Pensieve Discuss: Scalable Small-Group CS Tutoring System with AI

0
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- The provided paper discusses a novel method for generating creative and engaging titles for research papers.
- The authors propose a template-based approach that leverages language models to generate a diverse set of title options.
- The paper includes a technical explanation of the proposed method, as well as a critical analysis of its strengths and limitations.
Plain English Explanation
Titling a research paper can be a challenging task, as the title needs to be attention-grabbing, informative, and accurately reflect the content of the study. The authors of this paper have developed a novel approach to address this challenge.
Their method involves using language models – advanced AI systems trained on vast amounts of text data – to generate a diverse set of potential titles. The authors provide authors with a template that guides the language model in crafting titles that are creative, relevant, and engaging.
The authors critically analyze the strengths and limitations of their approach, acknowledging that while it can produce innovative titles, there are still some challenges in ensuring the generated titles accurately capture the essence of the research. They also note that further refinement and testing of the method is needed.
Overall, this paper presents an intriguing approach to the age-old problem of titling research papers, leveraging the power of AI to assist authors in crafting titles that are more compelling and impactful.
Technical Explanation
The authors propose a template-based approach to generating creative paper titles using language models. Their method involves defining a set of template structures that guide the language model in generating title options. These templates include slots for inserting key concepts, phrases, or other elements that are tailored to the specific research paper.
The language model is then trained on a large corpus of existing paper titles and other relevant text data. When presented with a new research paper, the model can draw upon its training to fill in the template slots with appropriate and engaging title components.
The authors evaluate the performance of their approach by having it generate title options for a set of research papers and then assessing the creativity, relevance, and accuracy of the generated titles. They find that the template-based method outperforms more simplistic title generation approaches, though there is still room for improvement in ensuring the titles fully capture the essence of the underlying research.
Critical Analysis
The authors acknowledge several limitations and areas for further exploration in their research. One key challenge is ensuring the generated titles accurately reflect the content and significance of the research paper. While the template-based approach can produce creative and attention-grabbing titles, there is a risk that the titles may not fully align with the paper's core insights and contributions.
Additionally, the authors note that their evaluation methodology, while informative, could be further refined to better assess the real-world usefulness of the generated titles. Seeking feedback from actual researchers and journal editors could provide valuable insights into the practical applications and limitations of the proposed method.
Another area for further investigation is the potential biases and limitations of the language models used in the title generation process. As with any AI system, these models may perpetuate or amplify societal biases present in the training data, which could manifest in the titles they produce.
Despite these limitations, the authors' template-based approach represents a promising step forward in leveraging AI to assist researchers in crafting more compelling and impactful paper titles. As the authors suggest, continued refinement and testing of this method could lead to valuable advancements in the field of research paper titling and, ultimately, help to improve the visibility and impact of important scientific discoveries.
Conclusion
This paper presents a novel, AI-driven approach to generating creative and engaging titles for research papers. By leveraging language models and a template-based framework, the authors demonstrate a promising method for assisting researchers in crafting titles that are more attention-grabbing and reflective of the paper's core content and significance.
While the authors acknowledge several limitations and areas for further exploration, their work represents an important step forward in utilizing AI to enhance the research publication process. As the scientific community continues to grapple with the challenge of paper titling, this template-based approach could serve as a valuable tool for helping researchers create titles that more effectively communicate the value and impact of their work.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers

0
Pensieve Discuss: Scalable Small-Group CS Tutoring System with AI
Yoonseok Yang, Jack Liu, J. D. Zamfirescu-Pereira, John DeNero
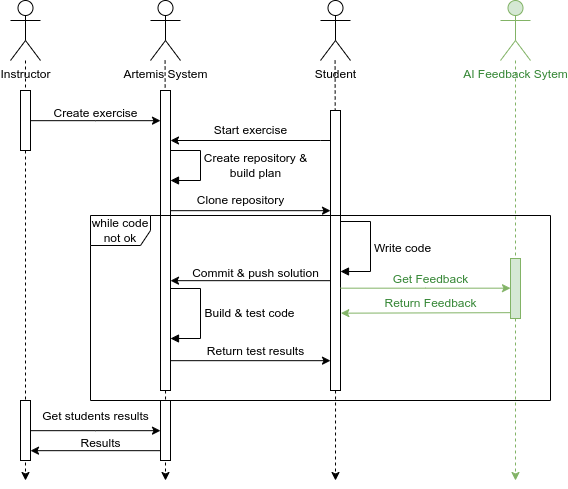
Small-group tutoring in Computer Science (CS) is effective, but presents the challenge of providing a dedicated tutor for each group and encouraging collaboration among group members at scale. We present Pensieve Discuss, a software platform that integrates synchronous editing for scaffolded programming problems with online human and AI tutors, designed to improve student collaboration and experience during group tutoring sessions. Our semester-long deployment to 800 students in a CS1 course demonstrated consistently high collaboration rates, positive feedback about the AI tutor's helpfulness and correctness, increased satisfaction with the group tutoring experience, and a substantial increase in question volume. The use of our system was preferred over an interface lacking AI tutors and synchronous editing capabilities. Our experiences suggest that small-group tutoring sessions are an important avenue for future research in educational AI.
Read more7/25/2024

0
AI-Tutoring in Software Engineering Education
Eduard Frankford, Clemens Sauerwein, Patrick Bassner, Stephan Krusche, Ruth Breu
With the rapid advancement of artificial intelligence (AI) in various domains, the education sector is set for transformation. The potential of AI-driven tools in enhancing the learning experience, especially in programming, is immense. However, the scientific evaluation of Large Language Models (LLMs) used in Automated Programming Assessment Systems (APASs) as an AI-Tutor remains largely unexplored. Therefore, there is a need to understand how students interact with such AI-Tutors and to analyze their experiences. In this paper, we conducted an exploratory case study by integrating the GPT-3.5-Turbo model as an AI-Tutor within the APAS Artemis. Through a combination of empirical data collection and an exploratory survey, we identified different user types based on their interaction patterns with the AI-Tutor. Additionally, the findings highlight advantages, such as timely feedback and scalability. However, challenges like generic responses and students' concerns about a learning progress inhibition when using the AI-Tutor were also evident. This research adds to the discourse on AI's role in education.
Read more4/8/2024


0
VizGroup: An AI-Assisted Event-Driven System for Real-Time Collaborative Programming Learning Analytics
Xiaohang Tang, Sam Wong, Kevin Pu, Xi Chen, Yalong Yang, Yan Chen
Programming instructors often conduct collaborative learning activities, like Peer Instruction, to foster a deeper understanding in students and enhance their engagement with learning. These activities, however, may not always yield productive outcomes due to the diversity of student mental models and their ineffective collaboration. In this work, we introduce VizGroup, an AI-assisted system that enables programming instructors to easily oversee students' real-time collaborative learning behaviors during large programming courses. VizGroup leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) to recommend event specifications for instructors so that they can simultaneously track and receive alerts about key correlation patterns between various collaboration metrics and ongoing coding tasks. We evaluated VizGroup with 12 instructors using a dataset collected from a Peer Instruction activity that was conducted in a large programming lecture. The results showed that compared to a version of VizGroup without the suggested units, VizGroup with suggested units helped instructors create additional monitoring units on previously undetected patterns on their own, covered a more diverse range of metrics, and influenced the participants' following notification creation strategies.
Read more4/16/2024
🤖

0
Intelligent Tutor: Leveraging ChatGPT and Microsoft Copilot Studio to Deliver a Generative AI Student Support and Feedback System within Teams
Wei-Yu Chen
This study explores the integration of the ChatGPT API with GPT-4 model and Microsoft Copilot Studio on the Microsoft Teams platform to develop an intelligent tutoring system. Designed to provide instant support to students, the system dynamically adjusts educational content in response to the learners' progress and feedback. Utilizing advancements in natural language processing and machine learning, it interprets student inquiries, offers tailored feedback, and facilitates the educational journey. Initial implementation highlights the system's potential in boosting students' motivation and engagement, while equipping educators with critical insights into the learning process, thus promoting tailored educational experiences and enhancing instructional effectiveness.
Read more5/24/2024