Pixels and Predictions: Potential of GPT-4V in Meteorological Imagery Analysis and Forecast Communication
2404.15166

0
0
👀
Abstract
Generative AI, such as OpenAI's GPT-4V large-language model, has rapidly entered mainstream discourse. Novel capabilities in image processing and natural-language communication may augment existing forecasting methods. Large language models further display potential to better communicate weather hazards in a style honed for diverse communities and different languages. This study evaluates GPT-4V's ability to interpret meteorological charts and communicate weather hazards appropriately to the user, despite challenges of hallucinations, where generative AI delivers coherent, confident, but incorrect responses. We assess GPT-4V's competence via its web interface ChatGPT in two tasks: (1) generating a severe-weather outlook from weather-chart analysis and conducting self-evaluation, revealing an outlook that corresponds well with a Storm Prediction Center human-issued forecast; and (2) producing hazard summaries in Spanish and English from weather charts. Responses in Spanish, however, resemble direct (not idiomatic) translations from English to Spanish, yielding poorly translated summaries that lose critical idiomatic precision required for optimal communication. Our findings advocate for cautious integration of tools like GPT-4V in meteorology, underscoring the necessity of human oversight and development of trustworthy, explainable AI.
Get summaries of the top AI research delivered straight to your inbox:
Overview
- Generative AI models like OpenAI's GPT-4V are rapidly gaining mainstream attention for their novel capabilities in areas like image processing and natural language communication.
- These large language models have the potential to enhance existing weather forecasting methods and improve communication of weather hazards to diverse communities and in different languages.
- However, challenges remain, such as the issue of "hallucinations" where the AI generates coherent but incorrect responses.
Plain English Explanation
This paper explores how a powerful AI language model called GPT-4V, developed by OpenAI, could potentially be used to interpret weather data and communicate weather hazards. The researchers looked at two specific tasks:
-
Generating a severe weather outlook by analyzing weather charts, and then evaluating how well the AI's outlook matched a forecast made by human meteorologists.
-
Producing weather hazard summaries in both English and Spanish, to see how well the AI could communicate the information in different languages.
The researchers found that the AI was generally able to generate a severe weather outlook that corresponded well with the human-made forecast. However, when it came to translating the information into Spanish, the AI's summaries were not as clear or precise as they needed to be. The translations tended to be more literal, rather than capturing the natural, idiomatic language that would be most effective for communicating the hazards.
This study highlights both the potential and the limitations of using AI like GPT-4V in the field of meteorology. While these models can assist with tasks like interpreting data and generating forecasts, they still require careful oversight and development to ensure the information they provide is trustworthy and communicated effectively, especially when it comes to translating content into different languages.
Technical Explanation
The researchers evaluated the performance of OpenAI's GPT-4V large language model in two key tasks related to weather forecasting and communication:
-
Generating a Severe Weather Outlook: The researchers provided the AI with weather charts and asked it to generate a severe weather outlook, similar to what a human meteorologist would produce. They then compared the AI's outlook to the actual forecast issued by the Storm Prediction Center, finding a strong correspondence between the two.
-
Producing Hazard Summaries in Multiple Languages: The researchers also tested the AI's ability to generate summaries of weather hazards in both English and Spanish. While the English summaries were effective, the Spanish translations tended to be more literal and lacked the idiomatic precision required for optimal communication.
The researchers note that while these large language models, like GPT-4V, show great promise in areas like image processing and natural language communication, they still face challenges, such as the issue of "hallucinations" where the AI generates coherent but incorrect responses.
Critical Analysis
The researchers acknowledge the limitations of their study and the need for further research. They emphasize the importance of human oversight and the development of trustworthy, explainable AI systems when integrating tools like GPT-4V into meteorological applications.
One potential concern raised is the quality of the Spanish translations produced by the AI. While the English summaries were effective, the Spanish versions lacked the nuance and idiomatic precision required for optimal communication of weather hazards. This highlights the need for more advanced natural language processing capabilities, particularly when it comes to translating content into different languages.
Conclusion
This study demonstrates both the potential and the limitations of using generative AI models like GPT-4V in the field of meteorology. While these models can assist with tasks like interpreting weather data and generating forecasts, they still require careful oversight and development to ensure the information they provide is trustworthy and communicated effectively, especially when it comes to translating content into different languages.
The researchers advocate for a cautious and thoughtful approach to integrating these technologies, underscoring the necessity of human expertise and the continued development of explainable AI systems to ensure the reliable and effective communication of critical weather information.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
GPT as Psychologist? Preliminary Evaluations for GPT-4V on Visual Affective Computing
Hao Lu, Xuesong Niu, Jiyao Wang, Yin Wang, Qingyong Hu, Jiaqi Tang, Yuting Zhang, Kaishen Yuan, Bin Huang, Zitong Yu, Dengbo He, Shuiguang Deng, Hao Chen, Yingcong Chen, Shiguang Shan

0
0
Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) are designed to process and integrate information from multiple sources, such as text, speech, images, and videos. Despite its success in language understanding, it is critical to evaluate the performance of downstream tasks for better human-centric applications. This paper assesses the application of MLLMs with 5 crucial abilities for affective computing, spanning from visual affective tasks and reasoning tasks. The results show that gpt has high accuracy in facial action unit recognition and micro-expression detection while its general facial expression recognition performance is not accurate. We also highlight the challenges of achieving fine-grained micro-expression recognition and the potential for further study and demonstrate the versatility and potential of gpt for handling advanced tasks in emotion recognition and related fields by integrating with task-related agents for more complex tasks, such as heart rate estimation through signal processing. In conclusion, this paper provides valuable insights into the potential applications and challenges of MLLMs in human-centric computing. Our interesting examples are at https://github.com/EnVision-Research/GPT4Affectivity.
4/11/2024
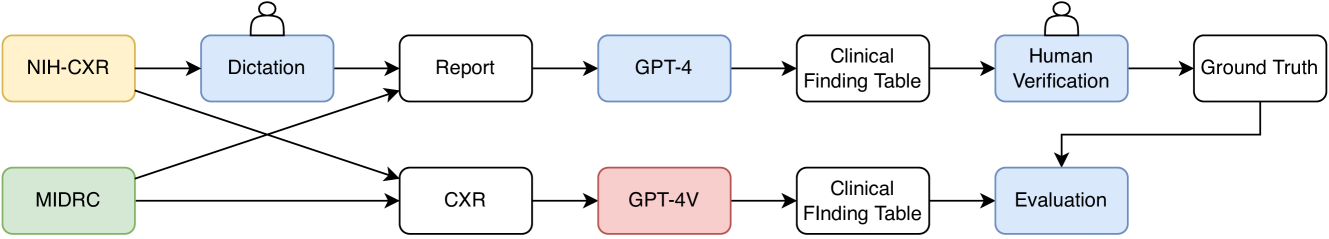
Evaluating GPT-4 with Vision on Detection of Radiological Findings on Chest Radiographs
Yiliang Zhou, Hanley Ong, Patrick Kennedy, Carol Wu, Jacob Kazam, Keith Hentel, Adam Flanders, George Shih, Yifan Peng

0
0
The study examines the application of GPT-4V, a multi-modal large language model equipped with visual recognition, in detecting radiological findings from a set of 100 chest radiographs and suggests that GPT-4V is currently not ready for real-world diagnostic usage in interpreting chest radiographs.
5/15/2024
🎯
Hidden Flaws Behind Expert-Level Accuracy of GPT-4 Vision in Medicine
Qiao Jin, Fangyuan Chen, Yiliang Zhou, Ziyang Xu, Justin M. Cheung, Robert Chen, Ronald M. Summers, Justin F. Rousseau, Peiyun Ni, Marc J Landsman, Sally L. Baxter, Subhi J. Al'Aref, Yijia Li, Alex Chen, Josef A. Brejt, Michael F. Chiang, Yifan Peng, Zhiyong Lu

0
0
Recent studies indicate that Generative Pre-trained Transformer 4 with Vision (GPT-4V) outperforms human physicians in medical challenge tasks. However, these evaluations primarily focused on the accuracy of multi-choice questions alone. Our study extends the current scope by conducting a comprehensive analysis of GPT-4V's rationales of image comprehension, recall of medical knowledge, and step-by-step multimodal reasoning when solving New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM) Image Challenges - an imaging quiz designed to test the knowledge and diagnostic capabilities of medical professionals. Evaluation results confirmed that GPT-4V performs comparatively to human physicians regarding multi-choice accuracy (81.6% vs. 77.8%). GPT-4V also performs well in cases where physicians incorrectly answer, with over 78% accuracy. However, we discovered that GPT-4V frequently presents flawed rationales in cases where it makes the correct final choices (35.5%), most prominent in image comprehension (27.2%). Regardless of GPT-4V's high accuracy in multi-choice questions, our findings emphasize the necessity for further in-depth evaluations of its rationales before integrating such multimodal AI models into clinical workflows.
4/24/2024
🌀
Harnessing GPT-4V(ision) for Insurance: A Preliminary Exploration
Chenwei Lin, Hanjia Lyu, Jiebo Luo, Xian Xu

0
0
The emergence of Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) marks a significant milestone in the development of artificial intelligence. Insurance, as a vast and complex discipline, involves a wide variety of data forms in its operational processes, including text, images, and videos, thereby giving rise to diverse multimodal tasks. Despite this, there has been limited systematic exploration of multimodal tasks specific to insurance, nor a thorough investigation into how LMMs can address these challenges. In this paper, we explore GPT-4V's capabilities in the insurance domain. We categorize multimodal tasks by focusing primarily on visual aspects based on types of insurance (e.g., auto, household/commercial property, health, and agricultural insurance) and insurance stages (e.g., risk assessment, risk monitoring, and claims processing). Our experiment reveals that GPT-4V exhibits remarkable abilities in insurance-related tasks, demonstrating not only a robust understanding of multimodal content in the insurance domain but also a comprehensive knowledge of insurance scenarios. However, there are notable shortcomings: GPT-4V struggles with detailed risk rating and loss assessment, suffers from hallucination in image understanding, and shows variable support for different languages. Through this work, we aim to bridge the insurance domain with cutting-edge LMM technology, facilitate interdisciplinary exchange and development, and provide a foundation for the continued advancement and evolution of future research endeavors.
4/16/2024