Revisiting Multi-User Downlink in IEEE 802.11ax: A Designers Guide to MU-MIMO
2406.05913

0
0
Abstract
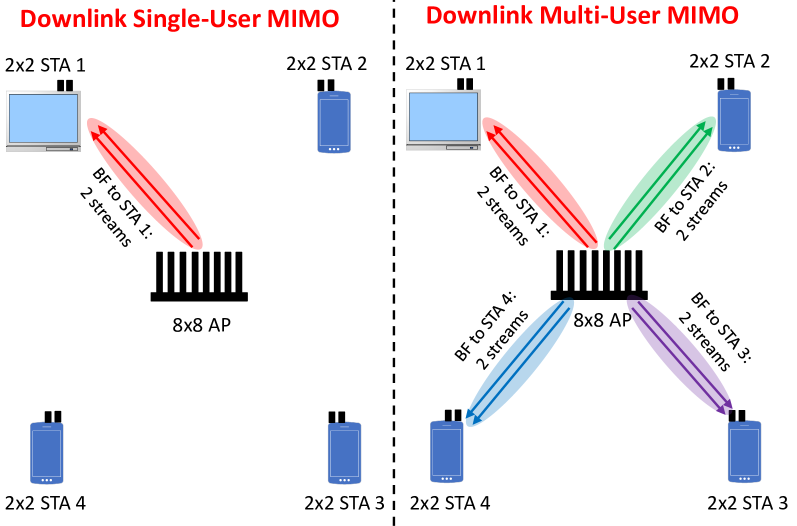
Downlink (DL) Multi-User (MU) Multiple Input Multiple Output (MU-MIMO) is a key technology that allows multiple concurrent data transmissions from an Access Point (AP) to a selected sub-set of clients for higher network efficiency in IEEE 802.11ax. However, DL MU-MIMO feature is typically turned off as the default setting in AP vendors' products, that is, turning on the DL MU-MIMO may not help increase the network efficiency, which is counter-intuitive. In this article, we provide a sufficiently deep understanding of the interplay between the various underlying factors, i.e., CSI overhead and spatial correlation, which result in negative results when turning on the DL MU-MIMO. Furthermore, we provide a fundamental guideline as a function of operational scenarios to address the fundamental question when the DL MU-MIMO should be turned on/off.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- Discusses the design considerations for multi-user multiple-input, multiple-output (MU-MIMO) in the IEEE 802.11ax wireless standard
- Examines two key factors that impact MU-MIMO performance: channel state information (CSI) overhead and spatial correlation
- Provides guidance for wireless system designers on optimizing MU-MIMO performance in 802.11ax networks
Plain English Explanation
The paper explores the challenges involved in effectively implementing multi-user MIMO (MU-MIMO) technology in the latest version of the Wi-Fi standard, IEEE 802.11ax. MU-MIMO allows a single wireless access point to communicate with multiple devices simultaneously, improving overall network throughput.
However, there are two key factors that can significantly impact the performance of MU-MIMO in 802.11ax networks:
-
CSI Overhead: The access point needs detailed information about the wireless channels to each device in order to coordinate the simultaneous transmissions. Gathering and communicating this channel state information (CSI) requires a significant amount of overhead, which can reduce the efficiency gains from MU-MIMO.
-
Spatial Correlation: If the devices are located too close together, their wireless channels become highly correlated, limiting the ability of MU-MIMO to provide independent data streams. This spatial correlation reduces the potential performance benefits.
The paper provides guidance to wireless system designers on how to navigate these tradeoffs and optimize MU-MIMO performance in 802.11ax networks. By understanding the impact of CSI overhead and spatial correlation, designers can make informed decisions about network topology, scheduling, and other key parameters to get the most out of this advanced wireless technology.
Technical Explanation
The paper Revisiting Multi-User Downlink in IEEE 802.11ax: A Designers Guide to MU-MIMO examines two key factors that impact the performance of multi-user multiple-input, multiple-output (MU-MIMO) in the IEEE 802.11ax wireless standard:
-
CSI Overhead: To enable MU-MIMO, the access point (AP) needs detailed information about the wireless channels to each connected device, known as channel state information (CSI). The process of acquiring and reporting this CSI introduces significant overhead, which can diminish the efficiency gains of MU-MIMO.
-
Spatial Correlation: If the devices are located too close together, their wireless channels become highly correlated, limiting the AP's ability to provide independent data streams to each device. This spatial correlation reduces the potential performance benefits of MU-MIMO.
The paper provides guidance to wireless system designers on how to navigate these tradeoffs and optimize MU-MIMO performance in 802.11ax networks. By understanding the impact of CSI overhead and spatial correlation, designers can make informed decisions about network topology, scheduling, and other key parameters to get the most out of this advanced wireless technology.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a comprehensive analysis of the key factors that impact MU-MIMO performance in 802.11ax networks, and offers valuable insights for wireless system designers. However, the research is limited to simulations and theoretical analysis, and may not fully capture the complexities of real-world deployment scenarios.
One potential area for further research is the impact of user mobility on MU-MIMO performance. As users move within the network, the spatial correlation between their channels may change, requiring the system to adapt accordingly. The paper does not address this dynamic aspect of MU-MIMO optimization.
Additionally, the paper focuses primarily on downlink (AP to device) MU-MIMO, but uplink (device to AP) MU-MIMO can also play a significant role in overall network performance. Complementary research on optimizing uplink MU-MIMO in 802.11ax could provide a more holistic understanding of the technology's capabilities and tradeoffs.
Conclusion
The paper "Revisiting Multi-User Downlink in IEEE 802.11ax: A Designers Guide to MU-MIMO" offers valuable guidance to wireless system designers on optimizing the performance of multi-user MIMO in the latest Wi-Fi standard, IEEE 802.11ax. By understanding the impact of CSI overhead and spatial correlation, designers can make informed decisions to balance the tradeoffs and get the most out of this advanced wireless technology.
As 802.11ax continues to be deployed, further research and real-world deployments will be needed to validate the insights from this paper and address any additional challenges that may arise. Nonetheless, this work provides a solid foundation for designers to build upon as they work to deliver high-performance, efficient wireless networks for the future.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
Joint Optimization on Uplink OFDMA and MU-MIMO for IEEE 802.11ax: Deep Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning Approach
Hyeonho Noh, Harim Lee, Hyun Jong Yang

0
0
This letter tackles a joint user scheduling, frequency resource allocation (USRA), multi-input-multi-output mode selection (MIMO MS) between single-user MIMO and multi-user (MU) MIMO, and MU-MIMO user selection problem, integrating uplink orthogonal frequency division multiple access (OFDMA) in IEEE 802.11ax. Specifically, we focus on textit{unsaturated traffic conditions} where users' data demands fluctuate. In unsaturated traffic conditions, considering packet volumes per user introduces a combinatorial problem, requiring the simultaneous optimization of MU-MIMO user selection and RA along the time-frequency-space axis. Consequently, dealing with the combinatorial nature of this problem, characterized by a large cardinality of unknown variables, poses a challenge that conventional optimization methods find nearly impossible to address. In response, this letter proposes an approach with deep hierarchical reinforcement learning (DHRL) to solve the joint problem. Rather than simply adopting off-the-shelf DHRL, we textit{tailor} the DHRL to the joint USRA and MS problem, thereby significantly improving the convergence speed and throughput. Extensive simulation results show that the proposed algorithm achieves significantly improved throughput compared to the existing schemes under various unsaturated traffic conditions.
4/4/2024
Joint AP-UE Association and Power Factor Optimization for Distributed Massive MIMO
Mohd Saif Ali Khan, Samar Agnihotri, Karthik R. M

0
0
The uplink sum-throughput of distributed massive multiple-input-multiple-output (mMIMO) networks depends majorly on Access point (AP)-User Equipment (UE) association and power control. The AP-UE association and power control both are important problems in their own right in distributed mMIMO networks to improve scalability and reduce front-haul load of the network, and to enhance the system performance by mitigating the interference and boosting the desired signals, respectively. Unlike previous studies, which focused primarily on addressing these two problems separately, this work addresses the uplink sum-throughput maximization problem in distributed mMIMO networks by solving the joint AP-UE association and power control problem, while maintaining Quality-of-Service (QoS) requirements for each UE. To improve scalability, we present an l1-penalty function that delicately balances the trade-off between spectral efficiency (SE) and front-haul signaling load. Our proposed methodology leverages fractional programming, Lagrangian dual formation, and penalty functions to provide an elegant and effective iterative solution with guaranteed convergence. Extensive numerical simulations validate the efficacy of the proposed technique for maximizing sum-throughput while considering the joint AP-UE association and power control problem, demonstrating its superiority over approaches that address these problems individually. Furthermore, the results show that the introduced penalty function can help us effectively control the maximum front-haul load.
5/14/2024

MIMO in network simulators: Design, implementation and evaluation of single-user MIMO in ns-3 5G-LENA
Biljana Bojovic, Sandra Lagen

0
0
MIMO technology has been studied in textbooks for several decades, and it has been adopted in 4G and 5G systems. Due to the recent evolution in 5G and beyond networks, designed to cover a wide range of use cases with every time more complex applications, it is essential to have network simulation tools (such as ns-3) to evaluate MIMO performance from the network perspective, before real implementation. Up to date, the well-known ns-3 simulator has been missing the inclusion of single-user MIMO (SU-MIMO) models for 5G. In this paper, we detail the implementation models and provide an exhaustive evaluation of SU-MIMO in the 5G-LENA module of ns-3. As per 3GPP 5G, we adopt a hybrid beamforming architecture and a closed-loop MIMO mechanism and follow all 3GPP specifications for MIMO implementation, including channel state information feedback with precoding matrix indicator and rank indicator reports, and codebook-based precoding following Precoding Type-I (used for SU-MIMO). The simulation models are released in open-source and currently support up to 32 antenna ports and 4 streams per user. The simulation results presented in this paper help in testing and verifying the simulated models, for different multi-antenna array and antenna ports configurations.
4/29/2024

Uplink resource allocation optimization for user-centric cell-free MIMO networks
Zehua Li, Raviraj Adve

0
0
We examine the problem of optimizing resource allocation in the uplink for a user-centric, cell-free, multi-input multi-output network. We start by modeling and developing resource allocation algorithms for two standard network operation modes. The centralized mode provides high data rates but suffers multiple issues, including scalability. On the other hand, the distributed mode has the opposite problem: relatively low rates, but is scalable. To address these challenges, we combine the strength of the two standard modes, creating a new semi-distributed operation mode. To avoid the need for information exchange between access points, we introduce a new quality of service metric to decentralize the resource allocation algorithms. Our results show that we can eliminate the need for information exchange with a relatively small penalty on data rates.
6/11/2024