Performance Analysis for Deterministic System using Time Sensitive Network
2404.13639

0
0
🚀
Abstract
Modern technology necessitates the use of dependable, fast, and inexpensive networks as the backbone for data transmission. Switched Ethernet coupled with the Time Sensitive Networking
Create account to get full access
Overview
- The provided paper discusses the importance of dependable, fast, and inexpensive networks as the backbone for modern data transmission.
- It explores the use of Switched Ethernet coupled with Time Sensitive Networking (TSN) as a solution to meet these requirements.
Plain English Explanation
In today's world, we rely heavily on digital data transmission for a wide range of applications, from video streaming to industrial automation. To support these modern technologies, we need robust, high-speed, and cost-effective network infrastructure. The paper examines the potential of using Switched Ethernet coupled with Time Sensitive Networking (TSN) as a solution to meet these demands.
Switched Ethernet is a type of computer networking technology that efficiently routes data between devices, ensuring reliable and secure communication. TSN, on the other hand, is a set of standards that enhance Ethernet's capabilities to support time-critical applications, such as industrial automation and real-time video streaming. By integrating these two technologies, the researchers aim to create a robust and versatile network infrastructure that can cater to the diverse needs of modern data-driven applications.
Technical Explanation
The paper explores the advantages of using Switched Ethernet with TSN as the foundation for data transmission. Switched Ethernet provides a reliable and scalable data communication system, capable of handling high-volume data traffic with low latency. TSN, on the other hand, introduces mechanisms to ensure that time-sensitive data, such as control signals or real-time video, is prioritized and delivered within strict time constraints.
The researchers discuss the architectural design of this integrated system, highlighting the key components and their interactions. They also present experimental findings that demonstrate the performance and reliability of the proposed network infrastructure, particularly in terms of network control algorithms and video streaming applications.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a comprehensive overview of the potential benefits of using Switched Ethernet with TSN for modern data transmission. However, it is important to consider the potential limitations and challenges associated with this approach.
The researchers acknowledge the need for further optimization and refinement of the network control algorithms to ensure seamless integration and reliable performance across diverse application scenarios. Additionally, the scalability and cost-effectiveness of the proposed solution in large-scale deployments may require additional investigation.
It is also crucial to consider the interoperability and compatibility of the Switched Ethernet and TSN technologies with existing network infrastructures, as well as the potential impact on overall system complexity and maintenance requirements.
Conclusion
The paper highlights the growing importance of dependable, fast, and cost-effective network infrastructure to support the ever-increasing demand for reliable data transmission in modern technology. The integration of Switched Ethernet and Time Sensitive Networking presents a promising approach to address these requirements, offering a robust and versatile network solution capable of handling a wide range of data-driven applications.
While the research provides valuable insights and experimental evidence, further exploration and refinement of the proposed system are necessary to fully realize its potential and address any remaining challenges. Ongoing advancements in network technologies and their effective integration will be crucial in shaping the future of reliable and efficient data communication systems.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
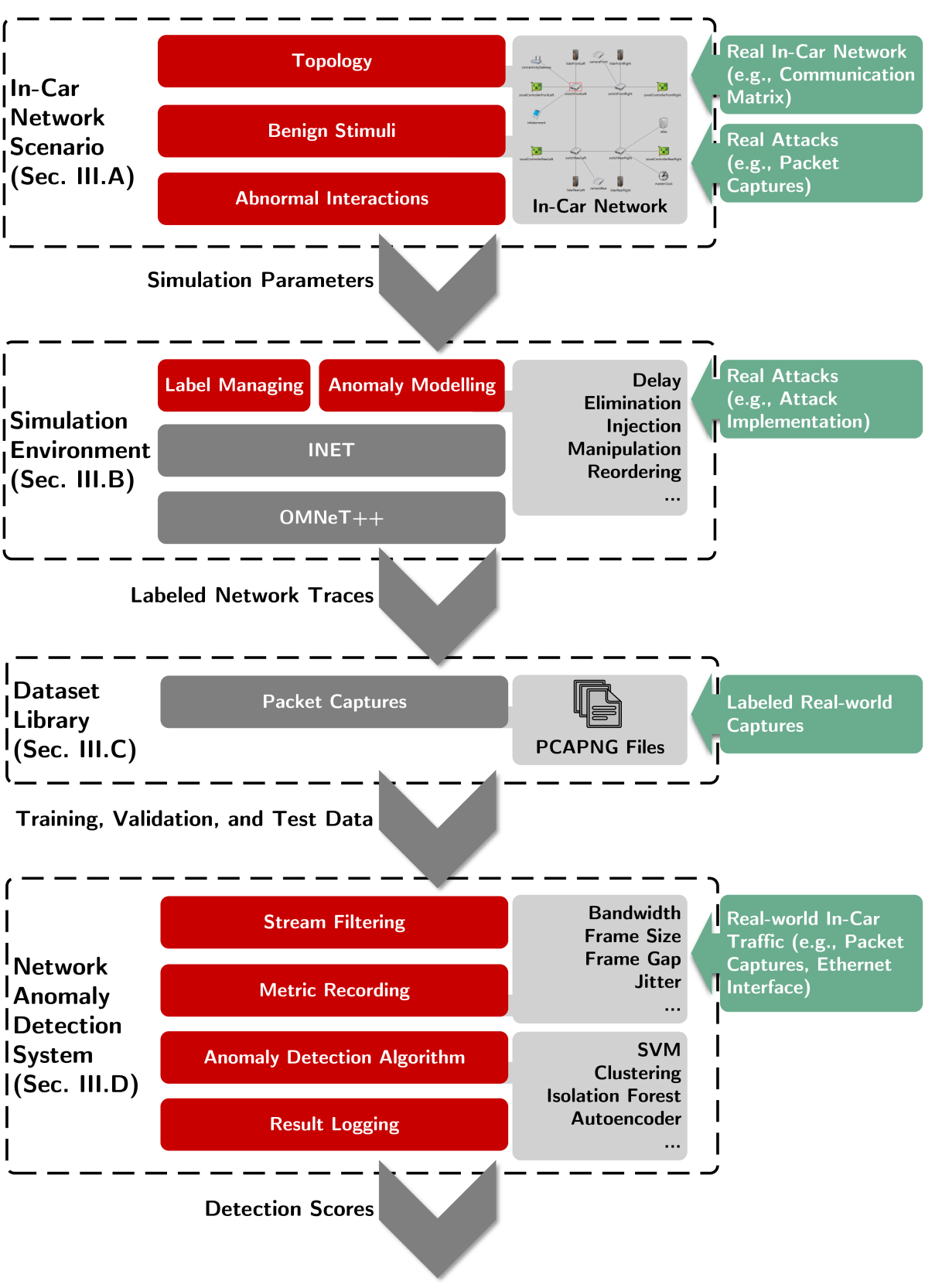
A Framework for the Systematic Assessment of Anomaly Detectors in Time-Sensitive Automotive Networks
Philipp Meyer, Timo Hackel, Teresa Lubeck, Franz Korf, Thomas C. Schmidt

0
0
Connected cars are susceptible to cyberattacks. Security and safety of future vehicles highly depend on a holistic protection of automotive components, of which the time-sensitive backbone network takes a significant role. These onboard Time-Sensitive Networks (TSNs) require monitoring for safety and -- as versatile platforms to host Network Anomaly Detection Systems (NADSs) -- for security. Still a thorough evaluation of anomaly detection methods in the context of hard real-time operations, automotive protocol stacks, and domain specific attack vectors is missing along with appropriate input datasets. In this paper, we present an assessment framework that allows for reproducible, comparable, and rapid evaluation of detection algorithms. It is based on a simulation toolchain, which contributes configurable topologies, traffic streams, anomalies, attacks, and detectors. We demonstrate the assessment of NADSs in a comprehensive in-vehicular network with its communication flows, on which we model traffic anomalies. We evaluate exemplary detection mechanisms and reveal how the detection performance is influenced by different combinations of TSN traffic flows and anomaly types. Our approach translates to other real-time Ethernet domains, such as industrial facilities, airplanes, and UAVs.
5/3/2024

On optimizing Inband Telemetry systems for accurate latency-based service deployments
Nataliia Koneva, Alfonso S'anchez-Maci'an, Jos'e Alberto Hern'andez, 'Oscar Gonz'alez de Dios

0
0
The power of Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence algorithms based on collected datasets, along with the programmability and flexibility provided by Software Defined Networking can provide the building blocks for constructing the so-called Zero-Touch Network and Service Management systems. However, the fuel towards this goal relies on the availability of sufficient and good-quality data collected from measurements and telemetry. This article provides a telemetry methodology to collect accurate latency measurements, as a first step toward building intelligent control planes that make correct decisions based on precise information.
6/24/2024
🚀
AI-based Dynamic Schedule Calculation in Time Sensitive Networks using GCN-TD3
Syed Tasnimul Islam, Anas Bin Muslim

0
0
Offline scheduling in Time Sensitive Networking (TSN) utilizing the Time Aware Shaper (TAS) facilitates optimal deterministic latency and jitter-bounds calculation for Time- Triggered (TT) flows. However, the dynamic nature of traffic in industrial settings necessitates a strategy for adaptively scheduling flows without interrupting existing schedules. Our research identifies critical gaps in current dynamic scheduling methods for TSN and introduces the novel GCN-TD3 approach. This novel approach utilizes a Graph Convolutional Network (GCN) for representing the various relations within different components of TSN and employs the Twin Delayed Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (TD3) algorithm to dynamically schedule any incoming flow. Additionally, an Integer Linear Programming (ILP) based offline scheduler is used both to initiate the simulation and serve as a fallback mechanism. This mechanism is triggered to recalculate the entire schedule when the predefined threshold of Gate Control List(GCL) length exceeds. Comparative analyses demonstrate that GCN-TD3 outperforms existing methods like Deep Double Q-Network (DDQN) and Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (DDPG), exhibiting convergence within 4000 epochs with a 90% dynamic TT flow admission rate while maintaining deadlines and reducing jitter to as low as 2us. Finally, two modules were developed for the OMNeT++ simulator, facilitating dynamic simulation to evaluate the methodology.
5/9/2024

Distributed Simulation for Digital Twins of Large-Scale Real-World DiffServ-Based Networks
Zhuoyao Huang, Nan Zhang, Jingran Shen, Georgios Diamantopoulos, Zhengchang Hua, Nikos Tziritas, Georgios Theodoropoulos

0
0
Digital Twin technology facilitates the monitoring and online analysis of large-scale communication networks. Faster predictions of network performance thus become imperative, especially for analysing Quality of Service (QoS) parameters in large-scale city networks. Discrete Event Simulation (DES) is a standard network analysis technology, and can be further optimised with parallel and distributed execution for speedup, referred to as Parallel Discrete Event Simulation (PDES). However, modelling detailed QoS mechanisms such as DiffServ requires complex event handling for each network router, which can involve excessive simulation events. In addition, current PDES for network analysis mostly adopts conservative scheduling, which suffers from excessive global synchronisation to avoid causality problems. The performance analysis of optimistic PDES for real-world large-scale network topology and complex QoS mechanisms is still inadequate. To address these gaps, this paper proposes a simulation toolkit, Quaint, which leverages an optimistic PDES engine ROSS, for detailed modelling of DiffServ-based networks. A novel event-handling model for each network router is also proposed to significantly reduce the number of events in complex QoS modelling. Quaint has been evaluated using a real-world metropolitan-scale network topology with 5,000 routers/switches. Results show that compared to the conventional simulator OMNeT++/INET, even the sequential mode of Quaint can achieve a speedup of 53 times, and the distributed mode has a speedup of 232 times. Scalability characterisation is conducted to portray the efficiency of distributed execution, and the results indicate the future direction for workload-aware model partitioning.
6/3/2024