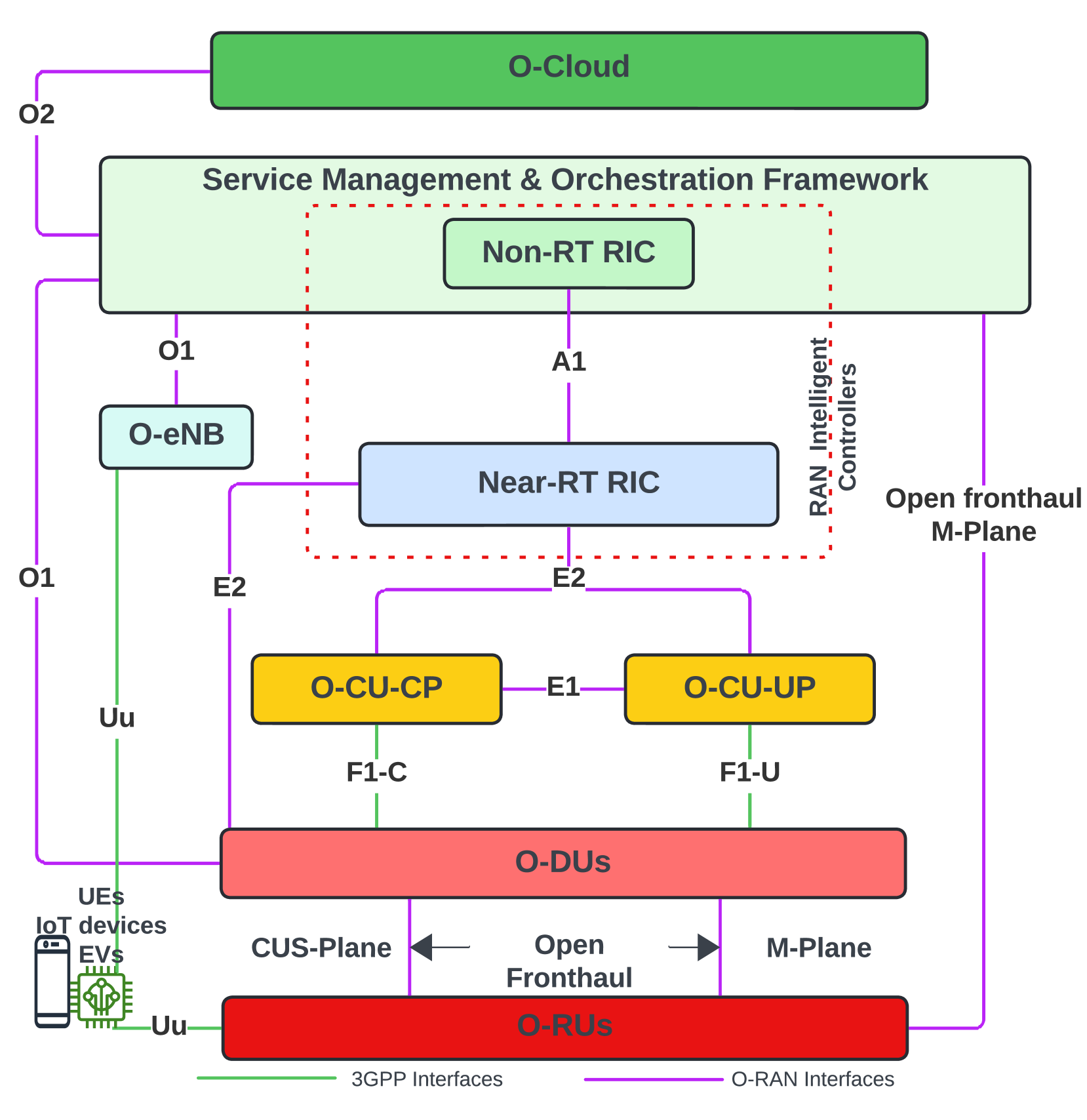

0
Exploiting and Securing ML Solutions in Near-RT RIC: A Perspective of an xApp
Thusitha Dayaratne, Viet Vo, Shangqi Lai, Sharif Abuadbba, Blake Haydon, Hajime Suzuki, Xingliang Yuan, Carsten Rudolph
Open Radio Access Networks (O-RAN) are emerging as a disruptive technology, revolutionising traditional mobile network architecture and deployments in the current 5G and the upcoming 6G era. Disaggregation of network architecture, inherent support for AI/ML workflows, cloud-native principles, scalability, and interoperability make O-RAN attractive to network providers for beyond-5G and 6G deployments. Notably, the ability to deploy custom applications, including Machine Learning (ML) solutions as xApps or rApps on the RAN Intelligent Controllers (RICs), has immense potential for network function and resource optimisation. However, the openness, nascent standards, and distributed architecture of O-RAN and RICs introduce numerous vulnerabilities exploitable through multiple attack vectors, which have not yet been fully explored. To address this gap and ensure robust systems before large-scale deployments, this work analyses the security of ML-based applications deployed on the RIC platform. We focus on potential attacks, defence mechanisms, and pave the way for future research towards a more robust RIC platform.
Read more6/19/2024