Smart Contract Coordinated Privacy Preserving Crowd-Sensing Campaigns

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- Describes a system for privacy-preserving crowd-sensing campaigns using smart contracts on a blockchain
- Aims to enable data collection while preserving participant privacy
- Includes a technical implementation and evaluation of the proposed system
Plain English Explanation
Privacy-preserving crowd-sensing is a way for organizations to gather useful data from a large number of people while protecting their personal information. This paper presents a system that uses smart contracts on a blockchain to coordinate these crowd-sensing campaigns in a privacy-preserving manner.
The key idea is to use the blockchain and smart contracts to manage the data collection process without the campaign organizer ever seeing the raw data from individual participants. Participants submit their data in a way that protects their privacy, and the smart contracts handle tasks like recruiting participants, distributing rewards, and aggregating the data.
This approach aims to enable useful data collection while respecting people's right to privacy. The paper provides a technical implementation and evaluation to demonstrate how this system could work in practice.
Technical Explanation
The proposed system uses a blockchain-based architecture with smart contracts to coordinate privacy-preserving crowd-sensing campaigns. The key components are:
- Participant Recruitment: Smart contracts are used to recruit participants, distribute tasks, and manage rewards.
- Privacy-Preserving Data Submission: Participants submit their data using differential privacy techniques to protect their privacy.
- Data Aggregation: The smart contracts aggregate the submitted data without ever accessing the raw participant data.
- Reward Distribution: Smart contracts handle the distribution of rewards to participants based on their contributions.
The paper describes the technical implementation of these components and provides an evaluation of the system's performance and privacy guarantees. The results demonstrate the feasibility of this approach for enabling crowd-sensing campaigns that preserve participant privacy.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a novel and promising approach to privacy-preserving crowd-sensing, but there are a few potential limitations and areas for further research:
- The paper focuses on the technical implementation and does not extensively discuss potential real-world deployment challenges, such as incentivizing participant engagement or ensuring broad adoption of the system.
- The privacy guarantees are based on theoretical models of differential privacy, and the paper does not provide empirical evidence of how well the system would hold up against sophisticated privacy attacks in practice.
- The evaluation is limited to simulations, and more real-world testing would be needed to fully validate the system's performance and scalability.
Overall, the research represents an important step towards enabling useful data collection while respecting individual privacy, but further work is needed to address these potential limitations and ensure the system's practical viability.
Conclusion
This paper presents a smart contract-based system for privacy-preserving crowd-sensing campaigns. By leveraging blockchain technology and differential privacy techniques, the proposed approach aims to enable valuable data collection while protecting the personal information of participants.
The technical implementation and evaluation demonstrate the feasibility of this approach, but additional research is needed to address potential real-world challenges and further validate the system's privacy guarantees and scalability. Nonetheless, this work represents an important contribution to the ongoing efforts to balance the need for data-driven insights with the fundamental right to privacy.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Smart Contract Coordinated Privacy Preserving Crowd-Sensing Campaigns
Luca Bedogni, Stefano Ferretti
Crowd-sensing has emerged as a powerful data retrieval model, enabling diverse applications by leveraging active user participation. However, data availability and privacy concerns pose significant challenges. Traditional methods like data encryption and anonymization, while essential, may not fully address these issues. For instance, in sparsely populated areas, anonymized data can still be traced back to individual users. Additionally, the volume of data generated by users can reveal their identities. To develop credible crowd-sensing systems, data must be anonymized, aggregated and separated into uniformly sized chunks. Furthermore, decentralizing the data management process, rather than relying on a single server, can enhance security and trust. This paper proposes a system utilizing smart contracts and blockchain technologies to manage crowd-sensing campaigns. The smart contract handles user subscriptions, data encryption, and decentralized storage, creating a secure data marketplace. Incentive policies within the smart contract encourage user participation and data diversity. Simulation results confirm the system's viability, highlighting the importance of user participation for data credibility and the impact of geographical data scarcity on rewards. This approach aims to balance data origin and reduce cheating risks.
Read more8/21/2024

0
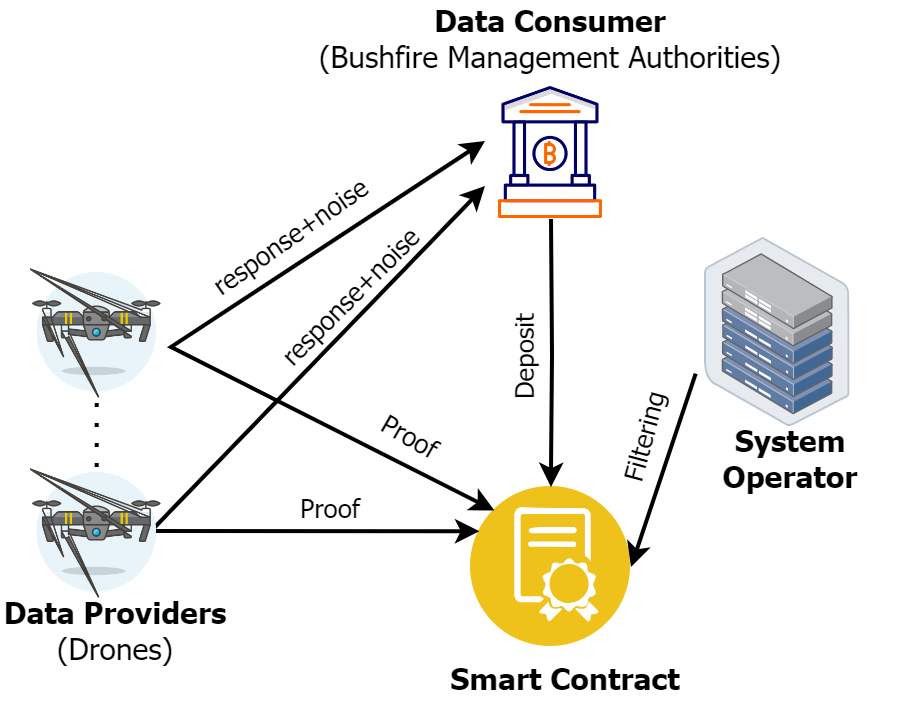
Privacy-First Crowdsourcing: Blockchain and Local Differential Privacy in Crowdsourced Drone Services
Junaid Akram, Ali Anaissi
We introduce a privacy-preserving framework for integrating consumer-grade drones into bushfire management. This system creates a marketplace where bushfire management authorities obtain essential data from drone operators. Key features include local differential privacy to protect data providers and a blockchain-based solution ensuring fair data exchanges and accountability. The framework is validated through a proof-of-concept implementation, demonstrating its scalability and potential for various large-scale data collection scenarios. This approach addresses privacy concerns and compliance with regulations like Australia's Privacy Act 1988, offering a practical solution for enhancing bushfire detection and management through crowdsourced drone services.
Read more7/2/2024


0
Insights from an experiment crowdsourcing data from thousands of US Amazon users: The importance of transparency, money, and data use
Alex Berke, Robert Mahari, Sandy Pentland, Kent Larson, D. Calacci
Data generated by users on digital platforms are a crucial resource for advocates and researchers interested in uncovering digital inequities, auditing algorithms, and understanding human behavior. Yet data access is often restricted. How can researchers both effectively and ethically collect user data? This paper shares an innovative approach to crowdsourcing user data to collect otherwise inaccessible Amazon purchase histories, spanning 5 years, from more than 5000 US users. We developed a data collection tool that prioritizes participant consent and includes an experimental study design. The design allows us to study multiple aspects of privacy perception and data sharing behavior. Experiment results (N=6325) reveal both monetary incentives and transparency can significantly increase data sharing. Age, race, education, and gender also played a role, where female and less-educated participants were more likely to share. Our study design enables a unique empirical evaluation of the privacy paradox, where users claim to value their privacy more than they do in practice. We set up both real and hypothetical data sharing scenarios and find measurable similarities and differences in share rates across these contexts. For example, increasing monetary incentives had a 6 times higher impact on share rates in real scenarios. In addition, we study participants' opinions on how data should be used by various third parties, again finding demographics have a significant impact. Notably, the majority of participants disapproved of government agencies using purchase data yet the majority approved of use by researchers. Overall, our findings highlight the critical role that transparency, incentive design, and user demographics play in ethical data collection practices, and provide guidance for future researchers seeking to crowdsource user generated data.
Read more5/15/2024
🤯

0
RollupTheCrowd: Leveraging ZkRollups for a Scalable and Privacy-Preserving Reputation-based Crowdsourcing Platform
Ahmed Mounsf Rafik Bendada, Mouhamed Amine Bouchiha, Mourad Rabah, Yacine Ghamri-Doudane
Current blockchain-based reputation solutions for crowdsourcing fail to tackle the challenge of ensuring both efficiency and privacy without compromising the scalability of the blockchain. Developing an effective, transparent, and privacy-preserving reputation model necessitates on-chain implementation using smart contracts. However, managing task evaluation and reputation updates alongside crowdsourcing transactions on-chain substantially strains system scalability and performance. This paper introduces RollupTheCrowd, a novel blockchain-powered crowdsourcing framework that leverages zkRollups to enhance system scalability while protecting user privacy. Our framework includes an effective and privacy-preserving reputation model that gauges workers' trustworthiness by assessing their crowdsourcing interactions. To alleviate the load on our blockchain, we employ an off-chain storage scheme, optimizing RollupTheCrowd's performance. Utilizing smart contracts and zero-knowledge proofs, our Rollup layer achieves a significant 20x reduction in gas consumption. To prove the feasibility of the proposed framework, we developed a proof-of-concept implementation using cutting-edge tools. The experimental results presented in this paper demonstrate the effectiveness and scalability of RollupTheCrowd, validating its potential for real-world application scenarios.
Read more7/4/2024