Quantifying the Impact of Frame Preemption on Combined TSN Shapers

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- This paper examines the impact of frame preemption on combined Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) shaping mechanisms.
- It evaluates the performance of TSN shapers, including the Time-Aware Shaper (TAS) and Credit-Based Shaper (CBS), under different preemption scenarios.
- The researchers use the OMNeT++ simulation platform to conduct their experiments and analyze the results.
Plain English Explanation
Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) is a set of standards that help ensure reliable and predictable data transmission over Ethernet networks. Two common TSN shaping mechanisms are the Time-Aware Shaper (TAS) and the Credit-Based Shaper (CBS).
The researchers in this paper wanted to understand how frame preemption, a technique that allows higher-priority frames to interrupt the transmission of lower-priority frames, affects the performance of these TSN shapers. They used a simulation tool called OMNeT++ to set up different scenarios and measure the impact.
Technical Explanation
The paper evaluates the performance of TAS and CBS shapers under various frame preemption conditions. The researchers used the OMNeT++ simulation platform to create a network topology with multiple traffic streams, including time-critical and best-effort traffic. They then studied the effects of different preemption policies on the latency, jitter, and throughput of the time-critical traffic.
The key findings of the paper include:
- Frame preemption can have a significant impact on the performance of TSN shapers, especially for time-critical traffic.
- The impact of preemption depends on factors such as the traffic mix, preemption policy, and shaper configuration.
- The TAS shaper is more sensitive to preemption than the CBS shaper, as it relies on a strict time-based scheduling approach.
- Careful configuration of the TSN shapers and preemption policies is required to maintain the desired quality of service for time-critical applications.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a useful analysis of the interplay between frame preemption and TSN shaping mechanisms. However, the researchers acknowledge that their study is limited to a specific network topology and traffic scenario. There may be other factors, such as the impact of network congestion or the presence of multiple preemption-enabled components, that could influence the performance of the TSN shapers.
Additionally, the paper does not explore the tradeoffs between different preemption policies or the potential for dynamic adjustment of the shaping parameters based on network conditions. Further research in these areas could provide more comprehensive insights into the design and optimization of TSN networks.
Conclusion
This paper highlights the importance of understanding the impact of frame preemption on the performance of combined TSN shaping mechanisms. The insights gained from this research can inform the design and configuration of TSN networks to ensure reliable and predictable data transmission for time-critical applications. As the adoption of TSN technologies continues to grow, addressing these technical challenges will be crucial for the successful deployment of these systems in industrial and automotive applications.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Quantifying the Impact of Frame Preemption on Combined TSN Shapers
Rubi Debnath, Philipp Hortig, Luxi Zhao, Sebastian Steinhorst
Different scheduling mechanisms in Time Sensitive Networking (TSN) can be integrated together to design and support complex architectures with enhanced capabilities for mixed critical networks. Integrating Frame Preemption (FP) with Credit-Based Shaper (CBS) and Gate Control List (GCL) opens up different modes and configuration choices resulting in a complex evaluation of several possibilities and their impact on the Quality of Service (QoS). In this paper, we implement and quantify the integration of preemptive CBS with GCL by incorporating FP into the architecture. Our experiments show that the end-to-end delay of Audio Video Bridging (AVB) flows shaped by CBS reduces significantly (up to 40%) when AVB flows are set to preemptable class. We further show that the jitter of Time Triggered (TT) traffic remains unaffected in with Hold/Release mode. Furthermore, we propose to introduce Guardband (GB) in the without Hold/Release to reduce the jitter of the TT flow. We compare all the different integration modes, starting with CBS with GCL, extending it further to FP. We evaluate all feasible combinations in both synthetic and realistic scenarios and offer recommendations for practical configuration methods.
Read more7/22/2024


0
On the Effect of TSN Forwarding Mechanisms on Best-Effort Traffic
Lisa Maile, Dominik Voitlein, Anna Arestova, Abdullah S. Alshra'a, Kai-Steffen J. Hielscher, Reinhard German
Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) enables the transmission of multiple traffic types within a single network. While the performance of high-priority traffic has been extensively studied in recent years, the performance of low-priority traffic varies significantly between different TSN forwarding algorithms. This paper provides an overview of existing TSN forwarding algorithms and discusses their impact on best-effort traffic. The effects are quantified through simulations of synthetic and realistic networks. The considered forwarding mechanisms are Strict Priority (SP), Asynchronous Traffic Shaper (ATS), Credit-Based Shaper (CBS), Enhanced Transmission Selection (ETS), and Time-Aware Shaper (TAS). The findings indicate that ATS, CBS, and ETS can significantly reduce queuing delays and queue lengths for best-effort traffic when compared to SP and TAS. This effect is enhanced when the reserved bandwidth for high priority queues - using CBS, ATS, or ETS - is reduced to the lowest possible value, within the reserved rate and latency requirements. Specifically, the simulations demonstrate that the choice of forwarding algorithm can improve the performance of low-priority traffic by up to twenty times compared to the least effective algorithm. This study not only provides a comprehensive understanding of the various TSN forwarding algorithms but can also serve as guidance at networks' design time to improve the performance for all types of traffic.
Read more8/6/2024


0
Multi-Stream TSN Gate Control Scheduling in the Presence of Clock Synchronization
Aviroop Ghosh, Saleh Yousefi, Thomas Kunz
With the advancement of technologies like Industry 4.0, communication networks must meet stringent requirements of applications demanding deterministic and bounded latencies. The problem is further compounded by the need to periodically synchronize network devices to a common time reference to address clock drifts. Existing solutions often simplify the problem by assuming either perfect synchronization or a worst-case error. Additionally, these approaches delay the scheduling process in network devices until the scheduled frame is guaranteed to have arrived in the device queue, inducing additional delays to the stream. A novel approach that completely avoids queuing delays is proposed, enabling it to meet even the strictest deadline requirement. Furthermore, both approaches can be enhanced by incorporating network-derived time-synchronization information. This is not only convenient for meeting deadline requirements but also improves bandwidth efficiency.
Read more7/15/2024
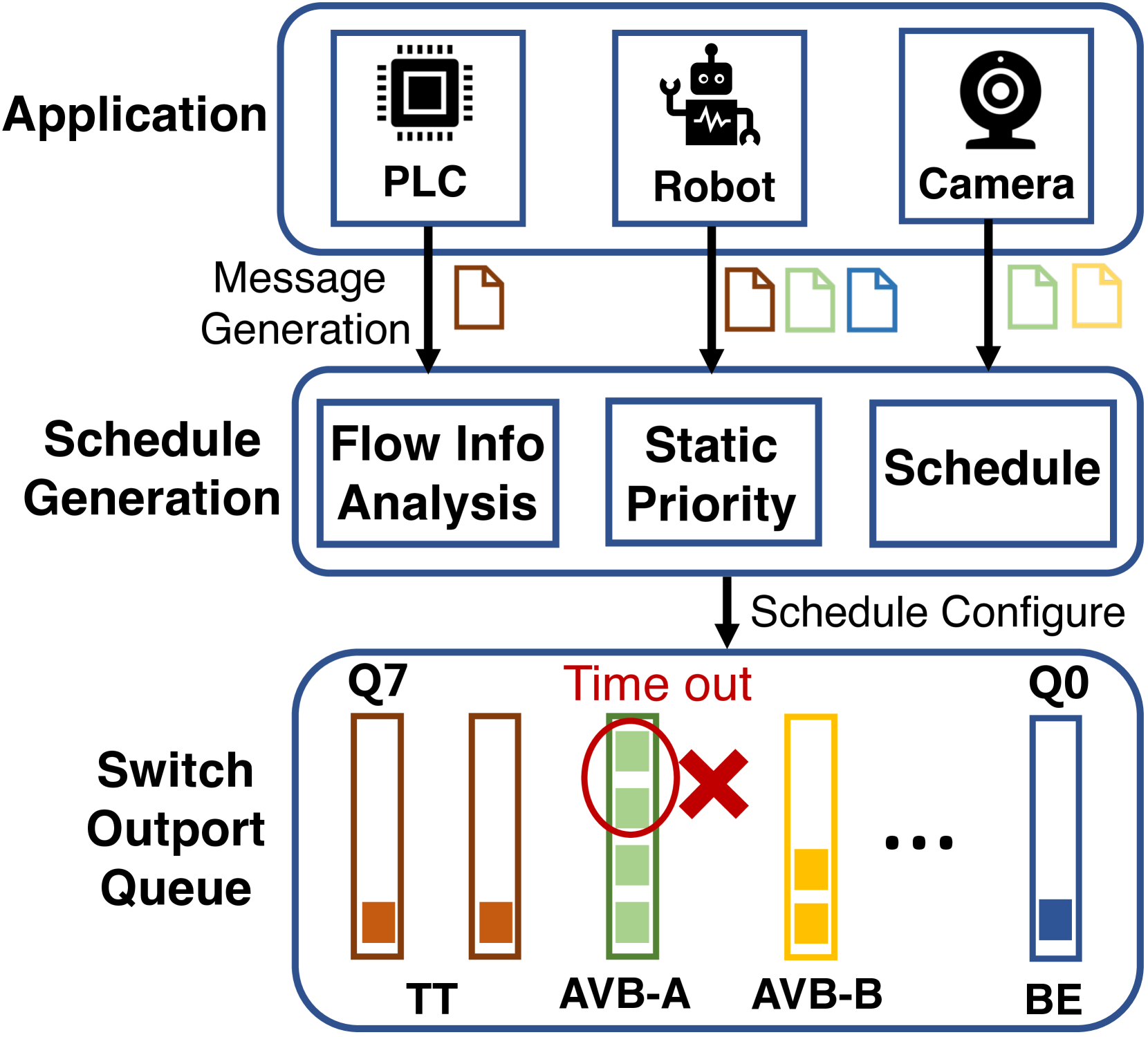

0
Exploiting Dependency-Aware Priority Adjustment for Mixed-Criticality TSN Flow Scheduling
Miao Guo, Yifei Sun, Chaojie Gu, Shibo He, Zhiguo Shi
Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) serves as a one-size-fits-all solution for mixed-criticality communication, in which flow scheduling is vital to guarantee real-time transmissions. Traditional approaches statically assign priorities to flows based on their associated applications, resulting in significant queuing delays. In this paper, we observe that assigning different priorities to a flow leads to varying delays due to different shaping mechanisms applied to different flow types. Leveraging this insight, we introduce a new scheduling method in mixed-criticality TSN that incorporates a priority adjustment scheme among diverse flow types to mitigate queuing delays and enhance schedulability. Specifically, we propose dependency-aware priority adjustment algorithms tailored to different link-overlapping conditions. Experiments in various settings validate the effectiveness of the proposed method, which enhances the schedulability by 20.57% compared with the SOTA method.
Read more7/2/2024