Personal LLM Agents: Insights and Survey about the Capability, Efficiency and Security
2401.05459

0
0

Abstract
Since the advent of personal computing devices, intelligent personal assistants (IPAs) have been one of the key technologies that researchers and engineers have focused on, aiming to help users efficiently obtain information and execute tasks, and provide users with more intelligent, convenient, and rich interaction experiences. With the development of smartphones and IoT, computing and sensing devices have become ubiquitous, greatly expanding the boundaries of IPAs. However, due to the lack of capabilities such as user intent understanding, task planning, tool using, and personal data management etc., existing IPAs still have limited practicality and scalability. Recently, the emergence of foundation models, represented by large language models (LLMs), brings new opportunities for the development of IPAs. With the powerful semantic understanding and reasoning capabilities, LLM can enable intelligent agents to solve complex problems autonomously. In this paper, we focus on Personal LLM Agents, which are LLM-based agents that are deeply integrated with personal data and personal devices and used for personal assistance. We envision that Personal LLM Agents will become a major software paradigm for end-users in the upcoming era. To realize this vision, we take the first step to discuss several important questions about Personal LLM Agents, including their architecture, capability, efficiency and security. We start by summarizing the key components and design choices in the architecture of Personal LLM Agents, followed by an in-depth analysis of the opinions collected from domain experts. Next, we discuss several key challenges to achieve intelligent, efficient and secure Personal LLM Agents, followed by a comprehensive survey of representative solutions to address these challenges.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- Explores the capabilities, efficiency, and security of personal LLM (large language model) agents
- Provides a historical overview of the development of intelligent personal assistants
- Discusses the technical details and insights from recent research on LLM-based autonomous agents
Plain English Explanation
This paper examines the current state of personal LLM (large language model) agents - software programs that use advanced language models to assist and interact with people. The researchers start by tracing the history of intelligent personal assistants, from early voice-controlled systems to modern AI-powered virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa.
They then dive into the technical details of recent research on LLM-based autonomous agents. These are systems that can understand natural language, reason about tasks, and take actions to help users, all powered by large language models. The paper explores the capabilities, efficiency, and security of these agents, looking at how well they can assist with various tasks, how resource-intensive they are to run, and how they can be made more secure and reliable.
Overall, the paper provides insights into the current state of the technology and highlights both the promise and the challenges of using LLMs to create intelligent personal assistants that can truly understand and assist humans in meaningful ways.
Technical Explanation
The paper begins by tracing the history of intelligent personal assistants, from early voice-controlled systems in the 1960s to modern AI-powered virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa. It then focuses on the recent development of LLM-based autonomous agents, which use large language models to understand natural language, reason about tasks, and take actions to assist users.
The researchers examine the capabilities of these agents, looking at how well they can perform a variety of tasks, from answering questions to completing complex workflows. They also investigate the efficiency of the systems, considering the computational resources required to run them and the trade-offs between performance and resource usage.
Finally, the paper explores the security aspects of personal LLM agents, discussing strategies for ensuring that they are reliable, trustworthy, and secure in their interactions with users.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a comprehensive overview of the current state of personal LLM agents, highlighting both the impressive capabilities of these systems and the significant challenges that researchers and developers still face. One potential limitation is that the analysis is largely based on existing research, and the authors do not present any new experimental results or novel approaches.
Additionally, the paper does not delve deeply into the broader societal implications of widespread adoption of intelligent personal assistants, such as issues of privacy, data security, and the potential displacement of human labor. These are important considerations that warrant further exploration and discussion.
Overall, the paper is a valuable resource for anyone interested in the current state of personal LLM agents and the future direction of this rapidly evolving field. However, readers should be encouraged to think critically about the research and consider the broader implications of this technology as it continues to advance.
Conclusion
This paper provides a comprehensive overview of the current state of personal LLM agents, exploring their capabilities, efficiency, and security. The researchers trace the history of intelligent personal assistants and then dive into the technical details of recent research on LLM-based autonomous agents.
The insights and analysis presented in this paper highlight both the promise and the challenges of using large language models to create intelligent personal assistants that can truly understand and assist humans in meaningful ways. As the technology continues to evolve, it will be important to consider the broader societal implications and to encourage critical thinking about the role of these systems in our lives.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
🤿
Human-Centered LLM-Agent User Interface: A Position Paper
Daniel Chin, Yuxuan Wang, Gus Xia

0
0
Large Language Model (LLM) -in-the-loop applications have been shown to effectively interpret the human user's commands, make plans, and operate external tools/systems accordingly. Still, the operation scope of the LLM agent is limited to passively following the user, requiring the user to frame his/her needs with regard to the underlying tools/systems. We note that the potential of an LLM-Agent User Interface (LAUI) is much greater. A user mostly ignorant to the underlying tools/systems should be able to work with a LAUI to discover an emergent workflow. Contrary to the conventional way of designing an explorable GUI to teach the user a predefined set of ways to use the system, in the ideal LAUI, the LLM agent is initialized to be proficient with the system, proactively studies the user and his/her needs, and proposes new interaction schemes to the user. To illustrate LAUI, we present Flute X GPT, a concrete example using an LLM agent, a prompt manager, and a flute-tutoring multi-modal software-hardware system to facilitate the complex, real-time user experience of learning to play the flute.
5/24/2024
💬
A Survey on Large Language Model based Autonomous Agents
Lei Wang, Chen Ma, Xueyang Feng, Zeyu Zhang, Hao Yang, Jingsen Zhang, Zhiyuan Chen, Jiakai Tang, Xu Chen, Yankai Lin, Wayne Xin Zhao, Zhewei Wei, Ji-Rong Wen

0
0
Autonomous agents have long been a prominent research focus in both academic and industry communities. Previous research in this field often focuses on training agents with limited knowledge within isolated environments, which diverges significantly from human learning processes, and thus makes the agents hard to achieve human-like decisions. Recently, through the acquisition of vast amounts of web knowledge, large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable potential in achieving human-level intelligence. This has sparked an upsurge in studies investigating LLM-based autonomous agents. In this paper, we present a comprehensive survey of these studies, delivering a systematic review of the field of LLM-based autonomous agents from a holistic perspective. More specifically, we first discuss the construction of LLM-based autonomous agents, for which we propose a unified framework that encompasses a majority of the previous work. Then, we present a comprehensive overview of the diverse applications of LLM-based autonomous agents in the fields of social science, natural science, and engineering. Finally, we delve into the evaluation strategies commonly used for LLM-based autonomous agents. Based on the previous studies, we also present several challenges and future directions in this field. To keep track of this field and continuously update our survey, we maintain a repository of relevant references at https://github.com/Paitesanshi/LLM-Agent-Survey.
4/5/2024
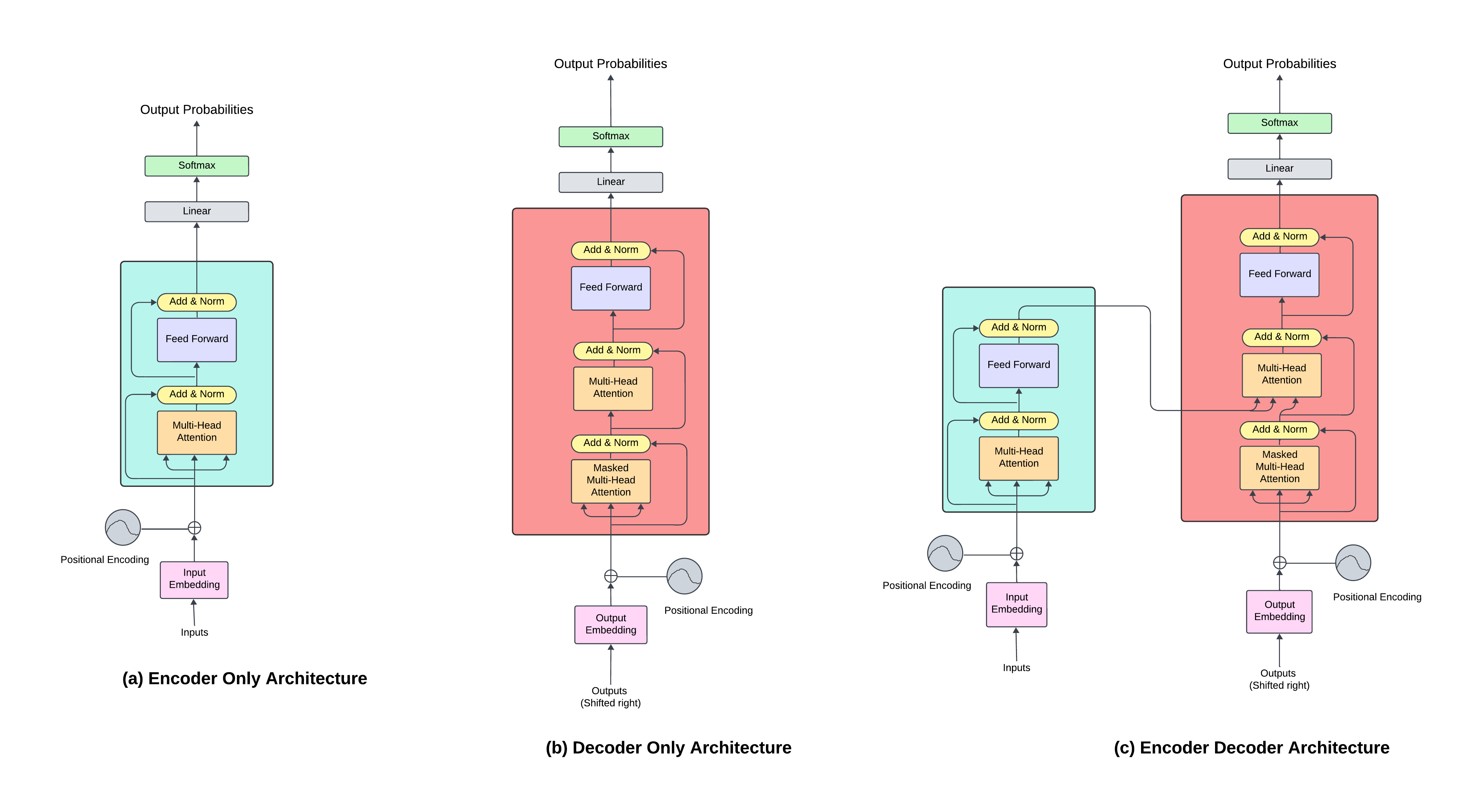
Exploring Autonomous Agents through the Lens of Large Language Models: A Review
Saikat Barua

0
0
Large Language Models (LLMs) are transforming artificial intelligence, enabling autonomous agents to perform diverse tasks across various domains. These agents, proficient in human-like text comprehension and generation, have the potential to revolutionize sectors from customer service to healthcare. However, they face challenges such as multimodality, human value alignment, hallucinations, and evaluation. Techniques like prompting, reasoning, tool utilization, and in-context learning are being explored to enhance their capabilities. Evaluation platforms like AgentBench, WebArena, and ToolLLM provide robust methods for assessing these agents in complex scenarios. These advancements are leading to the development of more resilient and capable autonomous agents, anticipated to become integral in our digital lives, assisting in tasks from email responses to disease diagnosis. The future of AI, with LLMs at the forefront, is promising.
4/9/2024
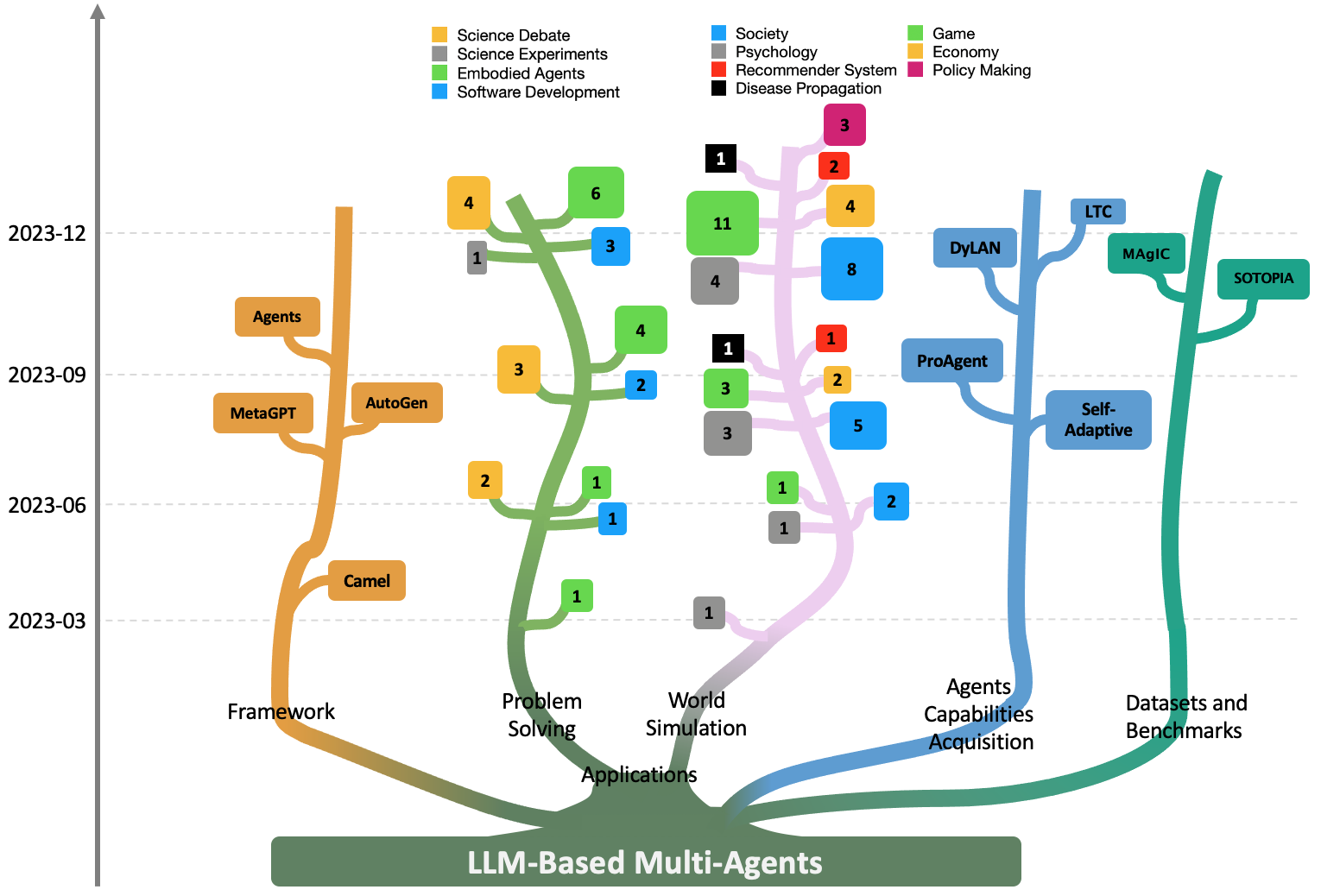
Large Language Model based Multi-Agents: A Survey of Progress and Challenges
Taicheng Guo, Xiuying Chen, Yaqi Wang, Ruidi Chang, Shichao Pei, Nitesh V. Chawla, Olaf Wiest, Xiangliang Zhang

0
0
Large Language Models (LLMs) have achieved remarkable success across a wide array of tasks. Due to the impressive planning and reasoning abilities of LLMs, they have been used as autonomous agents to do many tasks automatically. Recently, based on the development of using one LLM as a single planning or decision-making agent, LLM-based multi-agent systems have achieved considerable progress in complex problem-solving and world simulation. To provide the community with an overview of this dynamic field, we present this survey to offer an in-depth discussion on the essential aspects of multi-agent systems based on LLMs, as well as the challenges. Our goal is for readers to gain substantial insights on the following questions: What domains and environments do LLM-based multi-agents simulate? How are these agents profiled and how do they communicate? What mechanisms contribute to the growth of agents' capacities? For those interested in delving into this field of study, we also summarize the commonly used datasets or benchmarks for them to have convenient access. To keep researchers updated on the latest studies, we maintain an open-source GitHub repository, dedicated to outlining the research on LLM-based multi-agent systems.
4/22/2024