Performance Analysis of Underwater Acoustic Channel Amid Jamming by Random Jammers

0
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- This paper analyzes the performance of underwater acoustic communication channels under jamming attacks by random jammers.
- The researchers use stochastic geometry and Poisson point process models to study the availability, coverage, energy efficiency, and average rate of the underwater acoustic communication system.
- They consider different scenarios, including a baseline without jamming, jamming by a single jammer, and jamming by multiple random jammers.
Plain English Explanation
The paper looks at how underwater communication systems perform when they are being attacked by random jammers. Underwater communication is important for things like monitoring the ocean, controlling underwater vehicles, and enabling communication between submarines. However, these systems can be disrupted by malicious actors who try to jam or block the communication signals.
The researchers used advanced mathematical models, like stochastic geometry and Poisson point processes, to study different jamming scenarios. They looked at how available the communication channel is, how much area it can cover, how energy-efficient it is, and how fast the average data rate is. They compared a baseline scenario without any jamming to cases with a single jammer and multiple random jammers.
Technical Explanation
The authors use stochastic geometry and Poisson point process models to analyze the performance of an underwater acoustic communication system in the presence of random jammers. They consider three scenarios: no jamming, jamming by a single jammer, and jamming by multiple random jammers distributed according to a Poisson point process.
For each scenario, the authors evaluate four key performance metrics:
- Availability: The probability that the communication channel is available for use.
- Coverage: The area over which the communication system can provide service.
- Energy efficiency: The ratio of the average rate to the total transmit power.
- Average rate: The mean achievable data rate.
The authors derive analytical expressions for these metrics and study how they are affected by the system parameters, such as the transmit power, the number of jammers, and the intensity of the jammer distribution.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a thorough analysis of the impact of random jammers on the performance of underwater acoustic communication systems. The use of stochastic geometry and Poisson point process models allows the authors to obtain analytical expressions for the key performance metrics, which can provide guidance for system design and optimization.
However, the paper does not consider some practical factors that may affect the system performance, such as the mobility of the communication nodes and the jammers, the impact of environmental conditions on the acoustic channel, and the potential for adaptive or intelligent jamming strategies. Additionally, the paper does not explore the trade-offs between the different performance metrics, which could be valuable for system designers.
Further research could investigate the integration of underwater acoustic communication with other wireless technologies, as explored in the paper "Securing Hybrid Wireless Body Area Networks (HyWBAN)", or the use of advanced signal processing techniques for underwater target recognition, as discussed in the paper "Underwater Acoustic Target Recognition Based on Smoothness-Inducing Priors"](https://aimodels.fyi/papers/arxiv/underwater-acoustic-target-recognition-based-smoothness-inducing).
Conclusion
This paper provides a comprehensive analysis of the performance of underwater acoustic communication systems under jamming attacks by random jammers. The researchers use advanced mathematical models to derive analytical expressions for key performance metrics, such as availability, coverage, energy efficiency, and average rate. Their findings can inform the design of jamming-resilient underwater communication systems, which are critical for a wide range of applications, from ocean monitoring to submarine communications.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Performance Analysis of Underwater Acoustic Channel Amid Jamming by Random Jammers
Waqas Aman, Saif Al-Kuwari, Marwa Qaraqe
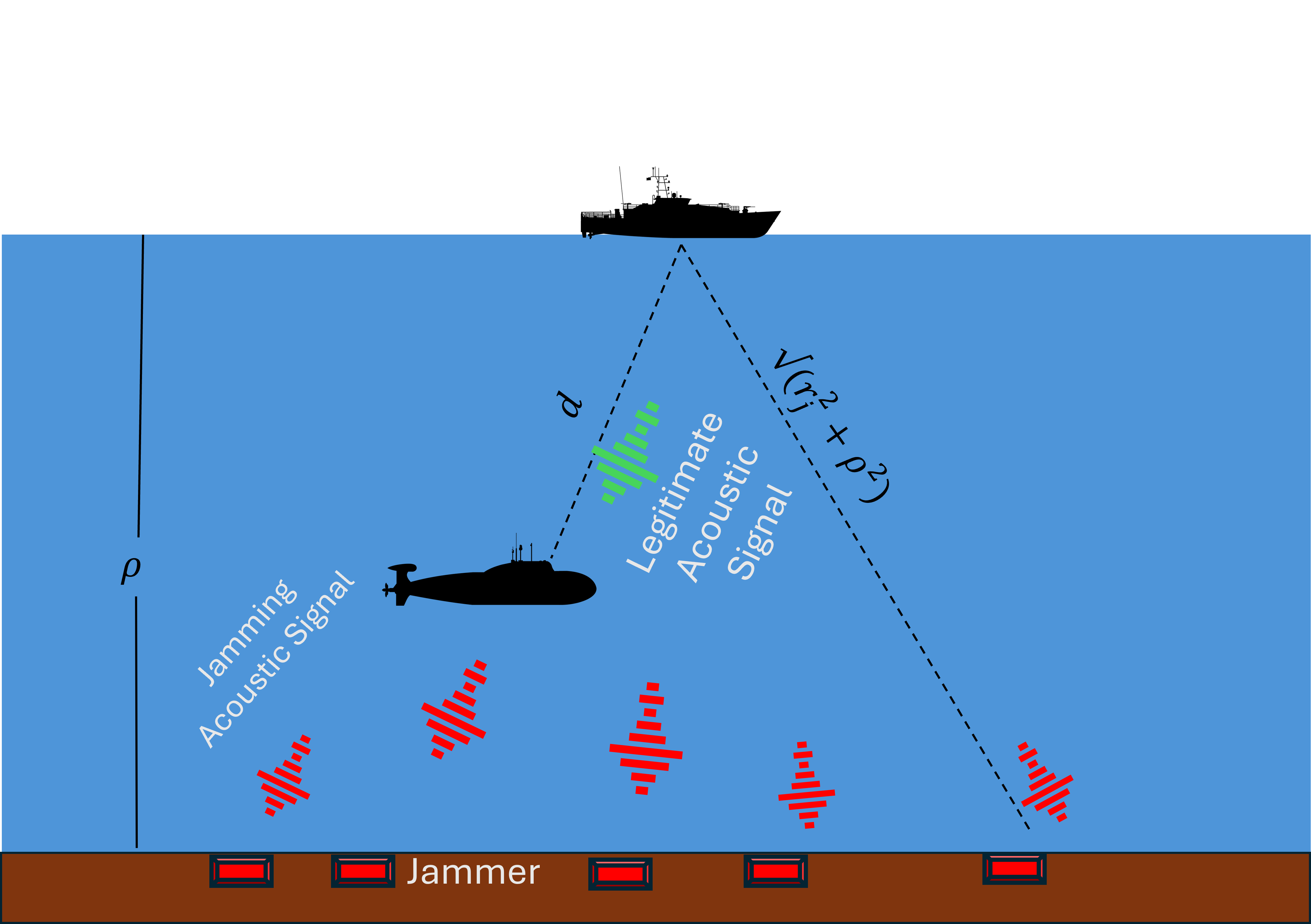
Underwater communication networks are increasingly popularized by various important maritime applications. However, this also leads to an increased threat landscape. This letter presents the first study that considers jamming attacks by random jammers present in the surroundings of legitimate transceivers in underwater acoustic communication systems. We investigate the impact of jamming attacks on various performance parameters of the legitimate underwater acoustic communication link. In particular, we investigate the legitimate link using stochastic geometry for important performance parameters, namely coverage probability, average rate, and energy efficiency of the link between two legitimate nodes, i.e., underwater and surface nodes. We then derive and present tractable expressions for these performance parameters. Finally, we performed a Monte Carlo simulation to validate our analysis. We plot the performance metrics against the transmit power, and jamming power for different intensities of the jammers in shallow, mid, and deep water scenarios. Results reveal that on average, jamming in deep water has a relatively high impact on the performance of legitimate link than in shallow water.
Read more5/7/2024


0
Underwater Acoustic Signal Denoising Algorithms: A Survey of the State-of-the-art
Ruobin Gao, Maohan Liang, Heng Dong, Xuewen Luo, P. N. Suganthan
This paper comprehensively reviews recent advances in underwater acoustic signal denoising, an area critical for improving the reliability and clarity of underwater communication and monitoring systems. Despite significant progress in the field, the complex nature of underwater environments poses unique challenges that complicate the denoising process. We begin by outlining the fundamental challenges associated with underwater acoustic signal processing, including signal attenuation, noise variability, and the impact of environmental factors. The review then systematically categorizes and discusses various denoising algorithms, such as conventional, decomposition-based, and learning-based techniques, highlighting their applications, advantages, and limitations. Evaluation metrics and experimental datasets are also reviewed. The paper concludes with a list of open questions and recommendations for future research directions, emphasizing the need for developing more robust denoising techniques that can adapt to the dynamic underwater acoustic environment.
Read more7/19/2024
🌐

0
A Multi-hop Secure UWOC assisted Local Area Network for UIoT and Underwater Monitoring
Maaz Salman, Javad Bolboli, Wan-Young Chung
Underwater environment is substantially less explored territory as compared to earth surface due to lack of robust underwater communication infrastructure. For Internet of Underwater things connectivity, underwater wireless optical communication can play a vital role, compared to conventional radio frequency communication, due to longer range, high data rate, low latency, and unregulated bandwidth. This study proposes underwater wireless optical communication driven local area network UWOC LAN, comprised of multiple network nodes with optical transceivers. Moreover, the temperature sensor data is encapsulated with individual authentication identity to enhance the security of the framework at the user end. The proposed system is evaluated in a specially designed water tank of 4 meters. The proposed system evaluation analysis shows that the system can transmit underwater temperature data reliably in real time. The proposed secure UWOC LAN is tested within a communication range of 16 meters by incorporating multi hop connectivity to monitor the underwater environment.
Read more4/1/2024


0
Jamming Intrusions in Extreme Bandwidth Communication: A Comprehensive Overview
Richa Priyadarshani, Ki-Hong Park, Yalcin Ata, Mohamed-Slim Alouini
As the evolution of wireless communication progresses towards 6G networks, extreme bandwidth communication (EBC) emerges as a key enabler to meet the ambitious key performance indicator set for this next-generation technology. 6G aims for peak data rates of 1 Tb/s, peak spectral efficiency of 60 b/s/Hz, maximum bandwidth of 100 GHz, and mobility support up to 1000 km/h, while maintaining a high level of security. The capability of 6G to manage enormous data volumes introduces heightened security vulnerabilities, such as jamming attacks, highlighting the critical need for in-depth research into jamming in EBC. Understanding these attacks is vital for developing robust countermeasures, ensuring 6G networks can maintain their integrity and reliability amidst these advanced threats. Recognizing the paramount importance of security in 6G applications, this survey paper explores prevalent jamming attacks and the corresponding countermeasures in EBC technologies such as millimeter wave, terahertz, free-space optical, and visible light communications. By comprehensively reviewing the literature on jamming in EBC, this survey paper aims to provide a valuable resource for researchers, engineers, and policymakers involved in the development and deployment of 6G networks. Understanding the nuances of jamming in different EBC technologies is essential for devising robust security mechanisms and ensuring the success of 6G communication systems in the face of emerging threats.
Read more4/1/2024