Redefining Qualitative Analysis in the AI Era: Utilizing ChatGPT for Efficient Thematic Analysis
2309.10771

0
0
Abstract
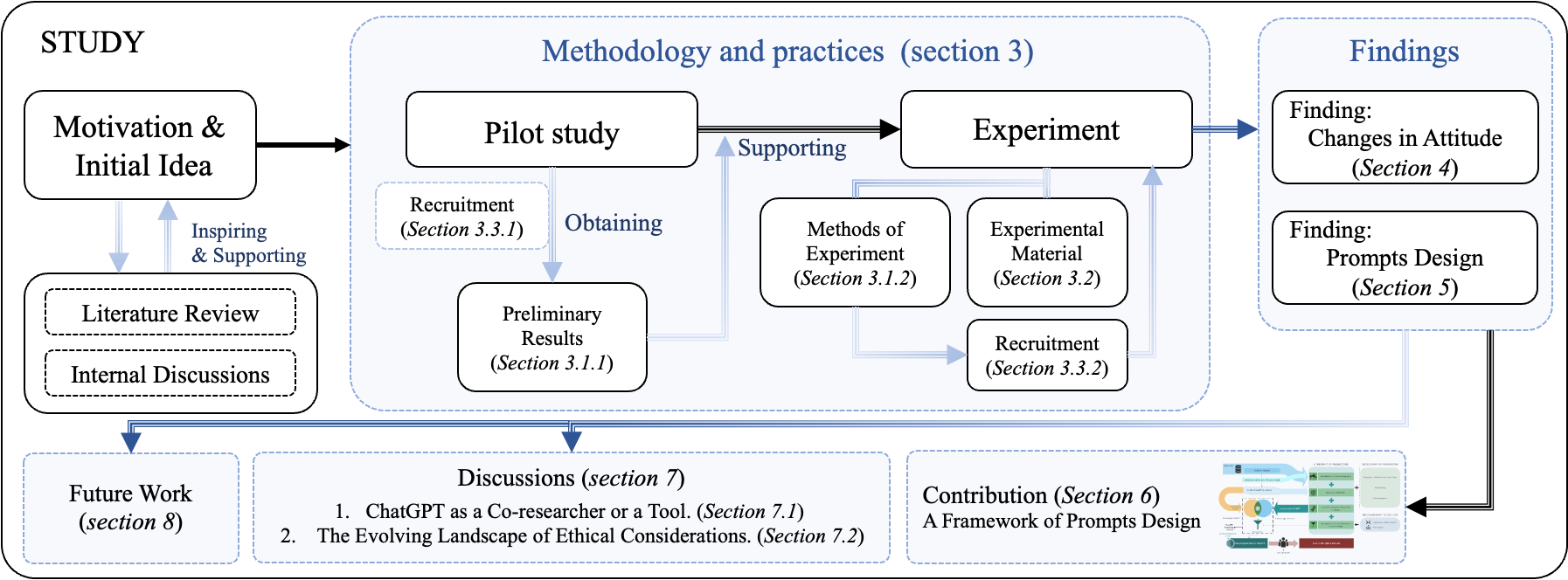
AI tools, particularly large-scale language model (LLM) based applications such as ChatGPT, have the potential to simplify qualitative research. Through semi-structured interviews with seventeen participants, we identified challenges and concerns in integrating ChatGPT into the qualitative analysis process. Collaborating with thirteen qualitative researchers, we developed a framework for designing prompts to enhance the effectiveness of ChatGPT in thematic analysis. Our findings indicate that improving transparency, providing guidance on prompts, and strengthening users' understanding of LLMs' capabilities significantly enhance the users' ability to interact with ChatGPT. We also discovered and revealed the reasons behind researchers' shift in attitude towards ChatGPT from negative to positive. This research not only highlights the importance of well-designed prompts in LLM applications but also offers reflections for qualitative researchers on the perception of AI's role. Finally, we emphasize the potential ethical risks and the impact of constructing AI ethical expectations by researchers, particularly those who are novices, on future research and AI development.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- The paper explores how the AI language model ChatGPT can be leveraged to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of qualitative thematic analysis, a widely used research method.
- It investigates the potential of ChatGPT to automate aspects of the thematic analysis process, such as coding and theme identification, while maintaining the depth and nuance of qualitative inquiry.
- The research aims to redefine qualitative analysis in the AI era, showcasing how emerging technologies can be integrated with established research methodologies to drive innovation.
Plain English Explanation
The paper examines how the AI chatbot ChatGPT can be used to improve the way researchers conduct qualitative thematic analysis. Thematic analysis is a common research method that involves identifying and analyzing patterns or themes in textual data, such as interview transcripts or written responses.
Traditionally, thematic analysis is a labor-intensive process that relies heavily on human interpretation and coding. The researchers in this paper explore how ChatGPT, a powerful language model, can be used to automate some of these tasks while still preserving the depth and nuance of qualitative research.
By integrating ChatGPT into the thematic analysis workflow, the researchers aim to make the process more efficient and effective. For example, ChatGPT could be used to help identify and code common themes in the data, freeing up researchers to focus on deeper, more interpretive work.
The researchers believe that this approach has the potential to redefine how qualitative analysis is conducted in the AI era, leveraging the strengths of both human and machine intelligence to drive innovation in research methodologies.
Technical Explanation
The paper presents a novel approach to conducting thematic analysis, a widely used qualitative research method, by integrating the AI language model ChatGPT. Thematic analysis involves identifying and analyzing patterns or themes within textual data, such as interview transcripts or open-ended survey responses.
Traditionally, thematic analysis is a labor-intensive process that relies heavily on human interpretation and coding. The researchers in this paper explore how ChatGPT can be leveraged to automate certain aspects of the thematic analysis workflow, while still preserving the depth and nuance of qualitative inquiry.
The researchers outline a multi-step process for incorporating ChatGPT into the thematic analysis pipeline. First, they use ChatGPT to assist with the initial coding of the textual data, identifying key themes and concepts. ChatGPT's language understanding capabilities are then used to group related codes into higher-level themes, a task that is typically challenging for automated systems.
The researchers also demonstrate how ChatGPT can be employed to generate summaries and interpretations of the identified themes, providing researchers with a starting point for deeper analysis and synthesis. By integrating ChatGPT into the thematic analysis process, the researchers aim to increase the efficiency and scalability of this qualitative research method, while maintaining the richness of human-centered interpretation.
The paper presents a series of case studies and examples to illustrate the potential benefits of this approach, highlighting how ChatGPT can streamline tasks such as data familiarization, code generation, and theme development. The researchers also discuss the limitations of their approach, acknowledging the importance of human oversight and the potential for bias in AI-assisted analysis.
Critical Analysis
The researchers make a compelling case for integrating ChatGPT into the thematic analysis process, demonstrating how the AI language model can be leveraged to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of this qualitative research method. By automating certain tasks, such as initial coding and theme identification, the researchers aim to free up researchers to focus on deeper, more interpretive work.
However, the paper does acknowledge several important limitations and considerations. One key concern is the potential for bias in the AI-assisted analysis, as ChatGPT's outputs can be influenced by the training data and prompts used. The researchers emphasize the need for human oversight and critical evaluation of the AI-generated insights to ensure the validity and reliability of the research findings.
Additionally, the paper notes that the integration of ChatGPT into thematic analysis is still a relatively new and evolving field, and further research is needed to fully understand the strengths, weaknesses, and best practices for this approach. Aspects such as the impact on data privacy, the suitability of ChatGPT for different types of qualitative data, and the long-term implications for qualitative research methodologies warrant further exploration.
Overall, the paper presents a promising and innovative approach to enhancing qualitative research methods through the integration of AI technologies. However, it is essential that researchers, practitioners, and policymakers continue to critically evaluate the implications and potential pitfalls of these emerging techniques to ensure they are deployed in an ethical and responsible manner.
Conclusion
This paper offers a compelling vision for redefining qualitative analysis in the AI era by leveraging the capabilities of the ChatGPT language model to streamline and enhance the thematic analysis process. By automating certain tasks, such as initial coding and theme identification, the researchers aim to increase the efficiency and scalability of this widely used qualitative research method, while still preserving the depth and nuance of human-centered interpretation.
The integration of ChatGPT into the thematic analysis workflow represents an important step forward in the intersection of AI and qualitative research. As the field of AI continues to advance, it is crucial that researchers explore how these powerful technologies can be responsibly and ethically integrated with established methodologies to drive innovation and progress.
While the paper acknowledges the limitations and potential risks of this approach, it ultimately presents a compelling case for the transformative potential of AI-assisted qualitative analysis. By embracing the strengths of both human and machine intelligence, the researchers believe that qualitative research can be redefined for the modern era, opening up new avenues for deeper insights and impactful discoveries.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
💬
Using ChatGPT for Thematic Analysis
Aleksei Turobov, Diane Coyle, Verity Harding

0
0
The utilisation of AI-driven tools, notably ChatGPT, within academic research is increasingly debated from several perspectives including ease of implementation, and potential enhancements in research efficiency, as against ethical concerns and risks such as biases and unexplained AI operations. This paper explores the use of the GPT model for initial coding in qualitative thematic analysis using a sample of UN policy documents. The primary aim of this study is to contribute to the methodological discussion regarding the integration of AI tools, offering a practical guide to validation for using GPT as a collaborative research assistant. The paper outlines the advantages and limitations of this methodology and suggests strategies to mitigate risks. Emphasising the importance of transparency and reliability in employing GPT within research methodologies, this paper argues for a balanced use of AI in supported thematic analysis, highlighting its potential to elevate research efficacy and outcomes.
5/16/2024
📊
Analyzing Chat Protocols of Novice Programmers Solving Introductory Programming Tasks with ChatGPT
Andreas Scholl, Daniel Schiffner, Natalie Kiesler

0
0
Large Language Models (LLMs) have taken the world by storm, and students are assumed to use related tools at a great scale. In this research paper we aim to gain an understanding of how introductory programming students chat with LLMs and related tools, e.g., ChatGPT-3.5. To address this goal, computing students at a large German university were motivated to solve programming exercises with the assistance of ChatGPT as part of their weekly introductory course exercises. Then students (n=213) submitted their chat protocols (with 2335 prompts in sum) as data basis for this analysis. The data was analyzed w.r.t. the prompts, frequencies, the chats' progress, contents, and other use pattern, which revealed a great variety of interactions, both potentially supportive and concerning. Learning about students' interactions with ChatGPT will help inform and align teaching practices and instructions for future introductory programming courses in higher education.
5/30/2024
🤖
Investigation of the effectiveness of applying ChatGPT in Dialogic Teaching Using Electroencephalography
Jiayue Zhang, Yiheng Liu, Wenqi Cai, Lanlan Wu, Yali Peng, Jingjing Yu, Senqing Qi, Taotao Long, Bao Ge

0
0
In recent years, the rapid development of artificial intelligence technology, especially the emergence of large language models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT, has presented significant prospects for application in the field of education. LLMs possess the capability to interpret knowledge, answer questions, and consider context, thus providing support for dialogic teaching to students. Therefore, an examination of the capacity of LLMs to effectively fulfill instructional roles, thereby facilitating student learning akin to human educators within dialogic teaching scenarios, is an exceptionally valuable research topic. This research recruited 34 undergraduate students as participants, who were randomly divided into two groups. The experimental group engaged in dialogic teaching using ChatGPT, while the control group interacted with human teachers. Both groups learned the histogram equalization unit in the information-related course Digital Image Processing. The research findings show comparable scores between the two groups on the retention test. However, students who engaged in dialogue with ChatGPT exhibited lower performance on the transfer test. Electroencephalography data revealed that students who interacted with ChatGPT exhibited higher levels of cognitive activity, suggesting that ChatGPT could help students establish a knowledge foundation and stimulate cognitive activity. However, its strengths on promoting students. knowledge application and creativity were insignificant. Based upon the research findings, it is evident that ChatGPT cannot fully excel in fulfilling teaching tasks in the dialogue teaching in information related courses. Combining ChatGPT with traditional human teachers might be a more ideal approach. The synergistic use of both can provide students with more comprehensive learning support, thus contributing to enhancing the quality of teaching.
6/12/2024
💬
ChatGPT as an inventor: Eliciting the strengths and weaknesses of current large language models against humans in engineering design
Daniel Nyg{aa}rd Ege, Henrik H. {O}vreb{o}, Vegar Stubberud, Martin Francis Berg, Christer Elverum, Martin Steinert, H{aa}vard Vestad

0
0
This study compares the design practices and performance of ChatGPT 4.0, a large language model (LLM), against graduate engineering students in a 48-hour prototyping hackathon, based on a dataset comprising more than 100 prototypes. The LLM participated by instructing two participants who executed its instructions and provided objective feedback, generated ideas autonomously and made all design decisions without human intervention. The LLM exhibited similar prototyping practices to human participants and finished second among six teams, successfully designing and providing building instructions for functional prototypes. The LLM's concept generation capabilities were particularly strong. However, the LLM prematurely abandoned promising concepts when facing minor difficulties, added unnecessary complexity to designs, and experienced design fixation. Communication between the LLM and participants was challenging due to vague or unclear descriptions, and the LLM had difficulty maintaining continuity and relevance in answers. Based on these findings, six recommendations for implementing an LLM like ChatGPT in the design process are proposed, including leveraging it for ideation, ensuring human oversight for key decisions, implementing iterative feedback loops, prompting it to consider alternatives, and assigning specific and manageable tasks at a subsystem level.
4/30/2024