ReWiTe: Realistic Wide-angle and Telephoto Dual Camera Fusion Dataset via Beam Splitter Camera Rig

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
• This paper introduces ReWiTe, a novel dual-camera dataset that captures realistic wide-angle and telephoto images using a beam splitter camera rig. • The dataset aims to enable research on algorithms that can seamlessly fuse data from wide-angle and telephoto cameras, a key capability for advanced mobile phone photography. • The paper also presents a comprehensive evaluation of popular image fusion methods on the ReWiTe dataset, providing insights into the current state of the art and areas for future improvement.
Plain English Explanation
The paper introduces a new dataset called ReWiTe that captures realistic images using a special camera setup. Most modern smartphones have two cameras - a wide-angle lens for capturing a broad view, and a telephoto lens for zooming in on distant subjects. This dataset aims to help researchers develop algorithms that can smoothly combine the data from these two cameras, which is an important feature for improving mobile phone photography.
To create the dataset, the researchers used a "beam splitter" camera rig, which splits the light entering the camera and sends it to two separate image sensors. This allows them to capture wide-angle and telephoto views of the same scene simultaneously, just like a smartphone. The resulting images are high-quality and realistic, providing a valuable resource for developing and testing image fusion algorithms.
The paper also evaluates several existing image fusion methods on the ReWiTe dataset, identifying their strengths and weaknesses. This provides useful insights for researchers working on improving mobile camera technology and enabling more advanced photography features on smartphones.
Technical Explanation
The paper introduces the ReWiTe dataset, which captures realistic wide-angle and telephoto dual-camera images using a beam splitter camera rig. The dataset is designed to enable research on algorithms that can seamlessly fuse data from wide-angle and telephoto cameras, a key capability for advanced mobile phone photography.
The authors built a custom camera rig using a beam splitter to capture aligned wide-angle and telephoto images of the same scene. This allows them to collect a diverse dataset of high-quality, realistic image pairs that can be used to train and evaluate image fusion algorithms. The dataset includes a wide variety of indoor and outdoor scenes, covering different lighting conditions, camera viewpoints, and subject distances.
The paper also presents a comprehensive evaluation of several popular image fusion methods on the ReWiTe dataset. The authors assess the performance of these algorithms across various metrics, including image quality, detail preservation, and dynamic range. The results provide valuable insights into the current state of the art and highlight areas for future improvement in dual-camera image fusion.
Critical Analysis
The ReWiTe dataset and the accompanying evaluation of image fusion algorithms represent a significant contribution to the field of mobile camera technology. The use of a beam splitter camera rig to capture realistic wide-angle and telephoto image pairs is a novel and effective approach, addressing the limitations of existing dual-camera datasets that often suffer from misalignment or unrealistic scene conditions.
However, the paper does not address the potential challenges of deploying such a specialized camera rig in a real-world mobile device setting. The size, weight, and power consumption of the beam splitter system may not be compatible with the constraints of modern smartphones. Additionally, the paper does not explore the impact of factors like sensor noise, motion blur, and lens distortion on the performance of image fusion algorithms, which are crucial considerations for mobile camera systems.
Further research is needed to investigate the scalability and practical applicability of the proposed approach, as well as to explore alternative techniques for capturing realistic wide-angle and telephoto image pairs that are more suitable for mobile device integration. Incorporating these considerations into future work would strengthen the relevance and impact of the ReWiTe dataset and the insights gained from the algorithm evaluation.
Conclusion
The ReWiTe dataset and the accompanying analysis of image fusion methods presented in this paper represent a significant step forward in enabling advanced mobile photography capabilities. By providing a realistic and high-quality dataset of wide-angle and telephoto image pairs, the researchers have created a valuable resource for developing and testing algorithms that can seamlessly combine data from multiple camera sensors.
The insights gained from the evaluation of existing fusion methods on the ReWiTe dataset can inform the design of more robust and effective algorithms, ultimately leading to improved image quality and enhanced photography features on smartphones and other mobile devices. As the field of computational photography continues to evolve, the ReWiTe dataset and the research it enables will play an important role in driving innovation and advancing the state of the art in mobile camera technology.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
ReWiTe: Realistic Wide-angle and Telephoto Dual Camera Fusion Dataset via Beam Splitter Camera Rig
Chunli Peng, Xuan Dong, Tiantian Cao, Zhengqing Li, Kun Dong, Weixin Li
The fusion of images from dual camera systems featuring a wide-angle and a telephoto camera has become a hotspot problem recently. By integrating simultaneously captured wide-angle and telephoto images from these systems, the resulting fused image achieves a wide field of view (FOV) coupled with high-definition quality. Existing approaches are mostly deep learning methods, and predominantly rely on supervised learning, where the training dataset plays a pivotal role. However, current datasets typically adopt a data synthesis approach generate input pairs of wide-angle and telephoto images alongside ground-truth images. Notably, the wide-angle inputs are synthesized rather than captured using real wide-angle cameras, and the ground-truth image is captured by wide-angle camera whose quality is substantially lower than that of input telephoto images captured by telephoto cameras. To address these limitations, we introduce a novel hardware setup utilizing a beam splitter to simultaneously capture three images, i.e. input pairs and ground-truth images, from two authentic cellphones equipped with wide-angle and telephoto dual cameras. Specifically, the wide-angle and telephoto images captured by cellphone 2 serve as the input pair, while the telephoto image captured by cellphone 1, which is calibrated to match the optical path of the wide-angle image from cellphone 2, serves as the ground-truth image, maintaining quality on par with the input telephoto image. Experiments validate the efficacy of our newly introduced dataset, named ReWiTe, significantly enhances the performance of various existing methods for real-world wide-angle and telephoto dual image fusion tasks.
Read more5/1/2024

0
Deep Hybrid Camera Deblurring for Smartphone Cameras
Jaesung Rim, Junyong Lee, Heemin Yang, Sunghyun Cho
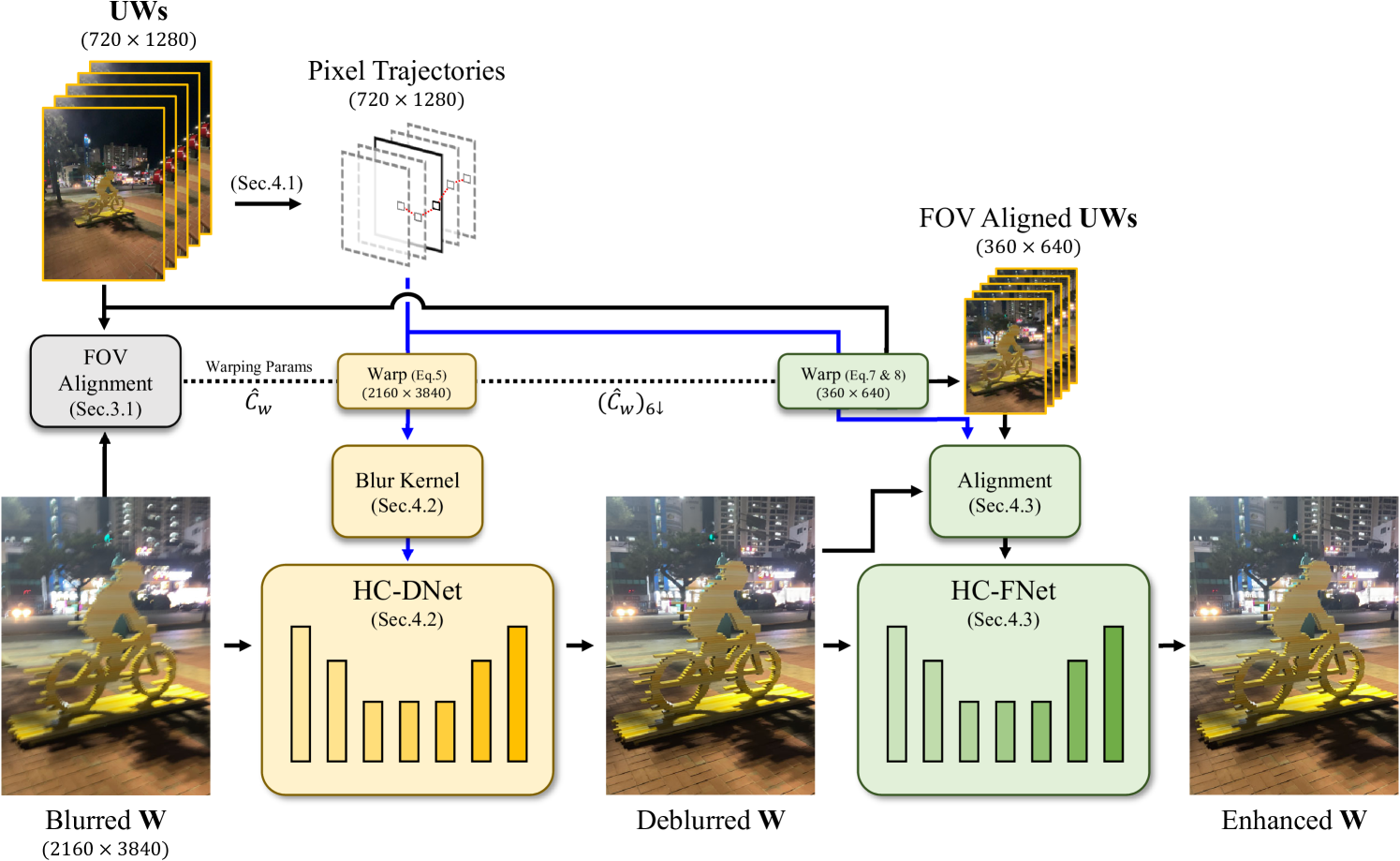
Mobile cameras, despite their significant advancements, still have difficulty in low-light imaging due to compact sensors and lenses, leading to longer exposures and motion blur. Traditional blind deconvolution methods and learning-based deblurring methods can be potential solutions to remove blur. However, achieving practical performance still remains a challenge. To address this, we propose a learning-based deblurring framework for smartphones, utilizing wide and ultra-wide cameras as a hybrid camera system. We simultaneously capture a long-exposure wide image and short-exposure burst ultra-wide images, and utilize the burst images to deblur the wide image. To fully exploit burst ultra-wide images, we present HCDeblur, a practical deblurring framework that includes novel deblurring networks, HC-DNet and HC-FNet. HC-DNet utilizes motion information extracted from burst images to deblur a wide image, and HC-FNet leverages burst images as reference images to further enhance a deblurred output. For training and evaluating the proposed method, we introduce the HCBlur dataset, which consists of synthetic and real-world datasets. Our experiments demonstrate that HCDeblur achieves state-of-the-art deblurring quality. Code and datasets are available at https://cg.postech.ac.kr/research/HCDeblur.
Read more7/26/2024


0
360 in the Wild: Dataset for Depth Prediction and View Synthesis
Kibaek Park, Francois Rameau, Jaesik Park, In So Kweon
The large abundance of perspective camera datasets facilitated the emergence of novel learning-based strategies for various tasks, such as camera localization, single image depth estimation, or view synthesis. However, panoramic or omnidirectional image datasets, including essential information, such as pose and depth, are mostly made with synthetic scenes. In this work, we introduce a large scale 360$^{circ}$ videos dataset in the wild. This dataset has been carefully scraped from the Internet and has been captured from various locations worldwide. Hence, this dataset exhibits very diversified environments (e.g., indoor and outdoor) and contexts (e.g., with and without moving objects). Each of the 25K images constituting our dataset is provided with its respective camera's pose and depth map. We illustrate the relevance of our dataset for two main tasks, namely, single image depth estimation and view synthesis.
Read more7/8/2024


0
PIV3CAMS: a multi-camera dataset for multiple computer vision problems and its application to novel view-point synthesis
Sohyeong Kim, Martin Danelljan, Radu Timofte, Luc Van Gool, Jean-Philippe Thiran
The modern approaches for computer vision tasks significantly rely on machine learning, which requires a large number of quality images. While there is a plethora of image datasets with a single type of images, there is a lack of datasets collected from multiple cameras. In this thesis, we introduce Paired Image and Video data from three CAMeraS, namely PIV3CAMS, aimed at multiple computer vision tasks. The PIV3CAMS dataset consists of 8385 pairs of images and 82 pairs of videos taken from three different cameras: Canon D5 Mark IV, Huawei P20, and ZED stereo camera. The dataset includes various indoor and outdoor scenes from different locations in Zurich (Switzerland) and Cheonan (South Korea). Some of the computer vision applications that can benefit from the PIV3CAMS dataset are image/video enhancement, view interpolation, image matching, and much more. We provide a careful explanation of the data collection process and detailed analysis of the data. The second part of this thesis studies the usage of depth information in the view synthesizing task. In addition to the regeneration of a current state-of-the-art algorithm, we investigate several proposed alternative models that integrate depth information geometrically. Through extensive experiments, we show that the effect of depth is crucial in small view changes. Finally, we apply our model to the introduced PIV3CAMS dataset to synthesize novel target views as an example application of PIV3CAMS.
Read more7/29/2024