Quantum Circuit Synthesis and Compilation Optimization: Overview and Prospects
2407.00736

0
0

Abstract
Quantum computing is regarded as a promising paradigm that may overcome the current computational power bottlenecks in the post-Moore era. The increasing maturity of quantum processors, especially superconducting ones, provides more possibilities for the development and implementation of quantum algorithms. As the crucial stages for quantum algorithm implementation, the logic circuit design and quantum compiling have also received significant attention, which covers key technologies such as quantum logic circuit synthesis (also widely known as quantum architecture search) and optimization, as well as qubit mapping and routing. Recent studies suggest that the scale and precision of related algorithms are steadily increasing, especially with the integration of artificial intelligence methods. In this survey, we systematically review and summarize a vast body of literature, exploring the feasibility of an integrated design and optimization scheme that spans from the algorithmic level to quantum hardware, combining the steps of logic circuit design and compilation optimization. Leveraging the exceptional cognitive and learning capabilities of AI algorithms, one can reduce manual design costs, enhance the precision and efficiency of execution, and facilitate the implementation and validation of the superiority of quantum algorithms on hardware.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper provides an overview of the current state of quantum circuit synthesis and compilation optimization, exploring the latest research and techniques in this rapidly evolving field.
- It covers various approaches to representing and optimizing quantum circuits, including Quantum Architecture Search and Quantum Arithmetic Circuits.
- The paper also discusses the use of Reinforcement Learning and Distributed Quantum Computing techniques to improve the efficiency and performance of quantum circuit compilation and transpiling.
Plain English Explanation
Quantum computers are the future of computing, with the potential to solve complex problems that are virtually impossible for classical computers. However, to fully utilize the power of quantum computers, we need to be able to efficiently represent and optimize the quantum circuits that run on them.
This paper provides an overview of the latest research in this area, exploring different ways to represent and optimize quantum circuits. For example, researchers are using machine learning techniques like Reinforcement Learning to automatically optimize the design of quantum circuits, making them more efficient and powerful.
The paper also discusses the use of Distributed Quantum Computing, which involves splitting quantum computations across multiple quantum devices to improve performance and scalability. Additionally, the paper covers Quantum Arithmetic Circuits, which are essential for performing complex calculations on quantum computers.
Overall, this paper provides a comprehensive overview of the current state of quantum circuit synthesis and compilation optimization, highlighting the latest research and techniques in this rapidly evolving field.
Technical Explanation
The paper begins by introducing the importance of efficient quantum circuit representation and optimization, as this is crucial for the practical implementation of quantum computers. It then delves into the various approaches researchers are taking to address this challenge.
One key area of focus is Quantum Architecture Search, which involves using machine learning techniques to automatically design and optimize quantum circuit architectures. This can help identify the most efficient circuit designs for specific computational tasks, improving the overall performance of quantum computers.
The paper also explores the use of Reinforcement Learning to optimize the compilation and transpiling of quantum circuits. By using reinforcement learning algorithms, researchers can develop automated systems that can learn to optimize circuit transformations, leading to significant improvements in efficiency and performance.
Furthermore, the paper discusses the role of Quantum Arithmetic Circuits in quantum computing, as these are essential for performing complex calculations. The paper provides a comprehensive overview of the current state of research in this area, highlighting the challenges and opportunities.
Finally, the paper explores the potential of Distributed Quantum Computing, which involves splitting quantum computations across multiple quantum devices. This approach can help improve the scalability and performance of quantum computing systems, as well as address some of the challenges associated with the limited resources of individual quantum devices.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a thorough and well-researched overview of the current state of quantum circuit synthesis and compilation optimization. It covers a wide range of relevant topics, including the latest techniques and approaches being explored by researchers in this field.
One potential limitation of the paper is that it does not delve deeply into the specific technical details of the various methods and techniques discussed. While this is understandable given the broad scope of the paper, some readers may wish for more in-depth technical explanations and analyses.
Additionally, the paper does not address some of the potential challenges and limitations associated with the approaches it discusses. For example, it does not explore the potential scalability issues that may arise with certain optimization techniques, or the potential impact of hardware constraints on the effectiveness of these methods.
Despite these minor limitations, the paper is a valuable resource for anyone interested in the current state of quantum circuit synthesis and compilation optimization. It provides a comprehensive and well-structured overview of the field, and serves as a useful starting point for further research and exploration.
Conclusion
This paper provides a comprehensive overview of the current state of quantum circuit synthesis and compilation optimization, highlighting the latest research and techniques in this rapidly evolving field. From Quantum Architecture Search and Quantum Arithmetic Circuits to the use of Reinforcement Learning and Distributed Quantum Computing, the paper provides a comprehensive overview of the latest research and techniques in this field.
The insights and findings presented in this paper have significant implications for the future development and practical implementation of quantum computers. By improving the efficiency and performance of quantum circuit synthesis and compilation, researchers can help unlock the full potential of quantum computing and drive forward the next generation of computational power.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
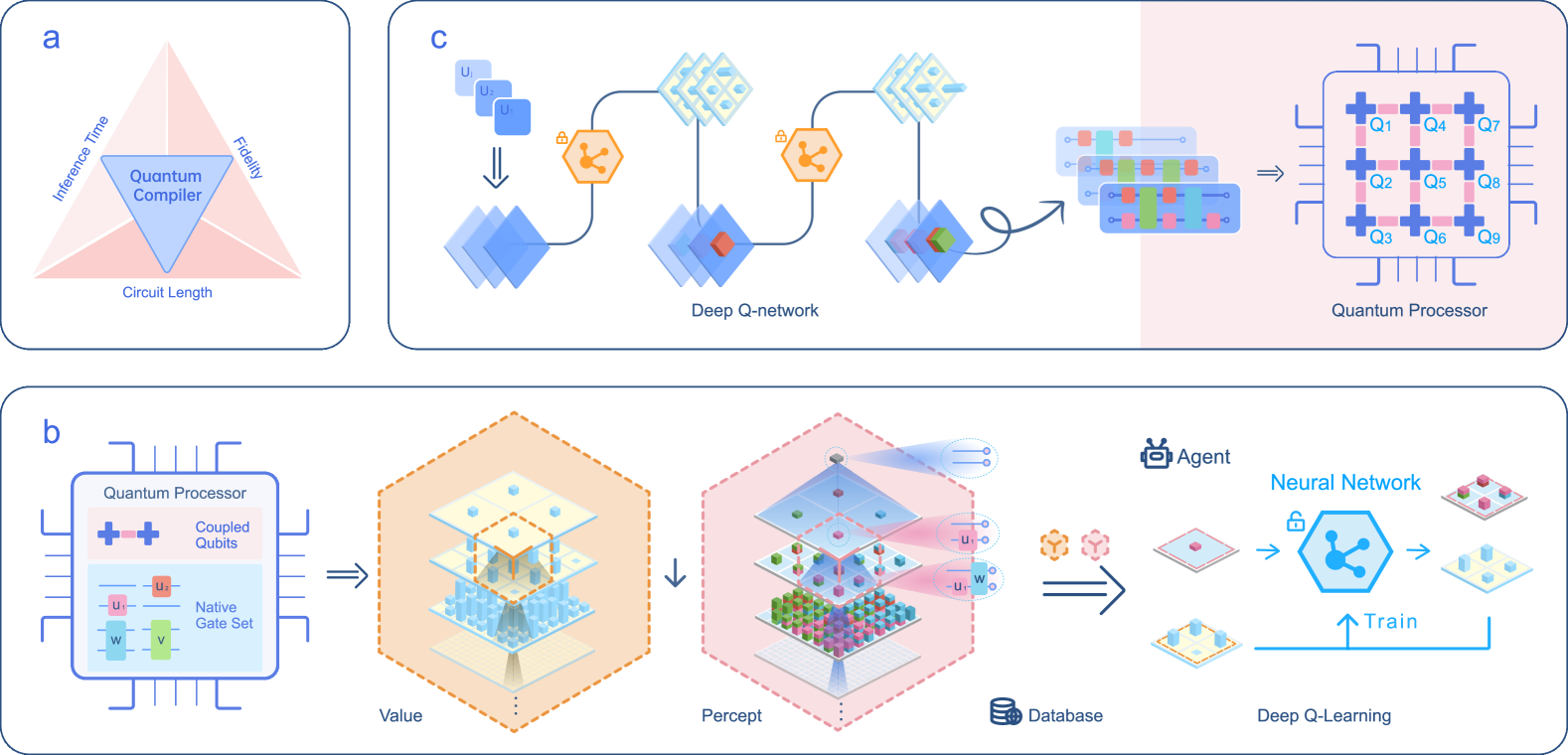
Quantum Compiling with Reinforcement Learning on a Superconducting Processor
Z. T. Wang, Qiuhao Chen, Yuxuan Du, Z. H. Yang, Xiaoxia Cai, Kaixuan Huang, Jingning Zhang, Kai Xu, Jun Du, Yinan Li, Yuling Jiao, Xingyao Wu, Wu Liu, Xiliang Lu, Huikai Xu, Yirong Jin, Ruixia Wang, Haifeng Yu, S. P. Zhao

0
0
To effectively implement quantum algorithms on noisy intermediate-scale quantum (NISQ) processors is a central task in modern quantum technology. NISQ processors feature tens to a few hundreds of noisy qubits with limited coherence times and gate operations with errors, so NISQ algorithms naturally require employing circuits of short lengths via quantum compilation. Here, we develop a reinforcement learning (RL)-based quantum compiler for a superconducting processor and demonstrate its capability of discovering novel and hardware-amenable circuits with short lengths. We show that for the three-qubit quantum Fourier transformation, a compiled circuit using only seven CZ gates with unity circuit fidelity can be achieved. The compiler is also able to find optimal circuits under device topological constraints, with lengths considerably shorter than those by the conventional method. Our study exemplifies the codesign of the software with hardware for efficient quantum compilation, offering valuable insights for the advancement of RL-based compilers.
6/19/2024

Quantum Architecture Search: A Survey
Darya Martyniuk, Johannes Jung, Adrian Paschke

0
0
Quantum computing has made significant progress in recent years, attracting immense interest not only in research laboratories but also in various industries. However, the application of quantum computing to solve real-world problems is still hampered by a number of challenges, including hardware limitations and a relatively under-explored landscape of quantum algorithms, especially when compared to the extensive development of classical computing. The design of quantum circuits, in particular parameterized quantum circuits (PQCs), which contain learnable parameters optimized by classical methods, is a non-trivial and time-consuming task requiring expert knowledge. As a result, research on the automated generation of PQCs, known as quantum architecture search (QAS), has gained considerable interest. QAS focuses on the use of machine learning and optimization-driven techniques to generate PQCs tailored to specific problems and characteristics of quantum hardware. In this paper, we provide an overview of QAS methods by examining relevant research studies in the field. We discuss main challenges in designing and performing an automated search for an optimal PQC, and survey ways to address them to ease future research.
6/11/2024

A Comprehensive Study of Quantum Arithmetic Circuits
Siyi Wang, Xiufan Li, Wei Jie Bryan Lee, Suman Deb, Eugene Lim, Anupam Chattopadhyay

0
0
In recent decades, the field of quantum computing has experienced remarkable progress. This progress is marked by the superior performance of many quantum algorithms compared to their classical counterparts, with Shor's algorithm serving as a prominent illustration. Quantum arithmetic circuits, which are the fundamental building blocks in numerous quantum algorithms, have attracted much attention. Despite extensive exploration of various designs in the existing literature, researchers remain keen on developing novel designs and improving existing ones. In this review article, we aim to provide a systematically organized and easily comprehensible overview of the current state-of-the-art in quantum arithmetic circuits. Specifically, this study covers fundamental operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, division and modular exponentiation. We delve into the detailed quantum implementations of these prominent designs and evaluate their efficiency considering various objectives. We also discuss potential applications of presented arithmetic circuits and suggest future research directions.
6/7/2024
🏅
Compiler for Distributed Quantum Computing: a Reinforcement Learning Approach
Panagiotis Promponas, Akrit Mudvari, Luca Della Chiesa, Paul Polakos, Louis Samuel, Leandros Tassiulas

0
0
The practical realization of quantum programs that require large-scale qubit systems is hindered by current technological limitations. Distributed Quantum Computing (DQC) presents a viable path to scalability by interconnecting multiple Quantum Processing Units (QPUs) through quantum links, facilitating the distributed execution of quantum circuits. In DQC, EPR pairs are generated and shared between distant QPUs, which enables quantum teleportation and facilitates the seamless execution of circuits. A primary obstacle in DQC is the efficient mapping and routing of logical qubits to physical qubits across different QPUs, necessitating sophisticated strategies to overcome hardware constraints and optimize communication. We introduce a novel compiler that, unlike existing approaches, prioritizes reducing the expected execution time by jointly managing the generation and routing of EPR pairs, scheduling remote operations, and injecting SWAP gates to facilitate the execution of local gates. We present a real-time, adaptive approach to compiler design, accounting for the stochastic nature of entanglement generation and the operational demands of quantum circuits. Our contributions are twofold: (i) we model the optimal compiler for DQC using a Markov Decision Process (MDP) formulation, establishing the existence of an optimal algorithm, and (ii) we introduce a constrained Reinforcement Learning (RL) method to approximate this optimal compiler, tailored to the complexities of DQC environments. Our simulations demonstrate that Double Deep Q-Networks (DDQNs) are effective in learning policies that minimize the depth of the compiled circuit, leading to a lower expected execution time and likelihood of successful operation before qubits decohere.
4/29/2024