Photonic Quantum Computers

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- Photonic quantum computers use light-based technology to perform quantum computations.
- Several companies and research teams are working on developing photonic quantum computing platforms, including iPronics, Quandela, ORCA, Xanadu, Jiuzhang, PsiQuantum, Quix Quantum, TundraSystems, TuringQ, QBoson, and Hamamatsu.
- Photonic quantum computing offers potential advantages over traditional electronic quantum computers, such as scalability, low energy consumption, and high-speed operation.
Plain English Explanation
Quantum computers use the strange laws of quantum physics to perform calculations much faster than classical computers. Photonic quantum computers are a type of quantum computer that use light, rather than electricity, to manipulate quantum information.
Several companies and research teams are working on developing these light-based quantum computing platforms. Some of the key players in this field include iPronics, Quandela, ORCA, Xanadu, Jiuzhang, PsiQuantum, Quix Quantum, TundraSystems, TuringQ, QBoson, and Hamamatsu.
Photonic quantum computers have some potential advantages over traditional electronic quantum computers. They may be more scalable, meaning they can be made larger and more powerful. They also have the potential to be more energy-efficient and operate at very high speeds. This makes them an attractive option for future quantum computing applications.
Technical Explanation
The research paper discusses the promising field of photonic quantum computing. In this approach, quantum information is encoded and processed using light, rather than the electronic circuits used in traditional quantum computers.
Several leading companies and research teams are working to develop photonic quantum computing platforms. For example, iPronics is developing programmable photonic circuits, while Quandela, ORCA, and Xanadu are exploring the use of photons for quantum information processing. Other notable players include Jiuzhang, PsiQuantum, Quix Quantum, TundraSystems, TuringQ, QBoson, and Hamamatsu.
Photonic quantum computers offer some potential advantages over electronic quantum computers. They may be more scalable, as it is easier to integrate large numbers of optical components on a chip. They also have the potential for very low energy consumption and high-speed operation, as photons can transmit information much faster than electrons. These attributes make photonic quantum computers an attractive option for future large-scale quantum computing applications.
Critical Analysis
The research paper provides a high-level overview of the photonic quantum computing field, highlighting the key players and potential advantages of this approach. However, it does not delve into the specific technical details or experimental results of the various research efforts.
One potential limitation is that the paper does not address the significant engineering challenges involved in building large-scale, fault-tolerant photonic quantum computers. Issues like photon loss, crosstalk, and the development of high-quality single-photon sources and detectors will need to be overcome before photonic quantum computers can become a practical reality.
Additionally, the paper does not compare the relative merits of photonic quantum computing to other quantum computing approaches, such as superconducting or trapped-ion systems. A more in-depth analysis of the tradeoffs and challenges of each platform would be helpful for assessing the long-term viability of photonic quantum computing.
Overall, the paper serves as a useful introduction to the field of photonic quantum computing and the key players involved. However, further research and development will be necessary to fully realize the potential of this technology.
Conclusion
Photonic quantum computers are an emerging field of quantum computing that use light-based technology to perform quantum computations. Several companies and research teams are working to develop these platforms, which offer potential advantages like scalability, energy efficiency, and high-speed operation.
While the paper provides a high-level overview of the photonic quantum computing landscape, significant engineering challenges remain to be solved before this technology can become a practical reality. Ongoing research and development in areas like photon sources, detectors, and integrated photonic circuits will be crucial for advancing the field of photonic quantum computing and realizing its full potential.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
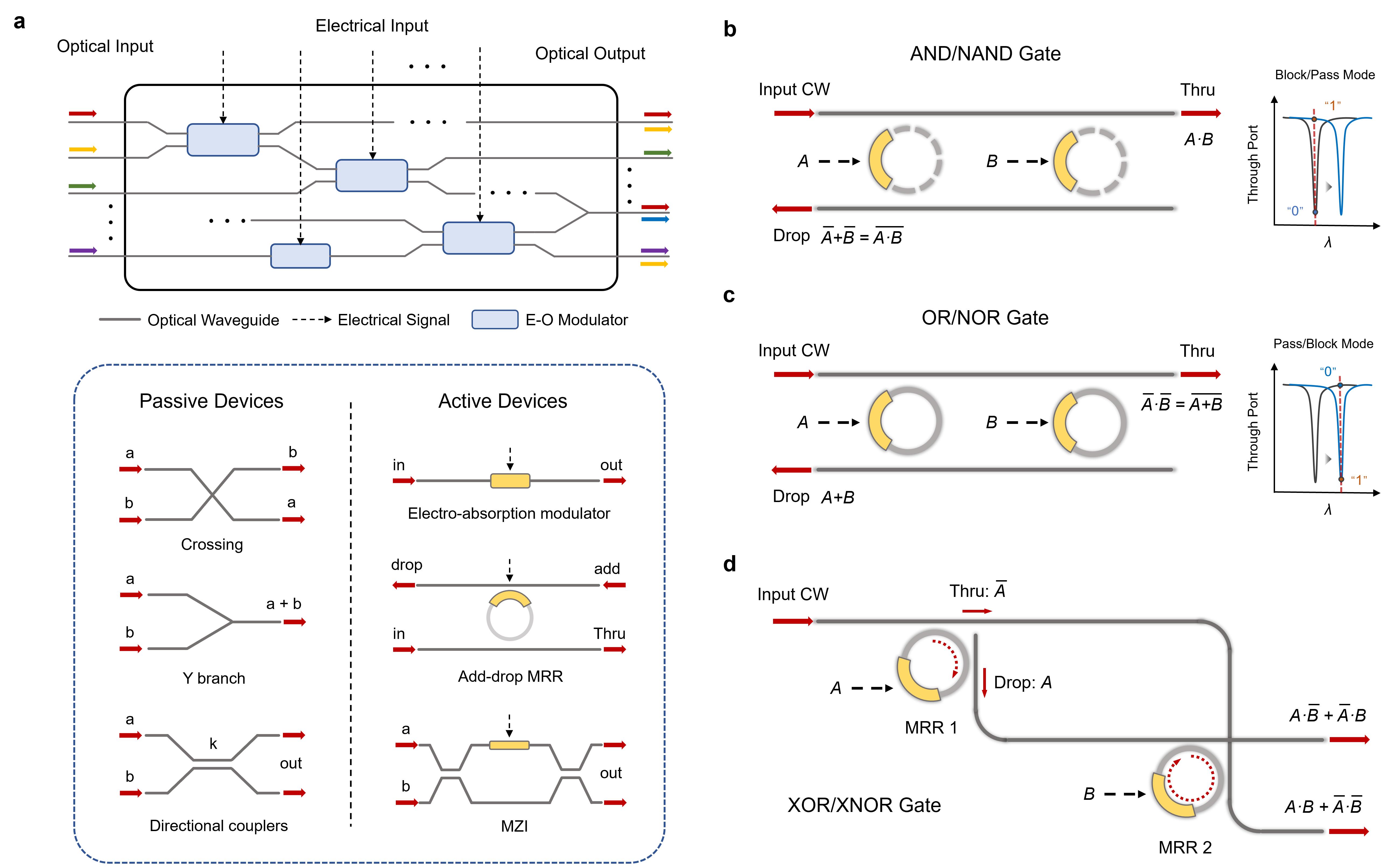
Photonic Quantum Computers
M. AbuGhanem
In the pursuit of scalable and fault-tolerant quantum computing architectures, photonic-based quantum computers have emerged as a leading frontier. This article provides a comprehensive overview of advancements in photonic quantum computing, developed by leading industry players, examining current performance, architectural designs, and strategies for developing large-scale, fault-tolerant photonic quantum computers. It also highlights recent groundbreaking experiments that leverage the unique advantages of photonic technologies, underscoring their transformative potential. This review captures a pivotal moment of photonic quantum computing in the noisy intermediate-scale quantum (NISQ) era, offering insights into how photonic quantum computers might reshape the future of quantum computing.
Read more9/14/2024

0
Photonic-Electronic Integrated Circuits for High-Performance Computing and AI Accelerators
Shupeng Ning, Hanqing Zhu, Chenghao Feng, Jiaqi Gu, Zhixing Jiang, Zhoufeng Ying, Jason Midkiff, Sourabh Jain, May H. Hlaing, David Z. Pan, Ray T. Chen
In recent decades, the demand for computational power has surged, particularly with the rapid expansion of artificial intelligence (AI). As we navigate the post-Moore's law era, the limitations of traditional electrical digital computing, including process bottlenecks and power consumption issues, are propelling the search for alternative computing paradigms. Among various emerging technologies, integrated photonics stands out as a promising solution for next-generation high-performance computing, thanks to the inherent advantages of light, such as low latency, high bandwidth, and unique multiplexing techniques. Furthermore, the progress in photonic integrated circuits (PICs), which are equipped with abundant photoelectronic components, positions photonic-electronic integrated circuits as a viable solution for high-performance computing and hardware AI accelerators. In this review, we survey recent advancements in both PIC-based digital and analog computing for AI, exploring the principal benefits and obstacles of implementation. Additionally, we propose a comprehensive analysis of photonic AI from the perspectives of hardware implementation, accelerator architecture, and software-hardware co-design. In the end, acknowledging the existing challenges, we underscore potential strategies for overcoming these issues and offer insights into the future drivers for optical computing.
Read more7/15/2024


0
Engineering Challenges in All-photonic Quantum Repeaters
Naphan Benchasattabuse, Michal Hajduv{s}ek, Rodney Van Meter
Quantum networking, heralded as the next frontier in communication networks, envisions a realm where quantum computers and devices collaborate to unlock capabilities beyond what is possible with the Internet. A critical component for realizing a long-distance quantum network, and ultimately, the Quantum Internet, is the quantum repeater. As with the race to build a scalable quantum computer with different technologies, various schemes exist for building quantum repeaters. This article offers a gentle introduction to the two-way ``all-photonic quantum repeaters,'' a recent addition to quantum repeater technologies. In contrast to conventional approaches, these repeaters eliminate the need for quantum memories, offering the dual benefits of higher repetition rates and intrinsic tolerance to both quantum operational errors and photon losses. Using visualization and simple rules for manipulating graph states, we describe how all-photonic quantum repeaters work. We discuss the problem of the increased volume of classical communication required by this scheme, which places a huge processing requirement on the end nodes. We address this problem by presenting a solution that decreases the amount of classical communication by three orders of magnitude. We conclude by highlighting other key open challenges in translating the theoretical all-photonic framework into real-world implementation, providing insights into the practical considerations and future research directions of all-photonic quantum repeater technology.
Read more5/17/2024

0
Quantum Computing: Vision and Challenges
Sukhpal Singh Gill, Oktay Cetinkaya, Stefano Marrone, Daniel Claudino, David Haunschild, Leon Schlote, Huaming Wu, Carlo Ottaviani, Xiaoyuan Liu, Sree Pragna Machupalli, Kamalpreet Kaur, Priyansh Arora, Ji Liu, Ahmed Farouk, Houbing Herbert Song, Steve Uhlig, Kotagiri Ramamohanarao
The recent development of quantum computing, which uses entanglement, superposition, and other quantum fundamental concepts, can provide substantial processing advantages over traditional computing. These quantum features help solve many complex problems that cannot be solved otherwise with conventional computing methods. These problems include modeling quantum mechanics, logistics, chemical-based advances, drug design, statistical science, sustainable energy, banking, reliable communication, and quantum chemical engineering. The last few years have witnessed remarkable progress in quantum software and algorithm creation and quantum hardware research, which has significantly advanced the prospect of realizing quantum computers. It would be helpful to have comprehensive literature research on this area to grasp the current status and find outstanding problems that require considerable attention from the research community working in the quantum computing industry. To better understand quantum computing, this paper examines the foundations and vision based on current research in this area. We discuss cutting-edge developments in quantum computer hardware advancement and subsequent advances in quantum cryptography, quantum software, and high-scalability quantum computers. Many potential challenges and exciting new trends for quantum technology research and development are highlighted in this paper for a broader debate.
Read more9/9/2024