Using ChatGPT for Thematic Analysis
2405.08828

0
0
💬
Abstract
The utilisation of AI-driven tools, notably ChatGPT, within academic research is increasingly debated from several perspectives including ease of implementation, and potential enhancements in research efficiency, as against ethical concerns and risks such as biases and unexplained AI operations. This paper explores the use of the GPT model for initial coding in qualitative thematic analysis using a sample of UN policy documents. The primary aim of this study is to contribute to the methodological discussion regarding the integration of AI tools, offering a practical guide to validation for using GPT as a collaborative research assistant. The paper outlines the advantages and limitations of this methodology and suggests strategies to mitigate risks. Emphasising the importance of transparency and reliability in employing GPT within research methodologies, this paper argues for a balanced use of AI in supported thematic analysis, highlighting its potential to elevate research efficacy and outcomes.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- Explores the use of ChatGPT, a large language model, for automating the thematic analysis process in qualitative research
- Compares manual coding approaches to GPT-driven coding, examining the potential benefits and challenges of each
- Presents a pilot study analyzing United Nations policy documents using both manual and GPT-driven coding methods
Plain English Explanation
This paper investigates how the artificial intelligence chatbot ChatGPT could be used to assist with thematic analysis - a common qualitative research method for identifying patterns and themes in text-based data.
The researchers compare the traditional manual approach to coding data, where a human researcher reads through the text and identifies key themes, to an automated approach using ChatGPT. The goal is to explore whether the language model can accurately capture the same themes that a human coder would, potentially saving time and effort in the analysis process.
The paper includes a pilot study where the researchers used both manual coding and ChatGPT-driven coding to analyze a set of United Nations policy documents. This allowed them to compare the results and assess the strengths and limitations of each approach.
Technical Explanation
The paper first provides an overview of thematic analysis, explaining how it involves closely reading through textual data, identifying recurring patterns and themes, and then organizing those themes into a coding framework. The authors contrast the traditional manual approach to this process with the potential for using a large language model like ChatGPT to automate parts of the coding.
In the pilot study, the researchers used a set of United Nations policy documents as the data for their analysis. They first had a human coder manually read through the documents and develop a coding framework based on the themes they identified. They then used ChatGPT to analyze the same documents, prompting the model to summarize the key themes and provide a coding structure.
The paper compares the results of the manual and ChatGPT-driven coding approaches, examining the extent to which the themes and codes aligned. It also discusses the advantages and disadvantages of each method, such as the speed and scalability of the automated approach versus the nuance and contextual understanding of the human coder.
Critical Analysis
The paper acknowledges several limitations of the pilot study, including the relatively small size of the document set and the fact that it only examined one specific domain (UN policy). The authors note that further research is needed to assess the generalizability of their findings to other types of qualitative data and research questions.
Additionally, the paper does not delve deeply into potential issues around bias in the ChatGPT-driven coding, such as the model potentially reflecting societal biases present in the training data. This is an important consideration when using AI systems for qualitative analysis.
Overall, the paper presents an interesting initial exploration of using language models like ChatGPT for thematic analysis, but more rigorous testing and critical evaluation will be needed to fully understand the strengths, limitations, and ethical implications of this approach.
Conclusion
This paper explores the potential for using the AI chatbot ChatGPT to assist with thematic analysis, a common qualitative research method. The authors compare manual coding by human researchers to an automated approach using the language model, presenting a pilot study on UN policy documents.
The results suggest that ChatGPT can capture many of the same themes as human coders, potentially offering a faster and more scalable analysis process. However, the paper also highlights important limitations and areas for further research, such as examining bias and testing the approach with a wider range of data types.
Overall, this work provides an interesting initial exploration of leveraging large language models for qualitative research, but more study is needed to fully assess the capabilities and limitations of this approach.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
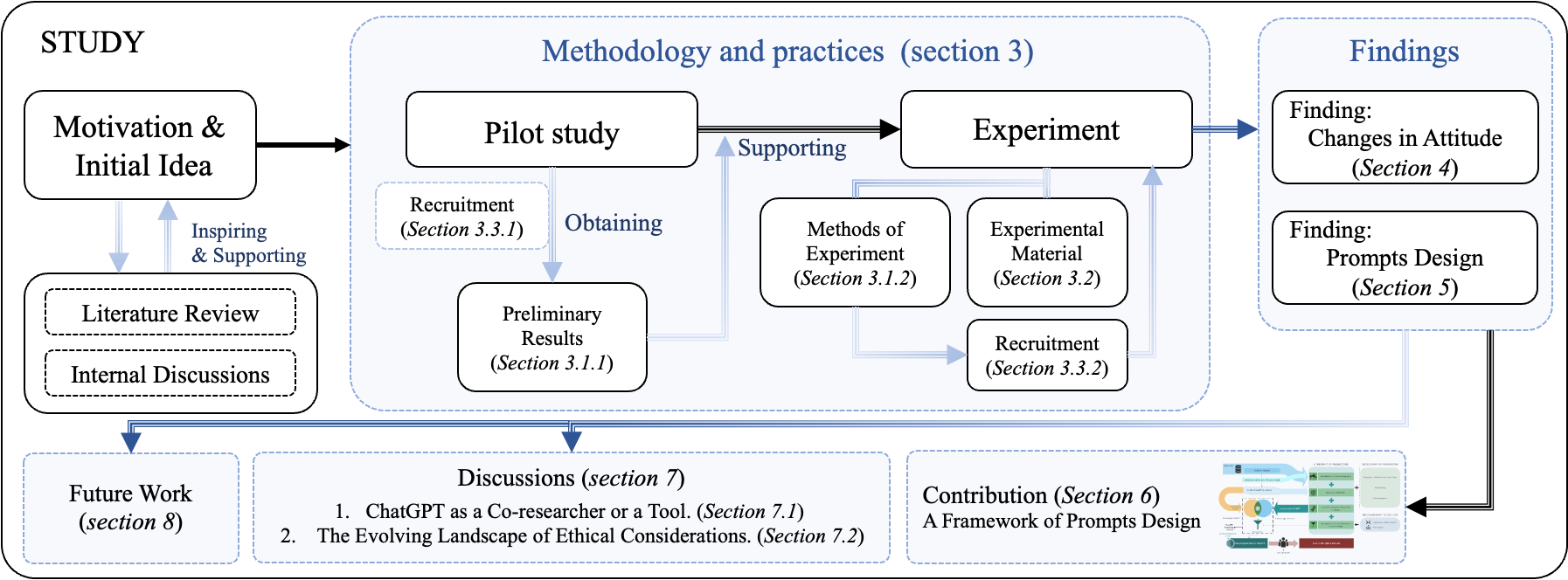
Redefining Qualitative Analysis in the AI Era: Utilizing ChatGPT for Efficient Thematic Analysis
He Zhang, Chuhao Wu, Jingyi Xie, Yao Lyu, Jie Cai, John M. Carroll

0
0
AI tools, particularly large-scale language model (LLM) based applications such as ChatGPT, have the potential to simplify qualitative research. Through semi-structured interviews with seventeen participants, we identified challenges and concerns in integrating ChatGPT into the qualitative analysis process. Collaborating with thirteen qualitative researchers, we developed a framework for designing prompts to enhance the effectiveness of ChatGPT in thematic analysis. Our findings indicate that improving transparency, providing guidance on prompts, and strengthening users' understanding of LLMs' capabilities significantly enhance the users' ability to interact with ChatGPT. We also discovered and revealed the reasons behind researchers' shift in attitude towards ChatGPT from negative to positive. This research not only highlights the importance of well-designed prompts in LLM applications but also offers reflections for qualitative researchers on the perception of AI's role. Finally, we emphasize the potential ethical risks and the impact of constructing AI ethical expectations by researchers, particularly those who are novices, on future research and AI development.
5/29/2024
📈
Beyond the Hype: A Cautionary Tale of ChatGPT in the Programming Classroom
Grant Oosterwyk, Pitso Tsibolane, Popyeni Kautondokwa, Ammar Canani

0
0
Due to the proliferation of Large Language Models research and the use of various Artificial Intelligence (AI) tools, the field of information systems (IS) and computer science (CS) has evolved. The use of tools such as ChatGPT to complete various student programming exercises (e.g., in Python) and assignments has gained prominence amongst various academic institutions. However, recent literature has suggested that the use of ChatGPT in academia is problematic and the impact on teaching and learning should be further scrutinized. More specifically, little is known about how ChatGPT can be practically used with code (programming) writing to complete programming exercises amongst IS and CS undergraduate university students. Furthermore, the paper provides insights for academics who teach programming to create more challenging exercises and how to engage responsibly in the use of ChatGPT to promote classroom integrity. In this paper, we used Complex Adaptive Systems (CAS) theory as a theoretical guide to understand the various dynamics through classroom code demonstrations. Using ChatGPT 3.5, we analyzed the various practical programming examples from past IS exercises and compared those with memos created by tutors and lecturers in a university setting. This paper highlights common ways of assessment, programming errors created by ChatGPT and the potential consideration for IS academics to ensure the development of critical programming skills among students.
6/18/2024
🌐
ChatGPT Is Here to Help, Not to Replace Anybody -- An Evaluation of Students' Opinions On Integrating ChatGPT In CS Courses
Bruno Pereira Cipriano, Pedro Alves

0
0
Large Language Models (LLMs) like GPT and Bard are capable of producing code based on textual descriptions, with remarkable efficacy. Such technology will have profound implications for computing education, raising concerns about cheating, excessive dependence, and a decline in computational thinking skills, among others. There has been extensive research on how teachers should handle this challenge but it is also important to understand how students feel about this paradigm shift. In this research, 52 first-year CS students were surveyed in order to assess their views on technologies with code-generation capabilities, both from academic and professional perspectives. Our findings indicate that while students generally favor the academic use of GPT, they don't over rely on it, only mildly asking for its help. Although most students benefit from GPT, some struggle to use it effectively, urging the need for specific GPT training. Opinions on GPT's impact on their professional lives vary, but there is a consensus on its importance in academic practice.
4/29/2024
⚙️
Ethical Implications of ChatGPT in Higher Education: A Scoping Review
Ming Li, Ariunaa Enkhtur, Fei Cheng, Beverley Anne Yamamoto

0
0
This scoping review explores the ethical challenges of using ChatGPT in higher education. By reviewing recent academic articles in English, Chinese, and Japanese, we aimed to provide a deep dive review and identify gaps in the literature. Drawing on Arksey and O'Malley's (2005) scoping review framework, we defined search terms and identified relevant publications from four databases in the three target languages. The research results showed that the majority of the papers were discussion papers, but there was some early empirical work. The ethical issues highlighted in these works mainly concern academic integrity, assessment issues, and data protection. Given the rapid deployment of generative artificial intelligence, it is imperative for educators to conduct more empirical studies to develop sound ethical policies for its use.
6/6/2024