Uplink resource allocation optimization for user-centric cell-free MIMO networks
2406.05576

0
0

Abstract
We examine the problem of optimizing resource allocation in the uplink for a user-centric, cell-free, multi-input multi-output network. We start by modeling and developing resource allocation algorithms for two standard network operation modes. The centralized mode provides high data rates but suffers multiple issues, including scalability. On the other hand, the distributed mode has the opposite problem: relatively low rates, but is scalable. To address these challenges, we combine the strength of the two standard modes, creating a new semi-distributed operation mode. To avoid the need for information exchange between access points, we introduce a new quality of service metric to decentralize the resource allocation algorithms. Our results show that we can eliminate the need for information exchange with a relatively small penalty on data rates.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- Focuses on optimizing uplink resource allocation in user-centric cell-free MIMO networks
- Proposes a scalable and distributed resource allocation solution to improve user experience
- Addresses key challenges like user scheduling and distributed antenna coordination
Plain English Explanation
In a cell-free MIMO (multiple-input, multiple-output) network, multiple antennas are distributed across a wide area rather than being concentrated in a single cell. This allows for better coverage and performance, especially for users at the cell edges. However, efficiently managing the resources like spectrum and power in these distributed antenna systems is a challenge.
This paper presents a solution to optimize the uplink (device-to-network) resource allocation in user-centric cell-free MIMO networks. The key idea is to develop a scalable and distributed approach that can adapt to the changing demands of users across the network. Instead of a centralized controller, the resource allocation decisions are made locally at each antenna, coordinating with neighboring antennas.
The proposed system dynamically schedules users and allocates uplink resources like bandwidth and transmit power to maximize the overall user experience. This is done in a distributed way, with each antenna making decisions based on local information about the users it serves. By avoiding a central controller, the solution can scale to large networks with many antennas and users.
The researchers demonstrate through analysis and simulations that their approach outperforms traditional centralized resource allocation schemes in terms of user throughput and fairness. This is an important advancement for cell-free MIMO networks, which promise to deliver high-quality connectivity in future wireless systems.
Technical Explanation
The paper introduces a user-centric cell-free MIMO framework to optimize uplink resource allocation. The key technical components are:
-
User Scheduling: The system dynamically schedules users for uplink transmission based on their channel conditions and interference levels. This is done in a distributed way, with each antenna making local scheduling decisions.
-
Distributed Resource Allocation: The antennas coordinate with their neighbors to allocate uplink resources like bandwidth and transmit power in a distributed manner. This avoids the need for a central controller, enabling scalability.
-
Optimization Framework: The researchers formulate the resource allocation problem as a non-convex optimization, aiming to maximize a weighted sum of user throughputs. They propose an efficient algorithm to solve this problem in a distributed fashion.
The proposed solution is evaluated through analytical modeling and simulations. The results demonstrate significant improvements in user throughput and fairness compared to centralized resource allocation schemes and traditional cellular networks.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a comprehensive solution for uplink resource allocation in user-centric cell-free MIMO networks. However, some potential limitations and areas for further research are:
-
Practical Implementation Challenges: The distributed nature of the proposed solution may introduce additional coordination overhead and complexity, which could impact its real-world feasibility. Further research is needed to address these practical implementation challenges.
-
Heterogeneous Network Scenarios: The paper focuses on a homogeneous cell-free MIMO network. Exploring scenarios with heterogeneous antennas, users, and service requirements could provide additional insights and enhance the applicability of the proposed approach.
-
Energy Efficiency Considerations: The paper primarily focuses on maximizing user throughput and fairness. Incorporating energy efficiency as an objective could be an interesting direction for future research, especially in the context of sustainability and green communications.
Overall, the paper presents a significant contribution to the field of user-centric cell-free MIMO networks, addressing the important challenge of uplink resource allocation. The proposed distributed approach shows promising results and lays the foundation for further advancements in this area.
Conclusion
This paper introduces a scalable and distributed solution for optimizing uplink resource allocation in user-centric cell-free MIMO networks. By leveraging a distributed user scheduling and resource allocation framework, the proposed approach can adapt to the changing demands of users and deliver improved throughput and fairness compared to traditional centralized schemes.
The research showcases the potential of user-centric cell-free MIMO architectures to enhance wireless network performance and user experience. As the demand for high-quality connectivity continues to grow, solutions like the one presented in this paper will play a crucial role in the development of future wireless systems.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers

Performance of Slotted ALOHA in User-Centric Cell-Free Massive MIMO
Dick Maryopi, Daud Al Adumy, Osman Musa, Peter Jung, Agus Virgono

0
0
To efficiently utilize the scarce wireless resource, the random access scheme has been attaining renewed interest primarily in supporting the sporadic traffic of a large number of devices encountered in the Internet of Things (IoT). In this paper we investigate the performance of slotted ALOHA -- a simple and practical random access scheme -- in connection with the grant-free random access protocol applied for user-centric cell-free massive MIMO. More specifically, we provide the expression of the sum-throughput under the assumptions of the capture capability owned by the centralized detector in the uplink. Further, a comparative study of user-centric cell-free massive MIMO with other types of networks is provided, which allows us to identify its potential and possible limitation. Our numerical simulations show that the user-centric cell-free massive MIMO has a good trade-off between performance and fronthaul load, especially at low activation probability regime.
5/29/2024
Joint AP-UE Association and Power Factor Optimization for Distributed Massive MIMO
Mohd Saif Ali Khan, Samar Agnihotri, Karthik R. M

0
0
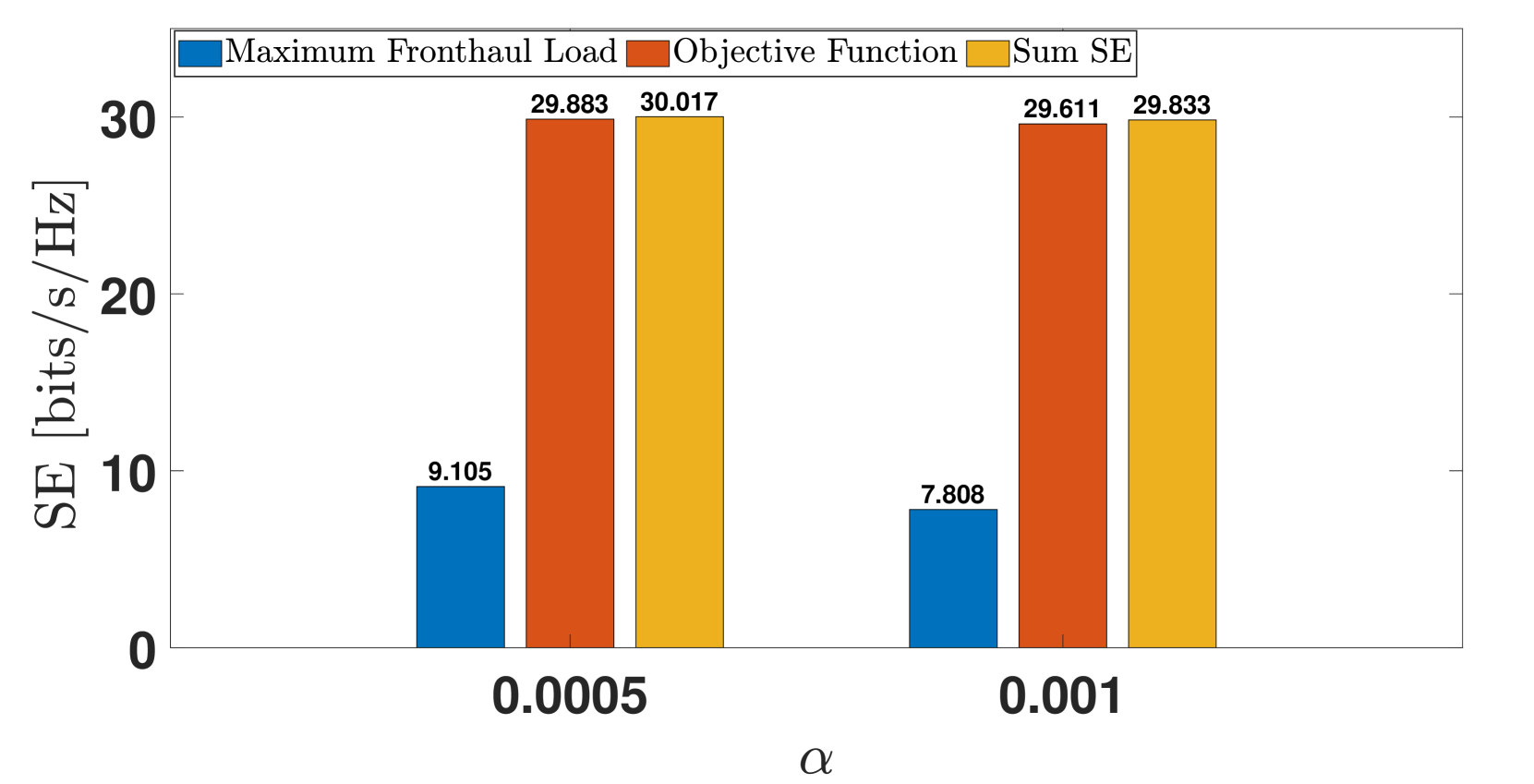
The uplink sum-throughput of distributed massive multiple-input-multiple-output (mMIMO) networks depends majorly on Access point (AP)-User Equipment (UE) association and power control. The AP-UE association and power control both are important problems in their own right in distributed mMIMO networks to improve scalability and reduce front-haul load of the network, and to enhance the system performance by mitigating the interference and boosting the desired signals, respectively. Unlike previous studies, which focused primarily on addressing these two problems separately, this work addresses the uplink sum-throughput maximization problem in distributed mMIMO networks by solving the joint AP-UE association and power control problem, while maintaining Quality-of-Service (QoS) requirements for each UE. To improve scalability, we present an l1-penalty function that delicately balances the trade-off between spectral efficiency (SE) and front-haul signaling load. Our proposed methodology leverages fractional programming, Lagrangian dual formation, and penalty functions to provide an elegant and effective iterative solution with guaranteed convergence. Extensive numerical simulations validate the efficacy of the proposed technique for maximizing sum-throughput while considering the joint AP-UE association and power control problem, demonstrating its superiority over approaches that address these problems individually. Furthermore, the results show that the introduced penalty function can help us effectively control the maximum front-haul load.
5/14/2024
Wireless Resource Optimization in Hybrid Semantic/Bit Communication Networks
Le Xia, Yao Sun, Dusit Niyato, Lan Zhang, Muhammad Ali Imran

0
0
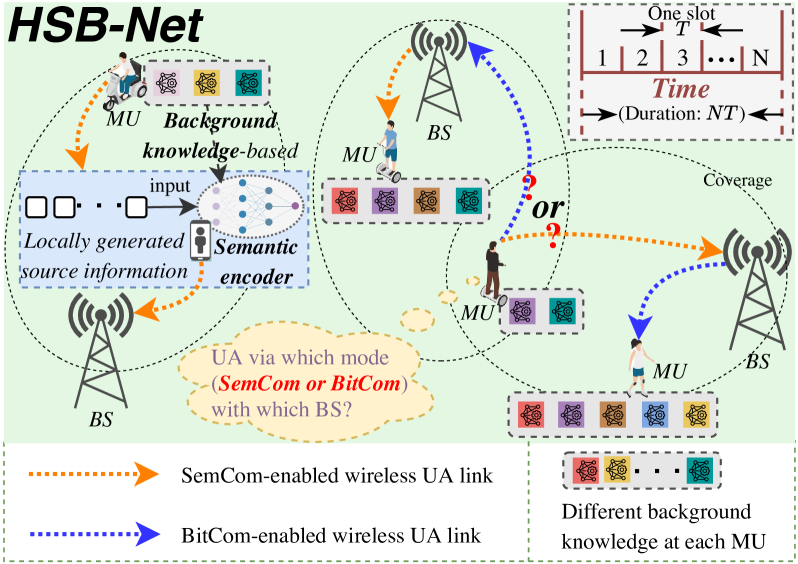
Recently, semantic communication (SemCom) has shown great potential in significant resource savings and efficient information exchanges, thus naturally introducing a novel and practical cellular network paradigm where two modes of SemCom and conventional bit communication (BitCom) coexist. Nevertheless, the involved wireless resource management becomes rather complicated and challenging, given the unique background knowledge matching and time-consuming semantic coding requirements in SemCom. To this end, this paper jointly investigates user association (UA), mode selection (MS), and bandwidth allocation (BA) problems in a hybrid semantic/bit communication network (HSB-Net). Concretely, we first identify a unified performance metric of message throughput for both SemCom and BitCom links. Next, we specially develop a knowledge matching-aware two-stage tandem packet queuing model and theoretically derive the average packet loss ratio and queuing latency. Combined with practical constraints, we then formulate a joint optimization problem for UA, MS, and BA to maximize the overall message throughput of HSB-Net. Afterward, we propose an optimal resource management strategy by utilizing a Lagrange primal-dual transformation method and a preference list-based heuristic algorithm with polynomial-time complexity. Numerical results not only demonstrate the accuracy of our analytical queuing model, but also validate the performance superiority of our proposed strategy compared with different benchmarks.
4/16/2024
User Association and Channel Allocation in 5G Mobile Asymmetric Multi-band Heterogeneous Networks
Miao Dai, Gang Sun, Hongfang Yu, Sheng Wang, Dusit Niyato

0
0
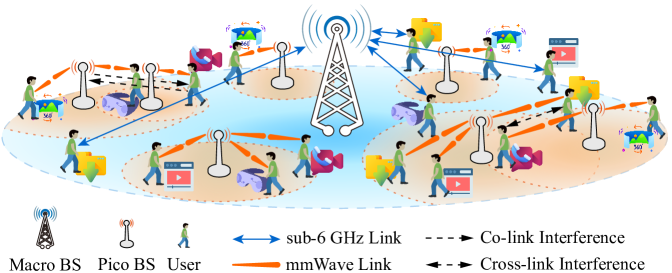
With the proliferation of mobile terminals and the continuous upgrading of services, 4G LTE networks are showing signs of weakness. To enhance the capacity of wireless networks, millimeter waves are introduced to drive the evolution of networks towards multi-band 5G heterogeneous networks. The distinct propagation characteristics of mmWaves and microwaves, as well as the vastly different hardware configurations of heterogeneous base stations, make traditional access strategies no longer effective. Therefore, to narrowing the gap between theory and practice, we investigate the access strategy in multi-band 5G heterogeneous networks, taking into account the characteristics of mobile users, asynchronous switching between uplink and downlink of pico base stations, asymmetric service requirements, and user communication continuity. We formulate the problem as integer nonlinear programming and prove its intractability. Thereby, we decouple it into three subproblems: user association, switch point selection, and subchannel allocation, and design an algorithm based on optimal matching and spectral clustering to solve it efficiently. The simulation results show that the proposed algorithm outperforms the comparison methods in terms of overall data rate, effective data rate, and number of satisfied users.
5/30/2024